Python While Loops: Because Life Shouldn't Be a Never-Ending Loop
 JMN
JMNTable of contents

In Python, a while loop is a control structure that allows you to repeatedly execute a block of code as long as the specified condition is true.
Basic Structure
The
whilekeyword is followed by a condition: This condition is a boolean expression that determines whether the loop should continue or not. As long as this condition remains true, the loop will keep executing.A colon (
:): The colon signifies the start of the code block that will be executed repeatedly.Indented code block: All the statements inside the code block are executed repeatedly until the condition becomes false. Indentation is crucial in Python, as it defines the scope of the code inside the loop.
Example 1
Type the below code to your editor.

- The
count int = 0: This line initializes a variable namedcountand sets its initial value to 0. The: intpart is a type hint, indicating thatcountis expected to hold an integer value.
while count < 5:: This line starts a while loop. The loop will continue to execute as long as the conditioncount < 5isTrue. In other words, it will keep running until thecountis no longer less than 5.print(f"Count is {count}"): Inside the loop, there's aprintstatement. It prints a message that includes the current value of thecountvariable. Thef"Count is {count}"is an f-string, which allows you to embed the value ofcountwithin the string.count += 1: This line increments thecountvariable by 1 in each iteration of the loop. This step is crucial because it ensures that the conditioncount < 5eventually becomesFalseafter the count reaches 5, terminating the loop as shown below.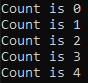
Example 2
In this instance, we will employ the input function. Please enter the following code:

user_input = input("Enter 'quit' to exit: "): This line prompts the user for input by displaying the message "Enter 'quit' to exit: " and stores the user's input as a string in the variableuser_input.while user_input != 'quit':: This line starts awhileloop that continues as long as the value ofuser_inputis not equal to the string 'quit'. In other words, it keeps running until the user types 'quit' to exit the loop.print(f"You entered: {user_input}"): Inside the loop, this line prints a message that includes what the user entered using an f-string. For example, if the user enters "hello," it will print "You entered: hello."user_input = input("Enter 'quit' to exit: "): After printing the message and displaying the prompt again, this line takes another user input and stores it in theuser_inputvariable. This new value is checked in the next iteration of the loop.Here's how the program works:
It starts by asking the user for input and stores it in
user_input.It enters the
whileloop and checks ifuser_inputis not equal to 'quit'.If the user enters anything other than 'quit', it prints the input and asks for input again.
This process repeats until the user enters 'quit', at which point the condition
user_input != 'quit'becomesFalse, and the loop exits.
In simple terms, this program keeps asking the user for input until the user types 'quit' to exit the program. It also informs the user of what they entered before asking for the next input as shown below.
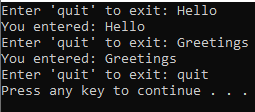
Example 3
In this code example, we will simulate a hypothetical space journey using a while loop to count backward. While this simulation doesn't involve actual space travel, it offers an engaging way to practice programming with a while loop by counting in reverse.
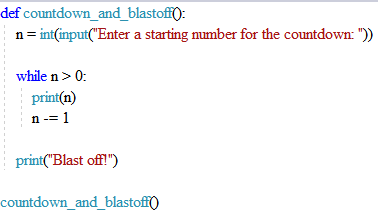
It takes user input to determine a starting number for a countdown.
The function then enters a
whileloop that continues as long as the value ofn(the starting number) is greater than 0.Inside the loop, it prints the current value of
nand then decrementsnby 1 in each iteration.Once the value of
nbecomes 0 (or less), the loop exits.After the loop, it prints "Blast off!" to indicate the end of the countdown.
Explanation
The user enters 5 as the starting number.
The
whileloop checks ifnis greater than 0, which is true (5 > 0).It prints the current value of
n, which is 5.It decrements
nby 1, so nownis 4.The loop continues, printing 4 and then decrementing
nto 3, and so on.This process repeats until
nbecomes 0.When
nreaches 0, the loop exits, and "Blast off!" is printed to signify the end of the countdown as shown below.
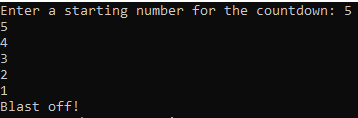
A lot of the key concepts related to while loops have been covered in this article. In our next installment, we will explore the topic of for loops. Thank you for your attention, and stay tuned for the upcoming article.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from JMN directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

JMN
JMN
I'm JMN (Jaffery Mwangi Ndisho), and I'm thrilled to share my passion for data analytics and programming with you. With a background in business and IT, I've always been fascinated by the power of algorithms and their ability to transform data into insights. Through this blog, I hope to share my learning journey and practical knowledge with you, as well as explore new techniques and applications in the field. Join me on this journey and let's discover the world of data analytics and programming together!