Graph RAG :Unleashing the Power of Knowledge Graphs with LLM
 NebulaGraph Database
NebulaGraph DatabaseIn the era of information overload, sifting through vast amounts of data to provide accurate search results in an engaging and comprehensible manner has become an uphill battle. Traditional search enhancement techniques often fall short when it comes to complex queries and the high demand brought by cutting-edge technologies like ChatGPT. This is where Graph RAG steps in – a game-changing concept crafted by NebulaGraph that promises to revolutionize the field.
“Graph RAG” is a concept pioneered by NebulaGraph. This technology harnesses the power of knowledge graphs in conjunction with Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide search engines with a more comprehensive contextual understanding. It assists users in obtaining smarter and more precise search results at a lower cost.
NebulaGraph's revolutionary Graph RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technique, which is based on knowledge graphs, is a breakthrough in this area. Graph RAG combines knowledge graphs with a large language model to provide more cost-effective, intelligent, and precise search results. Capable of deep integration with large language models such as Llama Index and LangChain, NebulaGraph is the first in the industry to propose the concept of Graph RAG. Besides, Graph RAG has also achieved excellent results in the field of vector database integration.
In this article, we will introduce the concept of Graph RAG and compare it with other RAG techniques. You are also welcome to visit the NebulaGraph‘s website to Try Demos.
Challenges Faced by Traditional Search Enhancement Techniques
Obtaining accurate search results is a challenge, especially with complex or long-tail queries when traditional search engines rely on keyword matching, which often does not meet the users' actual needs. The bottleneck of traditional search augmentation techniques is the lack of training data and text understanding, which makes them less effective when it comes to generating accurate, diverse and relevant information.
To address this problem, RAG came into being. RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) refers to the process of enhancing search results through RAG models. Specifically, it is a technique that combines retrieval and language generation to enhance the generation process. By using RAG, traditional search engines can generate more accurate and relevant search results.
However, the RAG technique still faces challenges in terms of training data and text understanding. These challenges include:
Train data: the RAG technique requires a large amount of data and computational resources for training and generating models, especially when handling multiple languages and complex tasks.
Text understanding: RAG needs to understand the intent of the query, but for complex queries or polysemous queries, RAG may have ambiguity or uncertainty, which affects the quality of the generated content.
Therefore, the problem of how to find more powerful retrieval enhancement techniques to obtain search results that better meet the searcher's expectations more efficiently is even more urgent.
What is Graph RAG?
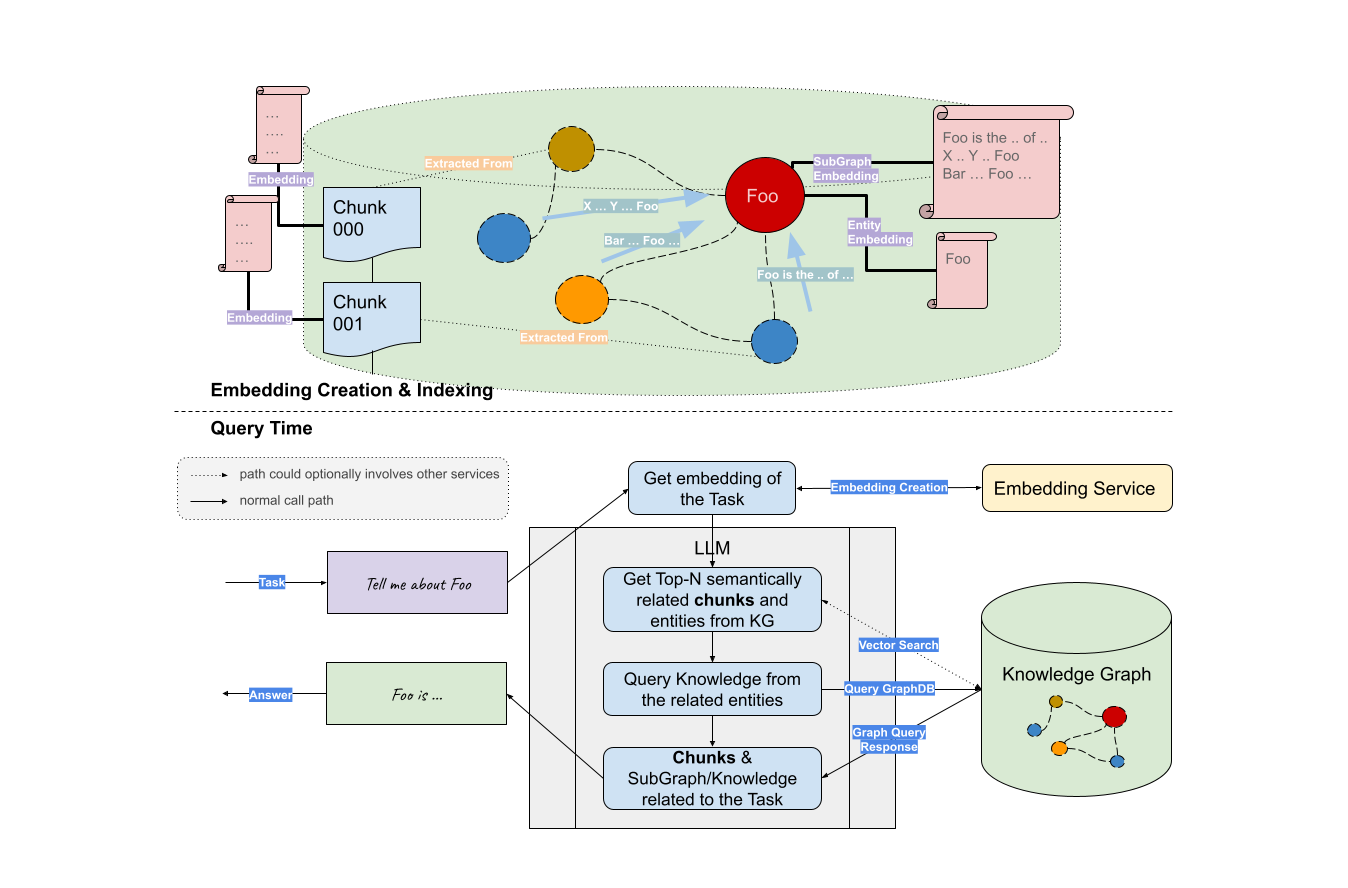
Graph RAG is proposed by NebulaGraph, which is a retrieval enhancement technique based on knowledge graphs. It uses a knowledge graph to show the relationship between entities and relationships and then uses the large language model LLM (Large Language Model) for retrieval enhancement.
As mentioned in the previous blog, the graph database is naturally suitable for storing and expressing complex context information by organizing and connecting information in a graphical format. By using graph technology to build a knowledge graph to enhance in-context learning, users can provide more context information to help large language models (LLM) better understand the relationship between entities and improve their expression and reasoning abilities.
Graph RAG equates the knowledge graph to a large-scale vocabulary, and entities and relationships correspond to words. In this way, Graph RAG can jointly model entities and relationships as units during retrieval, which can more accurately understand the query intent and provide more accurate search results.
Demo: Graph RAG vs. Vector RAG vs. Text2Cypher
In the following sections, we'll explore two demos that provide a visual comparison of Graph RAG with Vector RAG and Text2Cypher.
Graph RAG vs. Graph + Vector RAG
The GIT below compares the results returned by Vector RAG (vector retrieval) with Graph and Vector RAG (graph-enhanced vector retrieval).
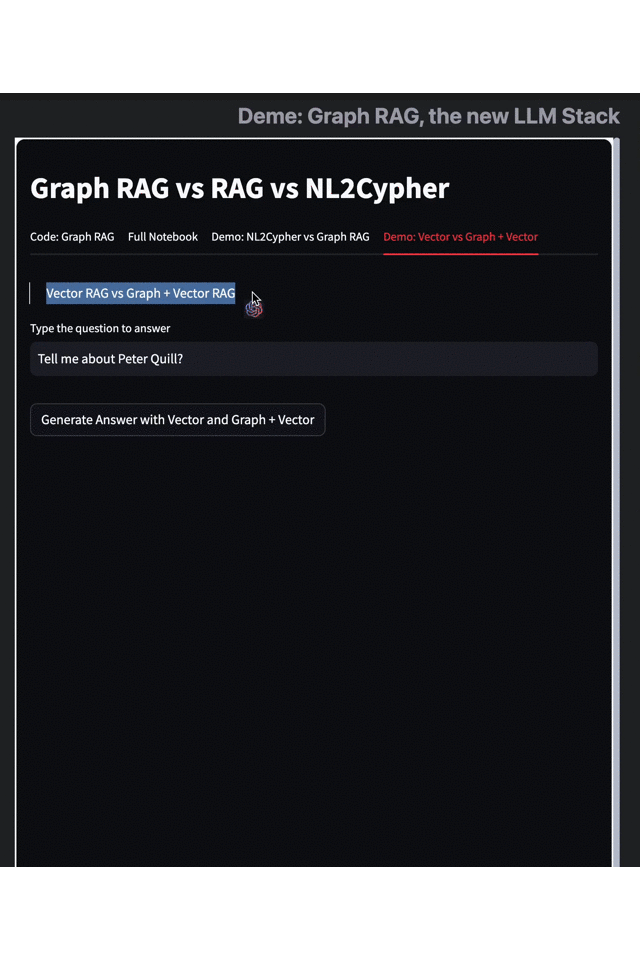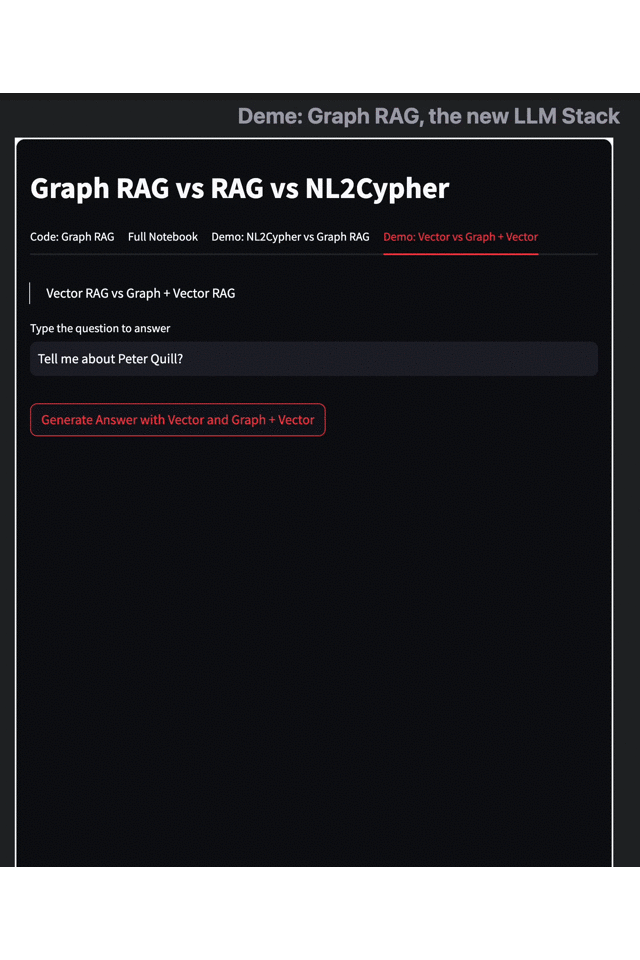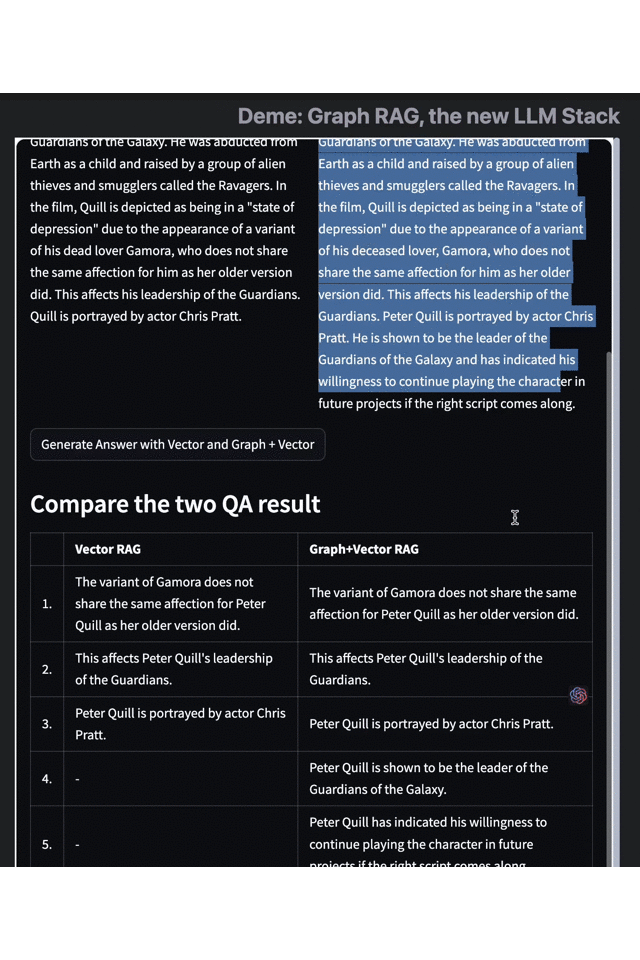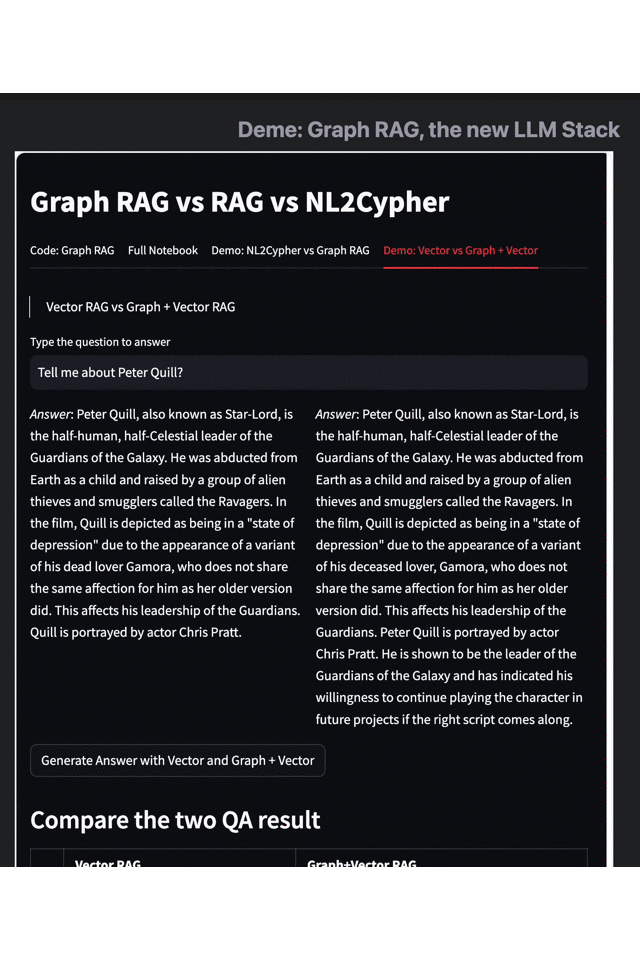
Results on the left: Vector RAG
Results on the right: Vector RAG with Graph
As an example, let's consider the data set of "Guardians of the Galaxy 3". When we search for "Peter Quill's related information," traditional retrieval techniques like vector retrieval engines only provide simple information on his identity, plot, and actors. However, with the Graph RAG-enhanced search results, we can obtain more information about the protagonist's skills, character goals, and identity changes.
This example highlights how Graph RAG effectively complements the shortcomings of traditional methods like embedding and vector retrieval and provides more in-depth knowledge and information relevant to the query. By combining knowledge graphs with large language models, Graph RAG can understand the relations between entities, equate knowledge graphs to large-scale vocabularies and better comprehend the intent of complex queries, leading to more accurate and relevant search results.
Graph RAG vs. Text2Cypher
Another interesting approach to knowledge graph-based LLM is Text2Cypher, which is a natural language generation graph query. This method does not rely on entity subgraph retrieval but translates tasks or questions into an answer-oriented graph query, which is essentially the same as what we commonly call Text2SQL.
Text2Cypher and Graph RAG differ mainly in their retrieval mechanisms. Text2Cypher generates graph pattern queries based on the knowledge graph schema and the given task, while (Sub)Graph RAG obtains relevant subgraphs to provide context. Both have their advantages, and you can get a more intuitive understanding of their characteristics through the following demo.
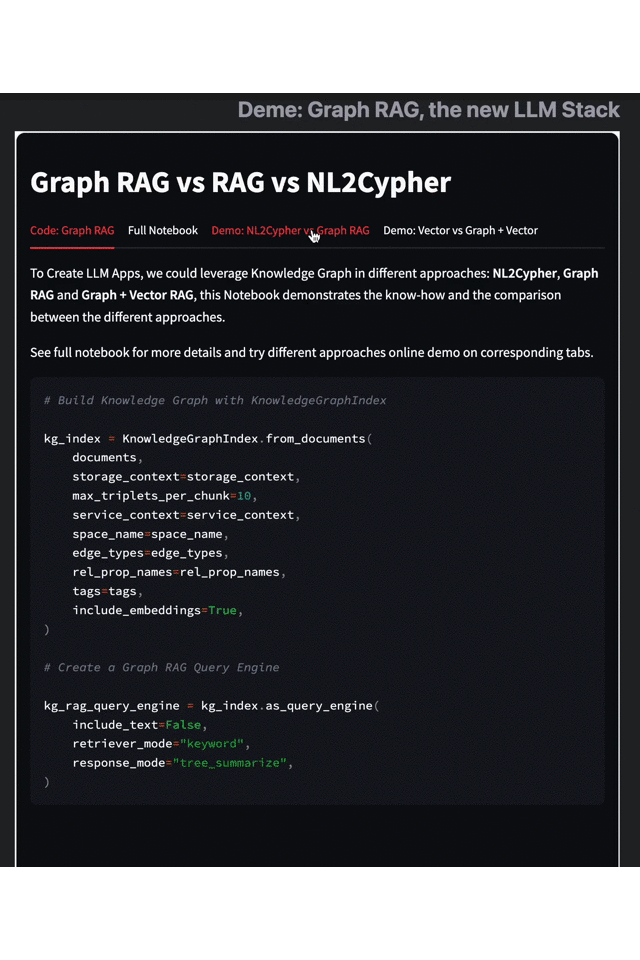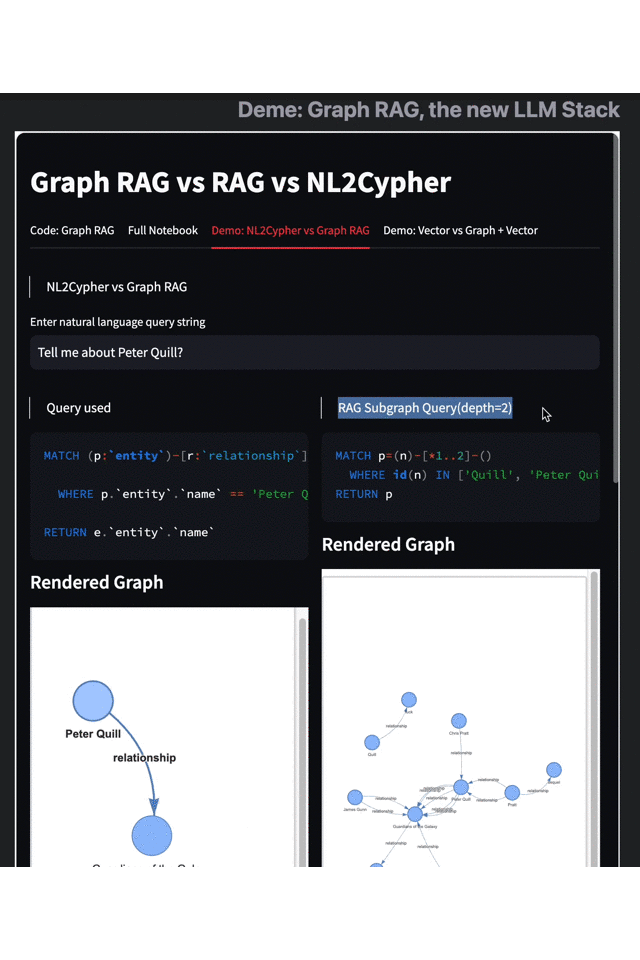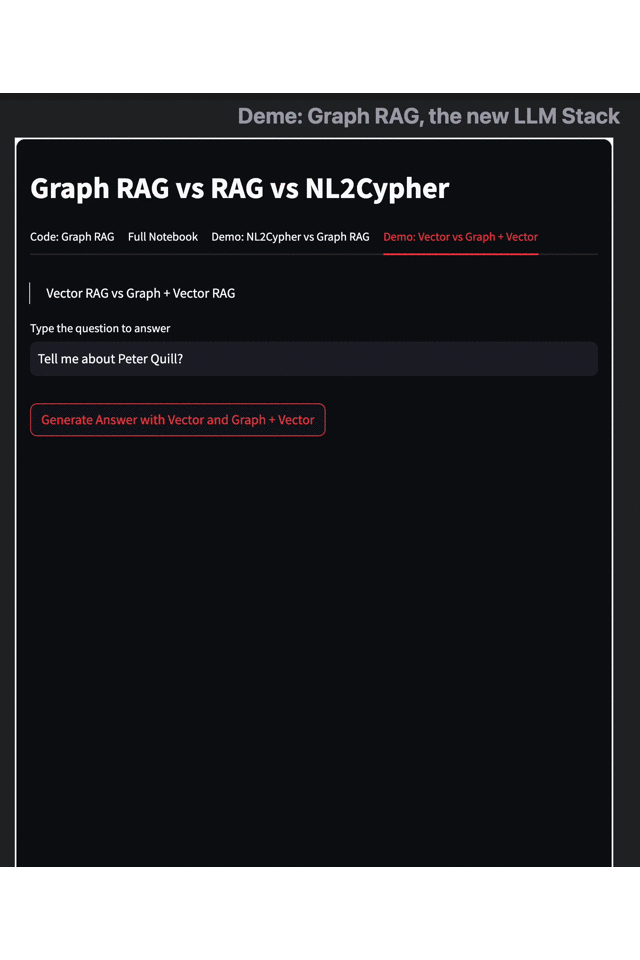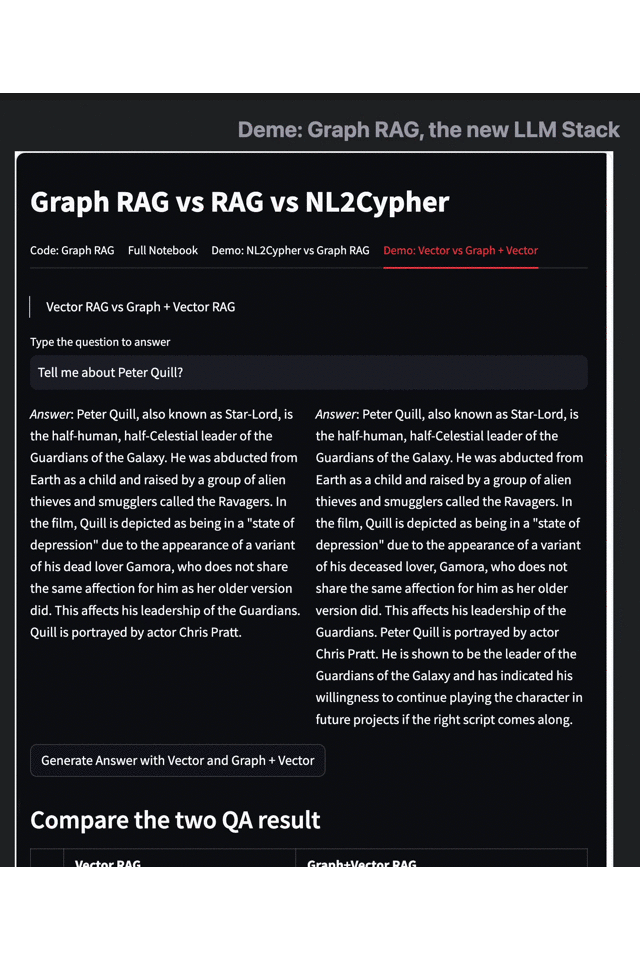
Results on the left: Text2Cypher
Results on the right: Graph RAG
From the above demo, it's evident that the two graph query modes exhibit pronounced differences in visualization. Retrieval using Graph RAG presents more comprehensive results. Users not only receive fundamental introductory information but also gain access to a range of outcomes based on associative searches and contextual inferences, such as "Peter Quill is the leader of the Guardians of the Galaxy," "This role implies that he will return in the sequel," and insights into the character's personality.
NebulaGraph : Build Your Enterprise-Specific Knowledge Graph Applications in One Step
NebulaGraph database has seamlessly integrated with large language model frameworks like Llama Index and LangChain.Therefore, developers can focus on LLM orchestration logic and pipeline design without having to deal with many details of abstraction and implementation and generate high-quality and low-cost enterprise-level large language model applications in one stop.
The advent of Graph RAG presents a breakthrough for processing and retrieving information on a massive scale. By fusing knowledge graphs and graph storage within the LLM stack, Graph RAG offers an unparalleled level of context learning. With the utilization of NebulaGraph, building Graph RAG is highly simplified and requires minimal effort, based on just three lines of code. Even more complex RAG logic, such as Vector RAG with graph can be easily integrated.
As graph technology and deep learning algorithms continue to advance, the adoption of Graph RAG in data processing and retrieval is set to become increasingly widespread. We invite you to contact us for a free trial of NebulaGraph database and to effortlessly create your knowledge graph application!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from NebulaGraph Database directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
