Apache ANT, Apache Maven, and Gradle: A Guide to Dependency Management and Build Automation in Software Development
 Anil Gulati
Anil GulatiTable of contents


Introduction
In the realm of software development, the efficient management of dependencies and the automation of build processes are crucial aspects that can significantly impact a project's success. This article delves into the world of Dependency and Build tools, providing insights into their importance and the key players in this field.
1. Dependencies in Software Development: Before we delve into the tools, it's essential to understand what dependencies are in the context of software development. Simply put, a dependency occurs when one component, let's call it 'A,' relies on another component, 'B,' to function correctly. In the software world, dependencies are external libraries or support systems required by an application for its successful execution. Examples of such dependencies include Zuul, Hystrix, Lombok, JDBC, and many more.
2. Challenges Before Dependency Management Tools: In the past, managing dependencies was a cumbersome task, fraught with challenges. Developers had to either manually download required libraries from the internet and integrate them into their projects or write scripts to automate this process. These approaches posed several problems:
Manual Downloading: Manually fetching dependencies from the internet was time-consuming and labour-intensive.
Script Reliance: Scripts for automated downloads were prone to failures if the source URLs changed.
Transitive Dependency Complexity: Identifying and managing transitive dependencies within the application was a complex ordeal.
- Dependency Management Tools: Dependency management tools come to the rescue by resolving and managing the dependencies required by an application. Let's explore three prominent tools in the Java ecosystem:
Apache ANT
Overview: Apache ANT, standing for "Another Neat Tool," is an open-source project by Apache dating back to 2000. It's primarily used for automating build processes in Java applications.
Key Features: ANT uses XML-based build files and offers flexibility by following the "Configuration over convention" principle. It organizes build processes into "Targets," with each target containing a set of executable tasks.
Example: Here's a simple ANT build.xml example:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project>
<target name="hello">
<echo>Hello, World</echo>
</target>
</project>
Basic Apache ANT Commands:
ant: This command runs the default target defined in the build.xml file.
ant [target]: Executes the specified target from the build.xml file.
ant -version: Displays the version of Apache ANT installed.
ant -projecthelp: Lists available targets in the build.xml file.
ant -f [build-file]: Specifies an alternative build file to use.
Apache Maven
Overview: Apache Maven, introduced in 2004, is a dependency management and build automation tool that prioritizes "Convention over configuration." It uses a "pom.xml" configuration file for project settings and dependency management.
Key Features: Maven automates dependency downloads, compiles source code, packages artifacts, runs tests, and handles deployments.
Example: A simplified "pom.xml" for a Maven project:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<!-- Project configuration -->
<dependencies>
<!-- Dependency declaration -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Basic Apache Maven Commands:
mvn clean: Deletes the target directory and all its contents.
mvn compile: Compiles the source code of the project.
mvn package: Packages the compiled code into a distributable format (e.g., JAR or WAR).
mvn test: Executes unit tests in the project.
mvn install: Installs the project's artifact into the local repository.
Gradle
Overview: Gradle, released in 2012, combines the best of both Apache ANT and Apache Maven while introducing a domain-specific language based on Groovy.
Key Features: It follows "Convention over configuration" and offers a more concise build configuration compared to Maven's XML. Gradle excels in handling transitive dependencies efficiently.
Example: A simple "build.gradle" for a Gradle project:
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.2.5.RELEASE'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.0.9.RELEASE'
id 'java'
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter'
}
Basic Gradle Commands:
./gradlew clean: Deletes the build directory.
./gradlew build: Compiles, tests, and packages the project.
./gradlew tasks: Lists available tasks in the project.
./gradlew dependencies: Displays the project's dependencies.
./gradlew assembleRelease: Assembles the release version of the project.
Repository Management: All these tools rely on repositories to fetch and manage dependencies. There are three types of repositories:
Local Repository: Located on the developer's machine.
Organization-Level/Remote Repository: Within the organization's network.
Central Repository: On the internet, maintained by the community.
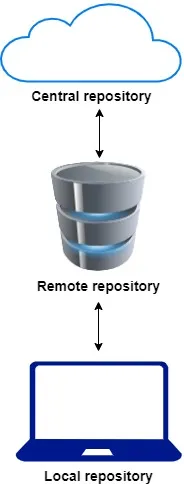
When a dependency is specified, these tools search for it first in the local repository, then in the organization-level repository, and finally in the central repository if needed.
Conclusion: In conclusion, understanding dependency and build tools is fundamental in modern software development. Each tool, whether it's Apache ANT, Apache Maven, or Gradle, offers unique features and approaches to streamline the development process. While ANT provides flexibility, Maven and Gradle simplify the management of dependencies and build processes. Choosing the right tool depends on your project's requirements and your team's preferences
Enjoyed This Article?
If you enjoy reading this post, got help, knowledge through it, and want to support my efforts please clap this article and follow.
To explore more of my work, visit my portfolio at anilgulati.com
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Anil Gulati directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Anil Gulati
Anil Gulati
Associate Software Engineer @YMSLI | Ex-SDE@Onelab Ventures | Full Stack Developer| Freelancer | Bibliophile | Technical Head @DITU ACM SC |