User experience: The good, the bad and the friendly.
 Oleh Chinenye
Oleh Chinenye
In today's digital age, our lives are intertwined with technology, whether it's choosing a preferred document editing software, streaming music, or even selecting a favourite cereal at the grocery store. What drives these choices and preferences? It's largely the User Experience (UX) we encounter while interacting with these products and services.
Understanding User Experience.
User experience, often abbreviated as UX, captures the total of an individual's interactions with a product, system, or service. It's a comprehensive term that encompasses the highs and lows, successes and failures, and a spectrum of emotions that users encounter along the way. UX isn't confined to digital realms alone. It extends to the ergonomic design of a chair, the usability of a door handle, or even the simplicity of unscrewing a cork. It's everywhere we interact with the world around us.
Don Norman, a cognitive scientist at Apple, coined the term "User Experience" in the 1990s. In an interview with the Nielsen Norman group, Norman explained UX as "everything that touches upon your experience with the product. It may not even be near the product. It may be when you're telling somebody else about it." Simply put, when you recall a product and feel either positively or negatively about it, that's your user experience with that product.
According to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), user experience is defined as "A person's perceptions and responses that result from the use or anticipated use of a product, system, or service." (ISO 9241-210, Ergonomics of human-system interaction—Part 210: Human-centered design for interactive systems).
The Components of UX Design.
User experience design is a multifaceted discipline with four major branches that share a common goal: to make the product user-centred, intuitive, usable, functional, meaningful, pleasurable, accessible, and more.
User Research: This branch involves systematically studying users to understand their behaviours, preferences, and needs. The data gathered informs design decisions, providing insights into user expectations and pain points.
Interaction Design: Focused on optimizing how users interact with digital products or interfaces, interaction design encompasses designing the layout, behaviour, and responsiveness of interactive elements to ensure a seamless and user-friendly experience.
Information Architecture: Information architecture is the process of structuring and organizing content in a way that makes it logical and user-friendly. It defines how information is labelled, categorized, and presented to facilitate easy navigation and retrieval.
Experience Strategy: Experience strategy is about creating a comprehensive plan that aligns a product or service with both user needs and business goals. It ensures that the user's journey is harmoniously integrated into the overall business strategy.
Good UX vs. Bad UX.
A user experience could be either good or bad and this is determined by various factors. Let’s look at these scenarios
Scenario 1
You know that moment when you open a website and it’s taking ages to load, when it finally loads, the page is a cluttered mess, and then an error message pops up, leaving you confused about what to do next? At this point, you’re getting pretty much frustrated and unable to complete the task that brought you to the page—this is a bad user experience. A bad user experience simply means all the obstacles and frustrations encountered while using a product.
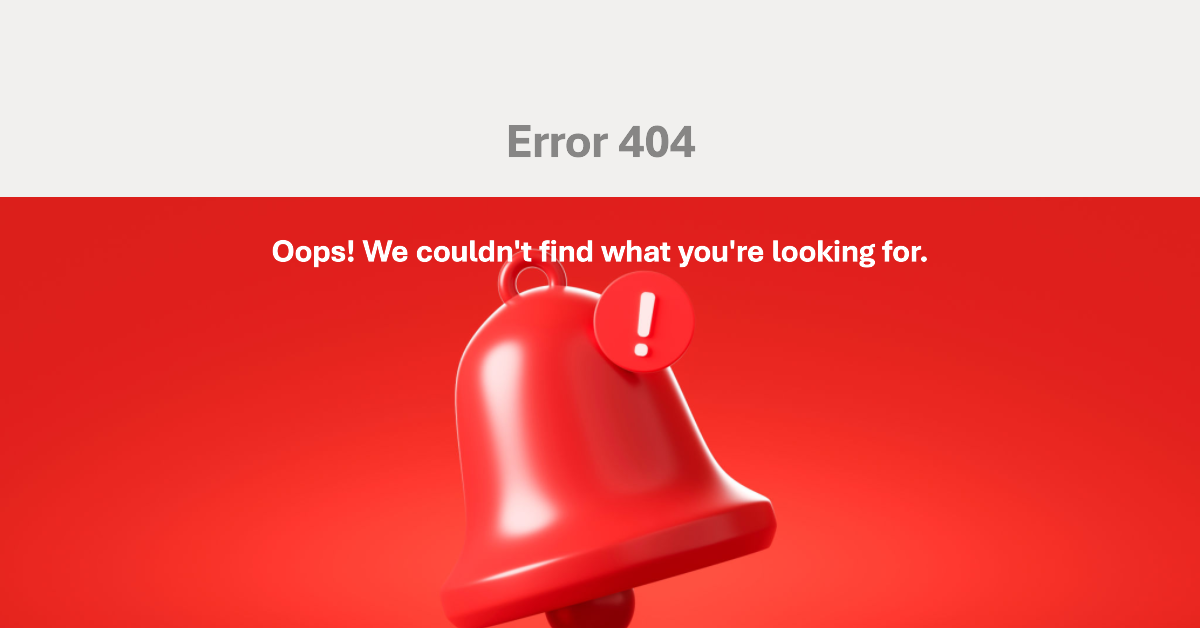
The image above shows you an error message, but what next? What should the user do? This is unfortunately left for the user to figure out. This experience can be made better. Let's see how in scenario 2
Scenario 2
Now let’s flip the coin, you open a website and the page loads pretty fast, with clear call-to-action buttons, and no clutters of elements, overall, you know what to do immediately and you complete the task that brought you to the page—now that’s a good user experience. Good user experience is all about the positive emotions, seamlessness, and functionality a product offers to the user.
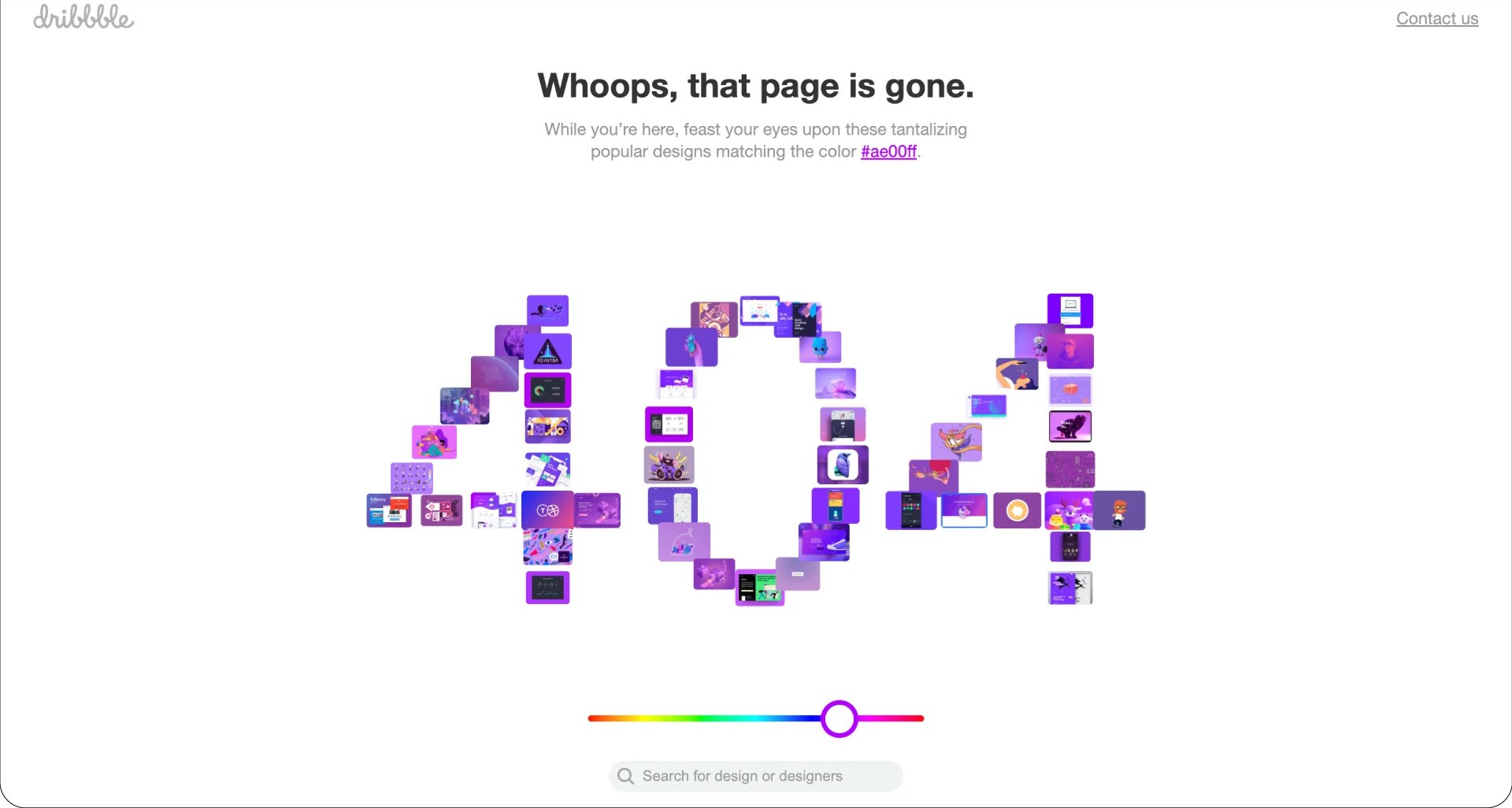
The above image is the error 404 message screen of dribbble. Here, the user’s frustrations can be pacified because there’s something fun on the screen and a search bar to bring the user back on track to achieving their goal.
We've delved into the realms of good and bad UX, discovering the frustration of poorly designed experiences and the joys of seamless functionality. But let's not forget that User Experience is not an immutable force that is left to fate. It's a design challenge that can be tackled head-on. From the study of user behaviours to crafting intuitive interfaces, from organizing information logically to aligning products with user needs and business goals, UX design has the power to shape the world around us.
Yours in pixels,
Nenye🤍
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Oleh Chinenye directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Oleh Chinenye
Oleh Chinenye
I am a UI/UX designer from Nigeria eager to learn, grow and share my story and connect with like-minded people.