Exploring Minikube: A Beginner's Guide to Local Kubernetes Development
 Rohit Deore
Rohit Deore
Introduction:
Kubernetes has become the preferred method for container orchestration, allowing developers to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications. Minikube is a valuable tool that enables developers to run a local Kubernetes cluster on their machine, providing a platform for development and testing.
What is Minikube?
Minikube is a lightweight, easy-to-use tool that allows you to run a single-node Kubernetes cluster on your local machine. It's designed for developers who want to experiment with Kubernetes or develop and test applications locally before deploying them to a production cluster.
Why Use Minikube?
1. Local Development Environment
Minikube provides a local environment that closely resembles a full-fledged Kubernetes cluster. This allows developers to develop and test applications in an environment that mirrors their production Kubernetes setup.
2. Resource Efficiency
Running a full Kubernetes cluster on your local machine can be resource-intensive. Minikube, on the other hand, provides a lightweight and resource-efficient alternative, allowing you to conserve system resources.
3. Isolation
Minikube encapsulates the entire Kubernetes cluster within a single virtual machine, ensuring that your local environment remains isolated from other applications and services on your machine.
4. Ease of Use
Minikube comes with a simple command-line interface, making it accessible even to beginners. Setting up a local Kubernetes environment is just a few commands away.
Getting Started with Minikube:
Step 1: Installation
- Install Minikube: Download and install Minikube from the official website. Follow the instructions for your operating system.
Step 2: Starting Minikube
Open your terminal or command prompt and run the following command to start Minikube:
minikube start
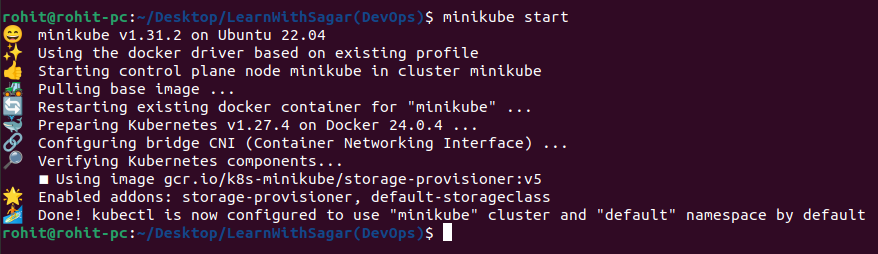
This command will download the necessary ISO image, create a virtual machine, and start the Kubernetes cluster.
Step 3: Interacting with Minikube
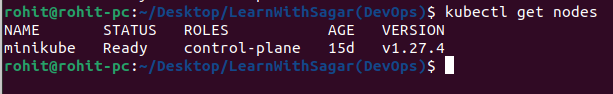
Now that you have Minikube up and running, you can interact with it using kubectl, the Kubernetes command-line tool.
kubectl get nodes
This command should display one node, which is your Minikube instance.
Step 4: Deploying Applications
You can now deploy your applications onto the Minikube cluster. Use YAML files to define deployments, services, and other Kubernetes objects.
Step 5: Accessing Applications
Services in Kubernetes allow you to expose your applications. For example, if you've deployed a web application, you can access it using the NodePort or LoadBalancer service types.
Keep Exploring...
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rohit Deore directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Rohit Deore
Rohit Deore
Student and Developer