1. Deployment Vs CICD
 Amrutha D
Amrutha D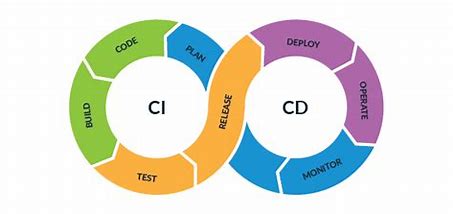
Continuous Deployment:
The step-by-step pipeline process when the developer develops the code in VCS for the production environment is called continuous deployment.
When the developer develops the code it sent to the VCS by using git, it cannot be sent to the production directly
Whatever code has been written and converted into some understandable language / installed some application/server which can understand the build/package that is sent to performance testing, then sent to the UAT/Pre-Production, before giving it to the customer the developer has to check the product has no faults in the production environment.
First building the package is sent to the system test environment & when executed all the system tests & are passed to performance testing once it is successful it is sent to UAT/ pre-production to do all the tests once everything is done without faults/bugs it was sent to the production to deliver the product to the customers.
According to the company's need, the production may have a few more steps to test the product/application for more quality.
when you try to automate the moment, developers develop the code till it reaches production, this pipeline process is called continuous deployment.
The process to reach from VCS to the production environment is called continuous deployment.
create a pipeline that tries to automate all the environments but not production, this is called continuous Delivery.
Deployment takes you to production, Delivery will not take you to production.
when the developers develop the code & send it to VCS & then build the package & make a small test whether it is working or not & send feedback to the developer on whether the code is working/not this is called continuous integration.
Continuous Deployment (Automate Everything)
Continuous Delivery (Automate everything apart from production)
Continuous Integration (Not automating everything, doing some basic checks & giving feedback to the developer.
for VCS the developers submit the code to git.
maven which helps in developing Java applications.
MS Build is used to build .net applications.
MS Build and Maven are used to build packages that are under servers. which are under servers.
GIT:
GIT is a place where developers store code.
whenever the developers submit the code to the GIT, it starts building the packages.
whenever it fails, send a mail to the developers, saying that it got errors. if it is successful next go into the system test environment.
Pipeline:
To build a pipeline we use CICD Engines, for CICD Engines we use Jenkins.
The purpose of the Azure DevOps tool is to build a pipeline.
using Azure DevOps tool we can deploy it anywhere.
using the Azure DevOps tool we can deploy it in AWS
AWS DevOps tool is used to deploy applications on any of the organizational servers.
Testing:
In manual testing and automated testing, the developer tests the applications whether it is working or not.
In packages, we have to deploy some applications on a server and create a test environment.
To create a test a test environment, gave the package to the tester asking him to test it manually.
if you give the package to the developers, they install & do all the necessary tests they inform you whether it is passing or not. will it be time to reduce the market?
not, our goal is to reduce the time to market. we want quick to the market. it is not possible, we have to automate this.
to automate the installation we need servers.
Working of Tools:
If we want to create servers, it's easy to create servers in the cloud, AWS/any virtual servers. for this, we need infra provisioning i.e. creating virtual servers in the cloud so we use Terraform to create servers.
If the application needs 10 servers at a time that can be created by Terraform.
Even if we have servers, we need to install packages in them for configuration.
For configuration, we use a tool called Ansible.
After creating Infrastructure from Terraform it will call the Ansible because in Terraform servers are created but applications are not deployed.
For the applications to be deployed we need configuration Management.
If we have a package we need to deploy it into the server and if don't have servers we need to create servers by using Terraform.
After creating servers we use Ansible for Application deployment.
After this, they will run automated tests and show results for this we use selenium tests and API automated tests to show the results.
If it fails they fail to build results, if they are successful they will run the build.
we can use the same results for the system test environment and production test environment, pre-prod and production.
whatever script we have written/work done for a system test environment, the same can be modified and used for all the environments.
The tools that we are going to use are Ansible and Terraform.
Containers, Docker, and Kubernetes are the new ways of running your applications.
for building the package we use Maven and MS Build.
If the organizations decide to use container technology, if your application is container-based we create a Docker-based package.
To deploy this Docker-based package We need Kubernetes.
We create Kubernetes from Terraform and deploy containers in Kubernetes.
If your application is containerized then we use docker, and Kubernetes for system tests, performance tests, UAT, and production environment.
We just come to know why we use these tools.
Terraform - To create infrastructure.
Ansible - to deploy Applications.
For build/package tools we need to create software packages.
Kubernetes - for containerized applications
Docker - for packaging the containerized applications.
To do the pipeline process activity it had to touch a lot of servers, if some servers fail in it, will it impact our work? yes because of that, we should do monitoring it is of two types.
Monitoring:
If we want to do application deployments we need to know the number of applications
- server monitoring/infra monitoring - it will check whether it is running/working or not
assuming that your application is deployed it is working but things are failing at production, we need to troubleshoot we it goes live.
If we give a new release to the application when customers try to access it but fail, then the customer chooses another application i.e. (if the flipchart fails then customer reaches the Amazon).
To avoid this application failure, we need two monitoring
servers monitoring- to check whether everything is alive/not.
- Application Monitoring- which tries to tell me my application is failing why is it failing?
for this, we need an Elastic
Google is doing DevOps because it has new features every time, Gmail getting new features, how is Google doing DevOps and running the production system?
Google released a book called "Site Reliability Engineering"(SRE) which has a prominent role in it.
In the SRE book, Google handles the production system with the help of an elastic stack.
There are many ways but do this with the elastic stack. so that people have more opportunities as SRE engineers.
Security:
In every phase of DevOps, if the developers develop the code, we do the security scans, if any issues in the code will lead to vulnerabilities/hacks.
starts security at every moment of the pipeline
Starts security in every phase/moment in the pipeline that is called DevSecOps. For this, we are learning certain tools,
we use
SCA ( Software component analysis)
SAST ( Static application security testing)
DAST ( Dynamic application security testing)
JOBS:
in this, we can apply for 4 positions;
DevOps Engineer
SRE Engineer
Cloud Ops Engineer- when mixing the cloud
when working as DevOps Engineers we will work on any of the areas from VCS to the Production environment. or can create pipelines from Scratch.
DevOps Engineers should know all of these things.
SonarQube, Artifactory are minor tools.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Amrutha D directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Amrutha D
Amrutha D
Gen AI Video Creator | Gen AIOps | AIOps Cloud DevOps Engineer | Let's Connect & share Technical knowledge & grow together in Technologies Everyday..