Building a Serverless Application Repository with Terraform
 Mahira Technology Private Limited
Mahira Technology Private Limited
Introduction :-
In the ever-evolving world of #CloudComputing, #serverless #architecture is becoming increasingly popular. One of the key aspects of this architecture is the ability to create, #deploy, and manage applications without worrying about infrastructure. To take full advantage of serverless technology, you need a structured and efficient way to manage your serverless applications. This is where #Terraform, the #infrastructure-as-code tool, comes into play.
Prerequisites :
AWS account
#AWS CLI installed and configured
#Terraform installed
Step-1 : AWS CLI Configuration
1.1. Ensure that you have the AWS CLI installed on your local machine.
1.2. Configure your AWS CLI with the necessary AWS credentials.
aws configure
Step-2 : Terraform Installation and Configuration
2.1. Install #Terraform on your local machine.
2.2. Verify the #Terraform installation.
terraform version
Step-3 : Creating the Terraform Project Structure
3.1. Create a new directory for your #Terraform project.
3.2. Organize your project directory with the following structure:
serverless-app-repo/
│ main.tf
│ lambda_function.zip
│ requirements.txt
│ lambda_function.py
main.tf: The main configuration file for defining AWS resources.lambda_function.zip: The Lambda #deployment package.requirements.txt: Dependencies for your Lambda function.lambda_function.py: The #Python code for your Lambda function.
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-central-1" # Update to match your AWS CLI profile region
profile = "default"
}
# Create an S3 bucket for storing application artifacts
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "app_repository" {
bucket = "serverless-app-repository" # Update the bucket name as needed
}
# Define IAM roles and policies
resource "aws_iam_role" "lambda_role" {
name = "lambda_execution_role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012–10–17",
Statement = [
{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole",
Effect = "Allow",
Principal = {
Service = "lambda.amazonaws.com"
}
}
]
})
}
# Define IAM policy for Lambda function
resource "aws_iam_policy" "lambda_policy" {
name = "lambda_policy"
description = "Policy for Lambda functions in the repository"
# Define your policy document here
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012–10–17",
Statement = [
{
Action = [
"lambda:InvokeFunction",
# Add other actions as needed
],
Effect = "Allow",
Resource = "*",
},
],
})
}
# Attach managed policies to the Lambda execution role
resource "aws_iam_policy_attachment" "lambda_role_policy_attachment" {
name = "lambda-policy-attachment"
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.lambda_policy.arn
roles = [aws_iam_role.lambda_role.name]
}
# Attach AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole managed policy
resource "aws_iam_policy_attachment" "lambda_basic_execution_attachment" {
name = "lambda-basic-execution-policy-attachment"
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole"
roles = [aws_iam_role.lambda_role.name]
}
# Define IAM policy for CloudWatch Logs
resource "aws_iam_policy" "cloudwatch_logs_policy" {
name = "cloudwatch_logs_policy"
description = "Policy for CloudWatch Logs access"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012–10–17",
Statement = [
{
Action = [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams",
],
Effect = "Allow",
Resource = "*",
},
],
})
}
# Attach CloudWatch Logs policy to the Lambda execution role
resource "aws_iam_policy_attachment" "cloudwatch_logs_attachment" {
name = "cloudwatch-logs-policy-attachment"
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.cloudwatch_logs_policy.arn
roles = [aws_iam_role.lambda_role.name]
}
# Define IAM policy for S3 full access
resource "aws_iam_policy" "s3_full_access_policy" {
name = "s3-full-access-policy"
description = "Policy for S3 full access"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012–10–17",
Statement = [
{
Action = [
"s3:*",
],
Effect = "Allow",
Resource = "*",
},
],
})
}
# Attach S3 full access policy to the Lambda execution role
resource "aws_iam_policy_attachment" "s3_full_access_attachment" {
name = "s3-full-access-policy-attachment"
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.s3_full_access_policy.arn
roles = [aws_iam_role.lambda_role.name]
}
# Define AWS Lambda function
resource "aws_lambda_function" "list_applications" {
filename = "list_applications.zip" # Specify the correct path to your deployment package
function_name = "newFunctionName" # Update with your desired function name
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_role.arn
handler = "list_applications.list_applications" # Specify the correct Python module and function name
runtime = "python3.8" # Use the correct Python runtime version
source_code_hash = filebase64sha256("list_applications.zip") # Ensure the package exists
}
# Create an AWS API Gateway for your repository
resource "aws_api_gateway_rest_api" "repository_api" {
name = "repository_api"
description = "Serverless Application Repository API"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_resource" "repository_resource" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.repository_api.id
parent_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.repository_api.root_resource_id
path_part = "v1"
}
Step-4 : Running Terraform
4.1. Initialize your #Terraform project.
terraform init
4.2. Review the execution plan to ensure there are no errors.
terraform plan
4.3. Apply the Terraform configuration to create AWS resources.
terraform apply
Step-5 : Testing the Serverless Application
5.1. Verify that all AWS resources have been created successfully.
5.2. Test your #serverless application by invoking the Lambda function.
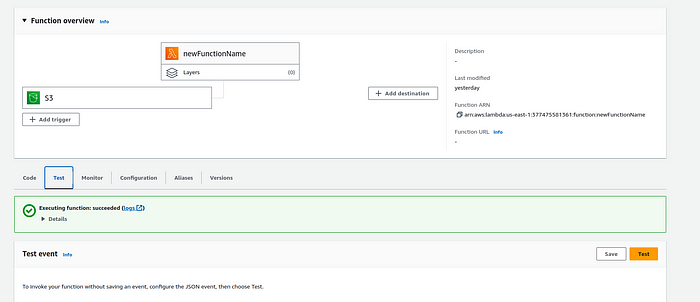
Step-6 : Viewing Logs
6.1. Access #CloudWatch Logs to view and #troubleshoot logs generated by your Lambda function.
Conclusion :-
Building a #Serverless Application #Repository with #Terraform is more than just a technical exercise; it’s a strategic move to enhance your #organization efficiency and agility. With #Terraform’s power to codify your #infrastructure, you can create a centralized repository for your serverless applications. This not only simplifies the #deployment process but also ensures #consistency and reliability.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mahira Technology Private Limited directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mahira Technology Private Limited
Mahira Technology Private Limited
A leading tech consulting firm specializing in innovative solutions. Experts in cloud, DevOps, automation, data analytics & more. Trusted technology partner.