Automating AWS CodePipeline Setup with Terraform: Streamline Your CI/CD Workflow
 Mahira Technology Private Limited
Mahira Technology Private Limited

Introduction:-
AWS #CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous delivery service that helps you automate your software release process. With CFV, an infrastructure-as-code tool, you can simplify the provisioning and configuration of #CodePipeline resources.
Prerequisites Before we begin, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
An AWS account with appropriate permissions to create #CodePipeline resources.
#Terraform installed on your local machine.
AWS CLI configured with your AWS credentials.
Step-1 :- create a folder named code-pipeline in your home directory.
Step-2 :- Setting Up Your #Terraform Configuration Files Create three files: main.tf,variable.tf , and output.tf in your code-pipeline folder. Open your preferred text editor and create these files.
Step -3 :- Writing the #Terraform Code Now, let’s dive into the main.tf file and start writing our #Terraform code. In this file, we'll configure the AWS provider and define the #CodePipeline resources required for our deployment. Here's an example of how you can define the #CodePipeline:
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1" # Replace with your desired AWS region
}
resource "aws_codepipeline" "my_pipeline" {
name = var.pipeline_name
role_arn = "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/CodePipelineServiceRole" # Replace with your pipeline service role ARN
artifact_store {
location = "my-pipeline-artifacts" # Replace with your desired S3 bucket name
type = "S3"
}
stage {
name = "Source"
action {
name = "SourceAction"
category = "Source"
owner = "AWS"
provider = "CodeCommit"
version = "1"
output_artifacts = ["SourceArtifact"]
configuration {
RepositoryName = var.source_repository
}
}
}
stage {
name = "Build"
action {
name = "BuildAction"
category = "Build"
owner = "AWS"
provider = "CodeBuild"
input_artifacts = ["SourceArtifact"]
version = "1"
configuration {
ProjectName = "my-codebuild-project" # Replace with your CodeBuild project name
EnvironmentVariables = [
{
name = "BUILD_SPEC"
value = var.buildspec_file
}
]
}
}
}
# Add additional stages and actions as needed
}
# Add any additional resources as needed
Step-4 :- Defining Input Variables In the variable.tf file, define the input variables needed for your #CodePipeline deployment. These variables will allow you to customize your pipeline based on your project's requirements. Here's an example of how you can define some essential variables:
variable "pipeline_name" {
description = "Name of the CodePipeline"
type = string
}
variable "source_repository" {
description = "URL of the source code repository"
type = string
}
variable "buildspec_file" {
description = "File path to the buildspec file"
type = string
}
# Add any additional variables as needed
Step-5 :- Defining Outputs In the output.tf file, define the outputs you want to retrieve after deploying the #CodePipeline resources. These outputs can include information such as the #CodePipeline ARN, S3 bucket name for artifacts, or any other relevant details.
output "pipeline_arn" {
value = aws_codepipeline.my_pipeline.arn
}
output "artifact_bucket" {
value = aws_codepipeline.my_pipeline.artifact_store[0].location
}
# Add any additional outputs as needed
Step-6 :- Deploying #CodePipeline Resources Now that we have defined our #Terraform code, it’s time to deploy our #CodePipeline resources. Follow these steps:
Open a terminal or command prompt and navigate to the directory where your #Terraform files are located.
Run the following command to initialize the #Terraform configuration:
terraform init
This command downloads the necessary provider plugins and sets up the backend for storing the #Terraform state.
- Next, run the command to validate the #Terraform configuration:
terraform validate
This command ensures that the syntax and structure of your #Terraform code are correct.
- Run the following command to see the execution plan and confirm the resources that #Terraform will create:
terrafom plan
Review the plan to ensure that it aligns with your expectations. It will show you the changes that #Terraform will make to create or modify resources.
- If the plan looks good, proceed to apply the changes by running the following command:
terraform apply
You will be prompted to confirm the deployment. Type “yes” and press Enter to proceed.
- #Terraform will now create the #CodePipeline resources based on your configuration. This process may take a few moments. Once completed, you will see the outputs defined in the output.tf file, such as the pipeline ARN and artifact bucket name.
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed #CodePipeline resources using #Terraform.
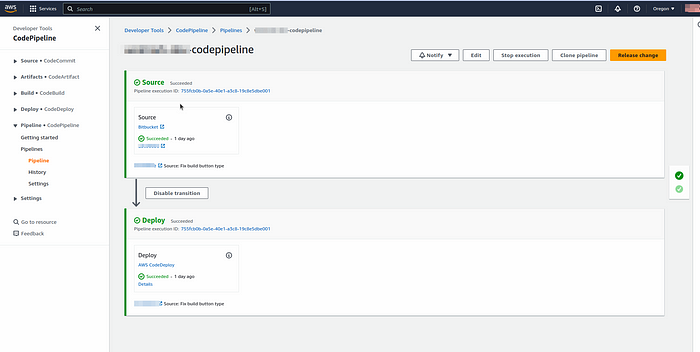
Step 7: Cleaning Up (Optional) If you want to remove the deployed #CodePipeline resources and destroy the infrastructure, follow these steps:
- In the same terminal or command prompt, run the following command:
terraform destroy
You will be prompted to confirm the destruction of the resources. Type “yes” and press Enter to proceed.
- #Terraform will destroy the #CodePipeline resources and any other resources defined in your #Terraform configuration.
Conclusion:-
In this guide, we learned how to deploy #CodePipeline resources using #Terraform. By following the step-by-step instructions, you gained the ability to automate your software delivery pipeline and maintain consistency in your deployments. #Terraform’s infrastructure-as-code approach allows for version-controlled, repeatable deployments, making it a powerful tool for managing your AWS infrastructure.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mahira Technology Private Limited directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mahira Technology Private Limited
Mahira Technology Private Limited
A leading tech consulting firm specializing in innovative solutions. Experts in cloud, DevOps, automation, data analytics & more. Trusted technology partner.