Ethereum scalability highlights
 Efstratios Gkoltsios
Efstratios Gkoltsios
Ethereum a glimpse into the past
Everybody knows the extraordinary Ethereum network and its meaning to the blockchain world. The uses of smart contracts, Defi, transactions, NFTs, gaming and so much more. With a market cap of 190 billion making it the second biggest cryptocurrency and reaching 550 billion market cap at its peak. There are nevertheless some valid concerns about its future and the future of blockchain as a whole.
After the booming of crypto (2021) with ETH soaring at 4,800$ the ETH fees were very high with the congestion of the network making the prices reach 30 -50$.
Also, another big factor is the TPS of a payment network (transactions per second), ethereum was able to do 10TPS comparing it to VISA’s 1200 TPS.
The Ethereum network was working also with the PoW (power of work) consensus mechanism which although its high security had a bad impact on the environment because it needed a lot of energy resources to function.
Despite the current Ethereum price being below 50% of the all-time highest prices of Ethereum, the volume of the daily transactions now varies on avg at 900k, 25% below the all-time highest daily volumes (1250k) in 2021, which is a good sign and fact for the usage and trust for the network by the masses. Below we can see the chart provided by Ethersacn.io
Ethereum Daily Transactions Chart
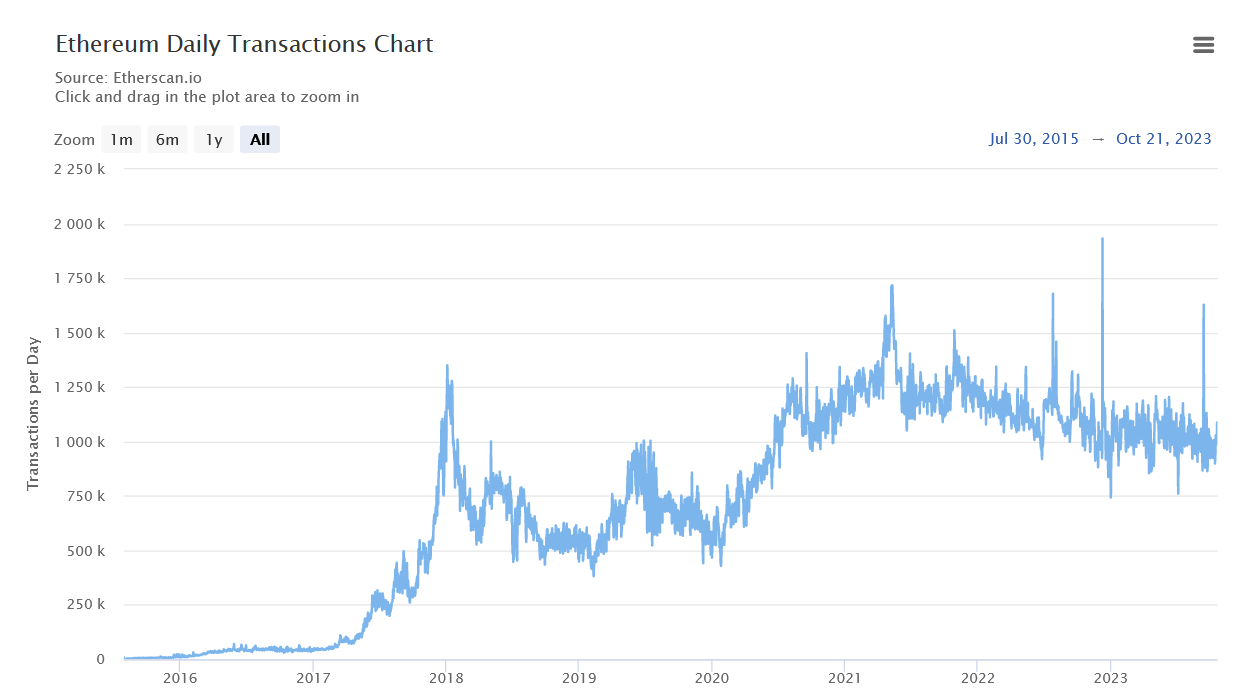
We also see in the below graph that the ERC20 token's daily transactions have gone up, so we can say that the total ERC20 transactions in the Ethereum network have stayed relatively the same.
ERC20 Daily Token Transfer Chart
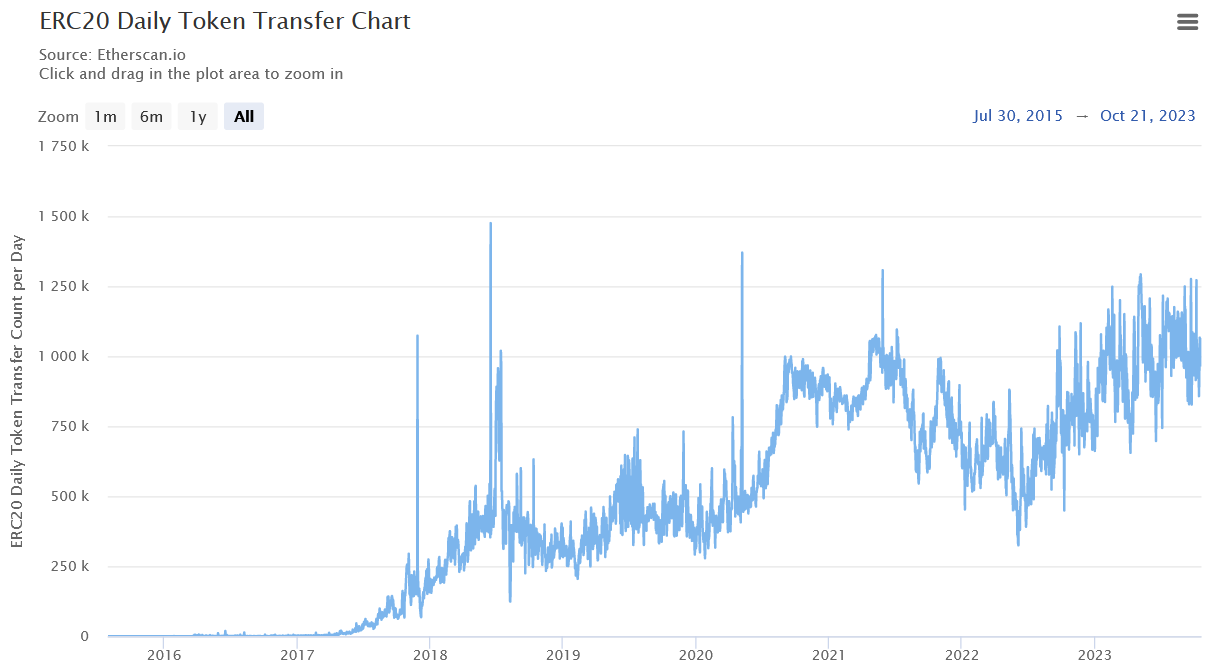
https://etherscan.io/chart/tokenerc-20txns
You can learn more about etherscan and its metrics in the Ethereum chain and also its association with Polygon.
Ethereum scaling solutions
Ethereum scaling solutions have taken place to solve the scaling and fees problem. The solutions include Ethereum going from PoW to PoS consensus mechanism ETH 2.0, the introduction of rollups that are on the Ethereum network performing as layer 2 chains and the symbiotic chain Polygon which was also present before. In this article, we are going to focus on those solutions only.
Ethereum 2.0 – the Merge
After countless tests and years of anticipation, the Ethereum team announced it would "merge" the PoW blockchain into the Beacon Chain in 2022. On September 15, at 6:43 AM UTC, Ethereum successfully transitioned to a PoS blockchain.
Although the Merge was one of the most significant upgrades in crypto history, it didn't directly impact Ethereum's transaction speeds or fees. Instead, the PoS consensus laid the groundwork for further upgrades that could make Ethereum faster and cheaper claiming that it would reach 100,000 TPS and 0.01$ per transaction. The most immediate effect of the Merge was a reduction in Ethereum's carbon footprint. Since there's no more need for GPU miners, Ethereum cut its electricity and net emissions by an estimated 99.95%. Thanks to Ethereum's PoS consensus, it went from being one of the biggest polluters to an eco-friendly blockchain.
Some good news for the Ethereum blockchain is that now with the implementation of rollups, the TPS went from 8 to almost 12 and the overall cost of transactions went from 12-15$ to less than 5$ always talking with averages, because due to network congestion (supply and demand) sometimes the prices range very widely from the average price.
Average Transaction Fee Chart
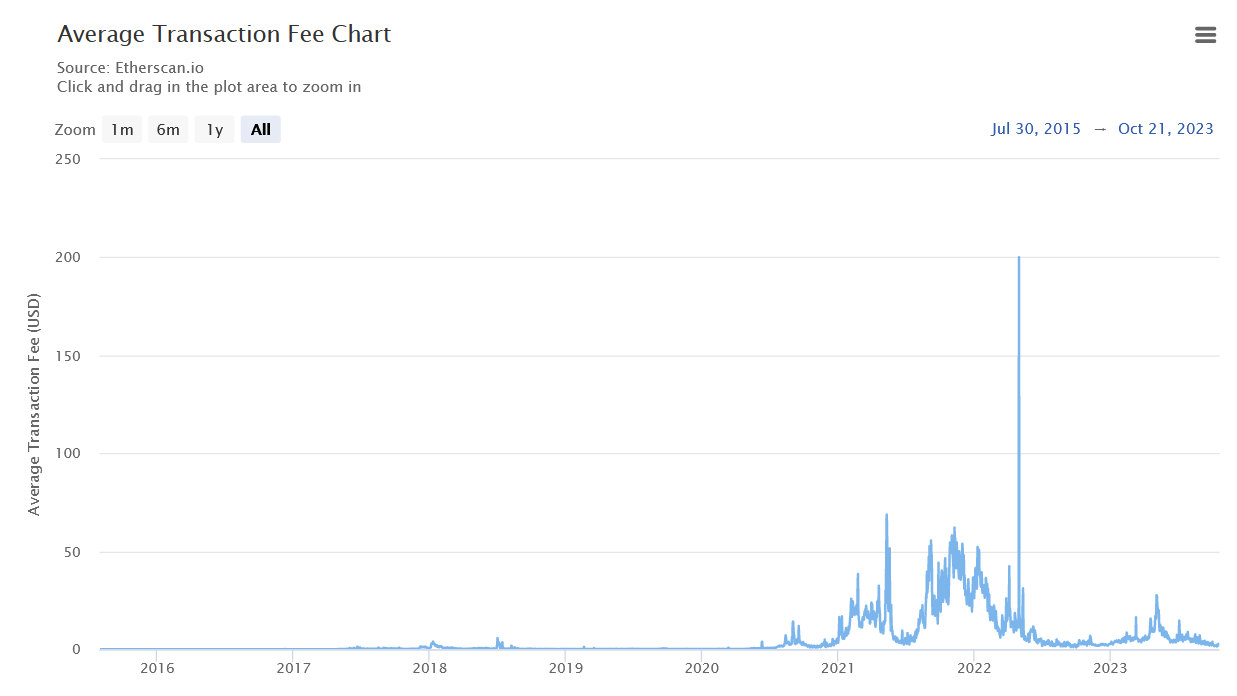
https://etherscan.io/chart/avg-txfee-usd
Introduction to the rollups technology
Rollups are a layer-2 scaling solution in blockchain technology, aiming to enhance the scalability of the underlying layer-1 blockchain.
They work by bundling multiple transactions together and executing them off-chain before posting a single aggregated transaction on the main blockchain, reducing congestion and lowering gas fees, you can see the TPS percentages on the Ethereum blockchain on this website https://ethtps.info/.
Rollups come in two main types: optimistic rollups and zk-rollups. Optimistic rollups such as Arbitrum and Optimism assume the validity of transactions by default but rely on a process to challenge and verify any incorrect transactions.
In contrast, zk-rollups such as zk-Sync utilize zero-knowledge proofs to cryptographically validate transactions without making assumptions, offering a more secure and efficient approach.
Rollups significantly increase the transaction throughput of the main blockchain, making it capable of handling a larger volume of transactions.
They have gained prominence as a vital scaling solution in Ethereum and other blockchain ecosystems, addressing network congestion and improving transaction efficiency. As of right now, most transactions happen with rollups because they are ~3-8x cheaper than Ethereum layer 1. Last but not least rollups tech is implemented also by the Polygon chain, as we will see in more detail below.
Polygon chain
One of the most popular scaling solutions for the Ethereum network is the Polygon blockchain. Polygon is called a "Commit Chain" because is a layer 2 chain but also a side chain. Polygon PoS is called "An EVM enabled sidechain" which sounds reasonable because it is a separate chain with a separate mechanism, but also its consensus mechanism has a lot of extra features that rely on the security of the main Ethereum layer. Polygon has transactions up to 7000TPS which makes its transactions big in volume fast and cheap but this comes with a cost in decentralization and security. In the Polygon network are included a lot of sidechains and plasma chains, Polygon is both a Layer 2 solution and a side-chain, with its PoS Chains interconnected and communicating with the Ethereum mainnet.
Polygon offers various scaling solutions, including sidechains, plasma chains, and standalone chains.
The platform reduces congestion, lowers transaction fees, and enhances transaction speeds by offloading transactions to these chains.
The platform has introduced a new side chain Polygon zkEVM. Also, they have proposed to make the current main chain Polygon POS to Polygon zkEvm validium.
.
The key difference here is that Polygon zkEVM is a zero-knowledge rollup, whereas Polygon PoS will become a zero-knowledge validium.
Polygon zkEVM does post transaction data back to the Ethereum mainnet. Meaning it will be comparatively less scalable, and more secure, making it suitable for projects such as high-value DeFi applications.
Polygon PoS (when upgraded) does not post transaction data back to Ethereum. Meaning it will be comparatively more scalable, and less secure, making it suitable for projects that have high transaction volume and require low transaction fees, e.g. gaming, social, and micro DeFi. (https://blog.jarrodwatts.com/polygon-pos-is-becoming-a-zkevm-validium-explained)
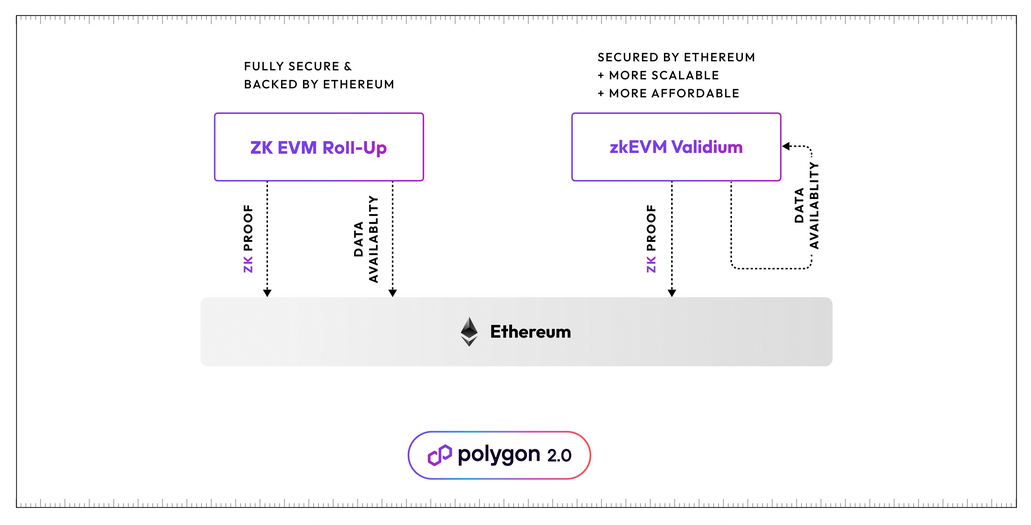
Summerise
Ethereum network is a brilliant technology but it needs fast changes and solutions to stay alive and compete in the finance environment and with the well-established banking system. For now, it seems that it emphasizes keeping decentralization scalability and security on equal terms making it unable for now to scale up to 100,000TPS. Nevertheless, the technology and landscape that provides for other networks (Defi, Daos, DApps) are priceless for the blockchain space as a whole and with solutions like rollups and other chains (Polygon-7000TPS) operating on the Ethereum network it has a firm grasp on the race of competition and also a promising one.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Efstratios Gkoltsios directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
