Working with Ansible {Part-12}
 Chirag Kukreja
Chirag Kukreja
Installing Apache through Ansible
Let's install the Apache through YAML using following code
---
- name: Installing Apache
hosts: Node-1
tasks:
- name: task1 Installing Apache
yum:
name: httpd
state: latest
- name: Enable service httpd
systemd:
name: httpd
enabled: true
- name: Copy file with owner and permissions
copy:
src: ./index.html
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
owner: apache
group: apache
notify: Restart Apache
handlers:
- name: Restart Apache
systemd:
state: restarted
daemon_reload: true
name: httpd
This Playbook is available on the internet.
Roles in Ansible
We can use Roles for reusing a set of tasks. Roles are good for organizing tasks and encapsulating data needed to accomplish those tasks.
ANSIBLE ROLES
Default-> It stores the data about role/application default variables e.g. if you want to run to port 80 or 8080 then variables need to be defined in this path.
Files-> It contains files that need to be transferred to the remote VM (static files) without variables.
Handlers-> They are triggers or tasks e.g. in the above playbook we are restarting the Apache. We can segregate all the handlers required in the playbook.
Meta-> This directory contains files that establish roles dependencies e.g. Author Name, Supported platform, and dependencies if any.
Template-> It contains files that need to be transferred to the remote VM with variable values
Tasks-> It contains all the tasks that are normally in the playbook e.g. Installing packages and copying files etc.
Vars-> Variables for the role can be specified in this directory and used in your configuration files both vars and default variables.
We can Organise playbooks into a directory structure called roles.
Adding more and more functionality to the playbooks will make it difficult to maintain in a single file.
Now, For installing Apache we will create the roles for our Ansible playbook.
There are 4 sections in the above playbook
i) Name
ii) hosts
iii) tasks
iv) handlers
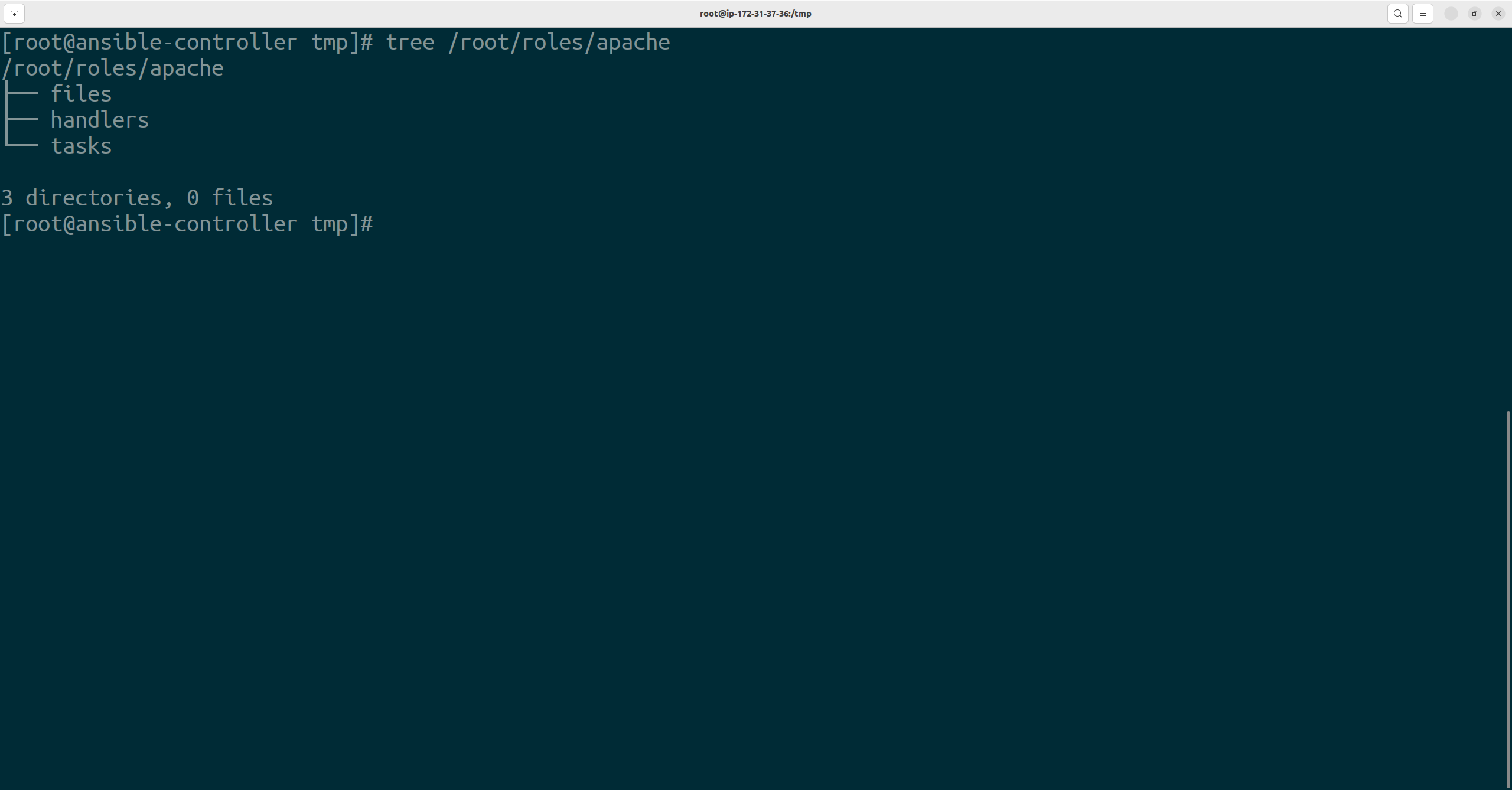
To achieve Roles we will create 3 directories
i) handlers
ii) tasks
iii) files
Let's create the directories in Apache
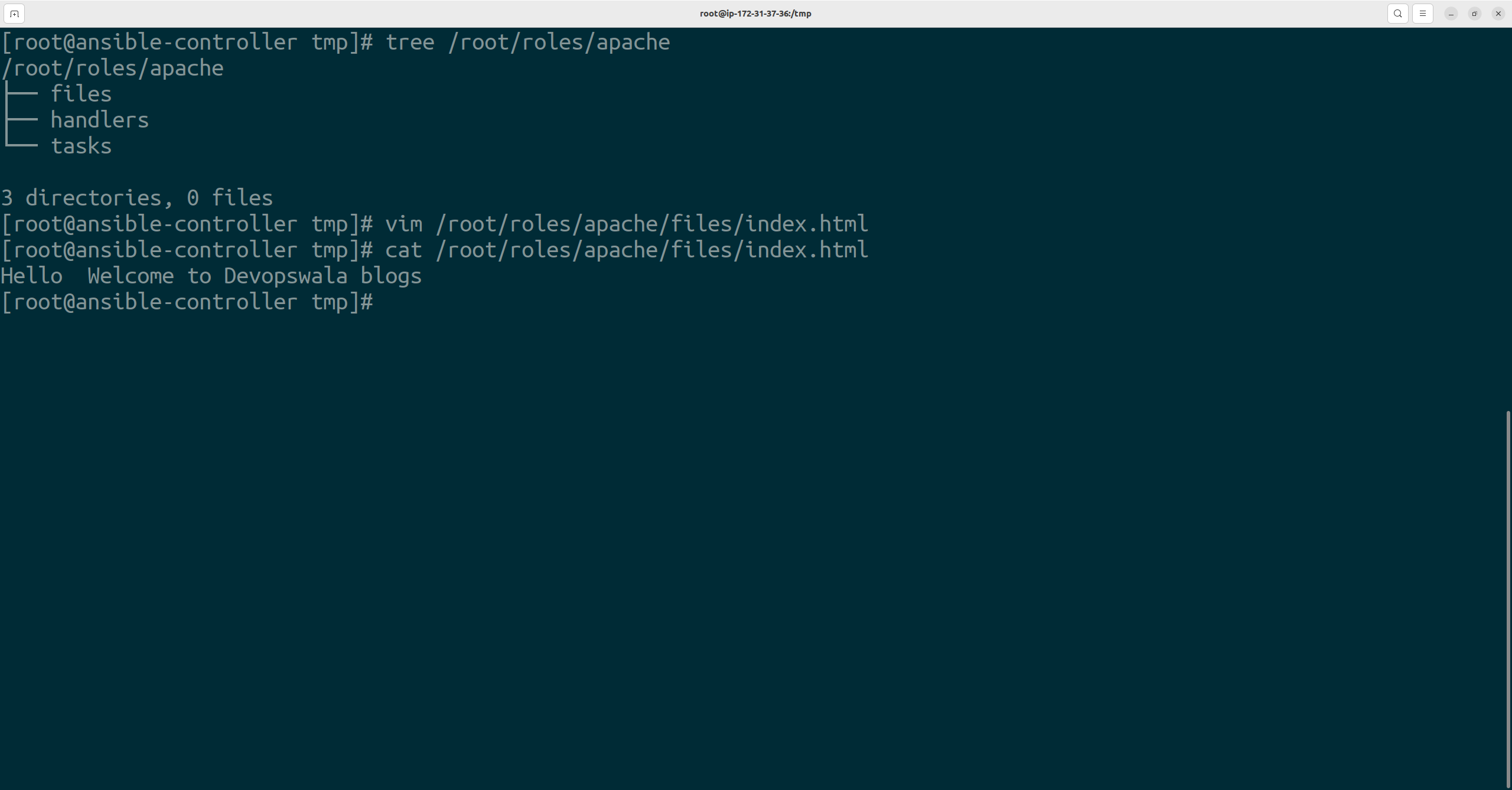
Now, Create the index.html in the files directory
After this, let's define the handlers section with the main.yaml in the handlers directory
- name: Restart Apache systemd: state: restarted daemon_reload: true name: httpd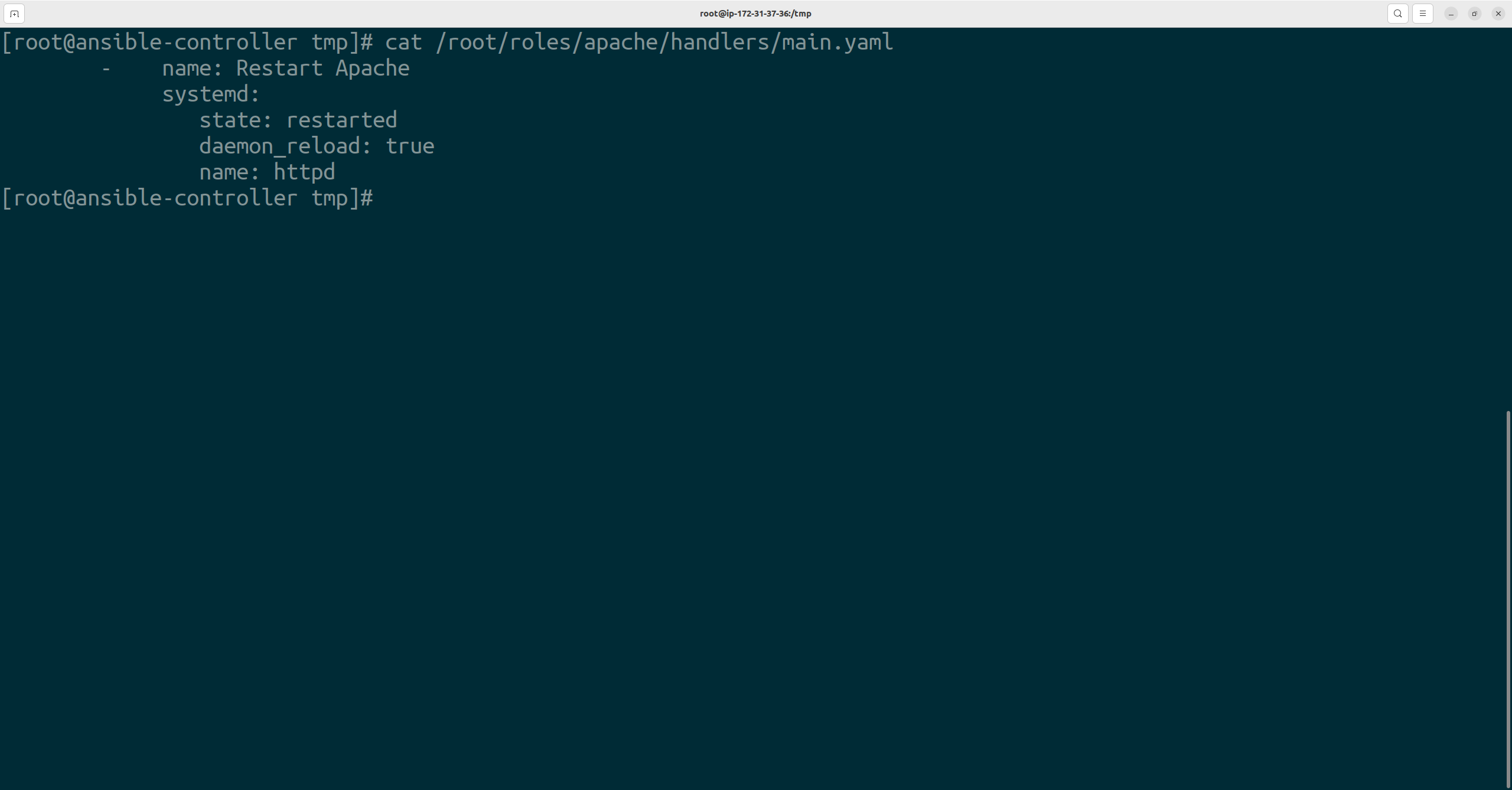
Let's define the tasks section in the tasks directory with main.yaml
- name: task1 Installing Apache yum: name: httpd state: latest - name: Enable service httpd systemd: name: httpd enabled: true - name: Copy file with owner and permissions copy: src: ./index.html dest: /var/www/html/index.html owner: apache group: apache notify: Restart ApacheLet's see the tree structure as follows and we can see that our role is ready.
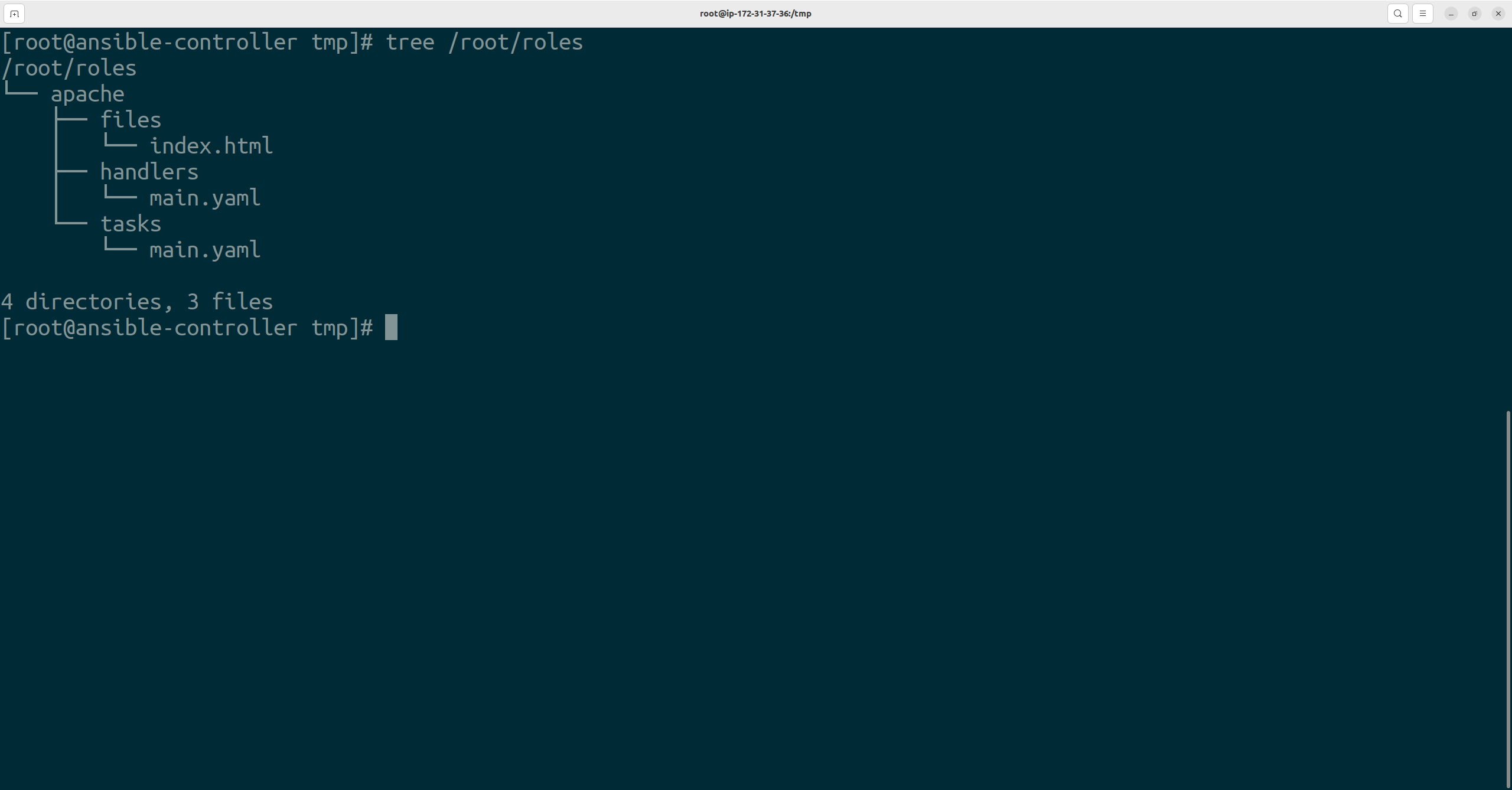
Now, For our application 1, we need to install Apache. Let's see How we are going to install that
--- - name: Installing Apache for application Through Roles hosts: Node-2 roles: - apache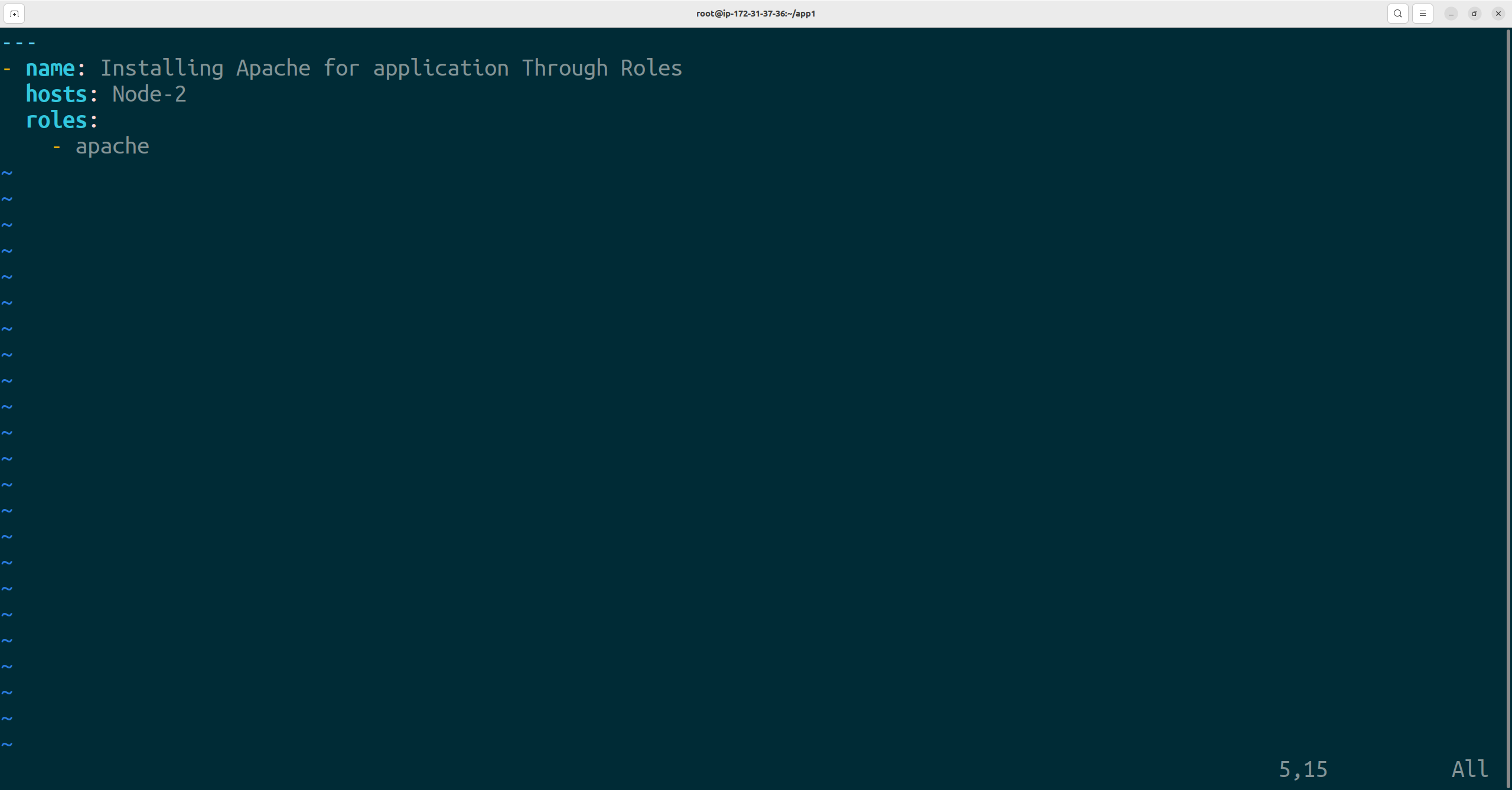
Now, to install the Apache via roles we need to copy Ansible files (mykey.pem, ansiblehosts, ansible.cfg) to the app1 directory.
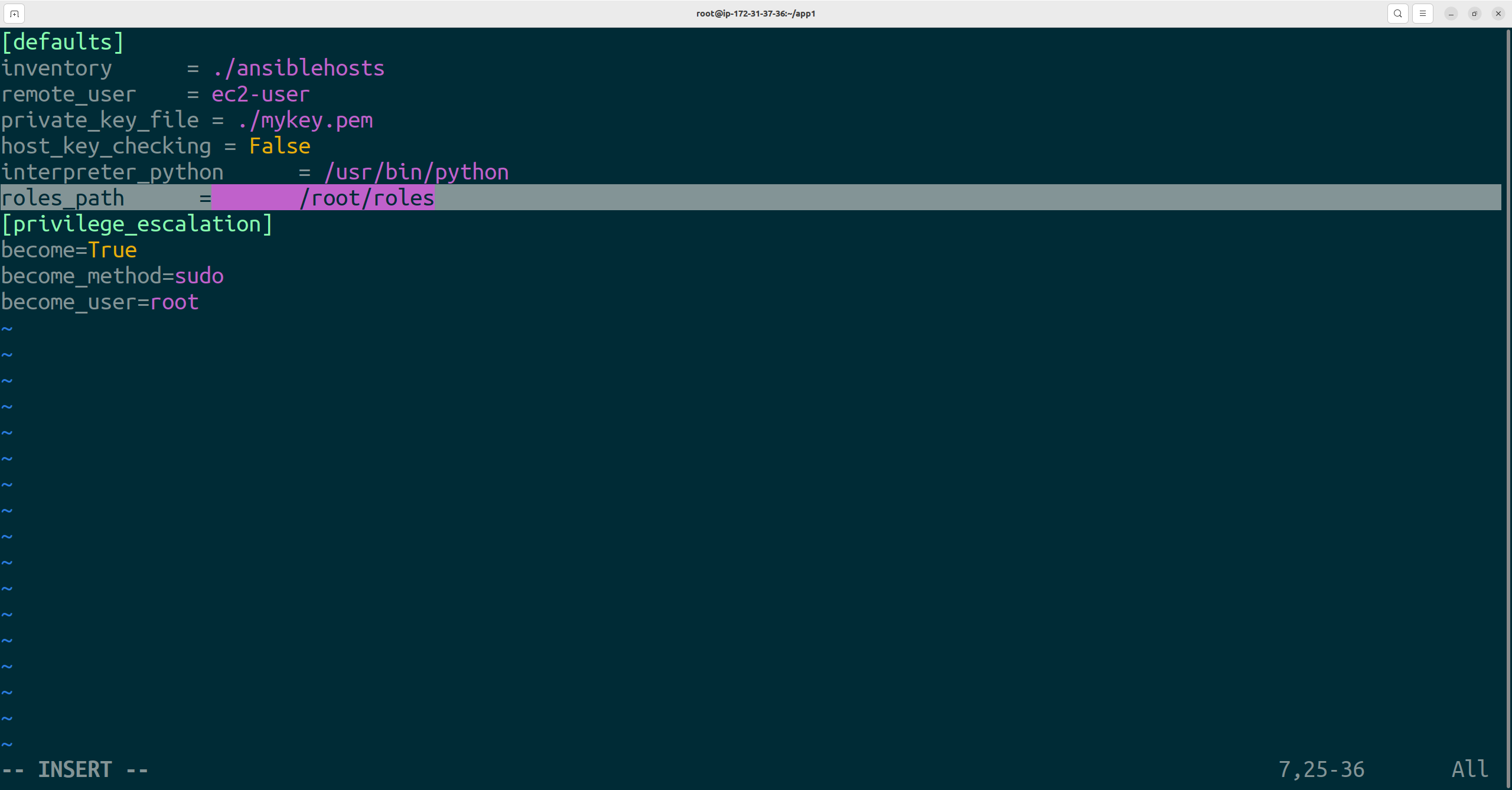
Now, give the roles_path to the ansible.cfg file and save the file.
Now, Execute the Ansible-Playbook and observe whether the index.html content is getting displayed or not.
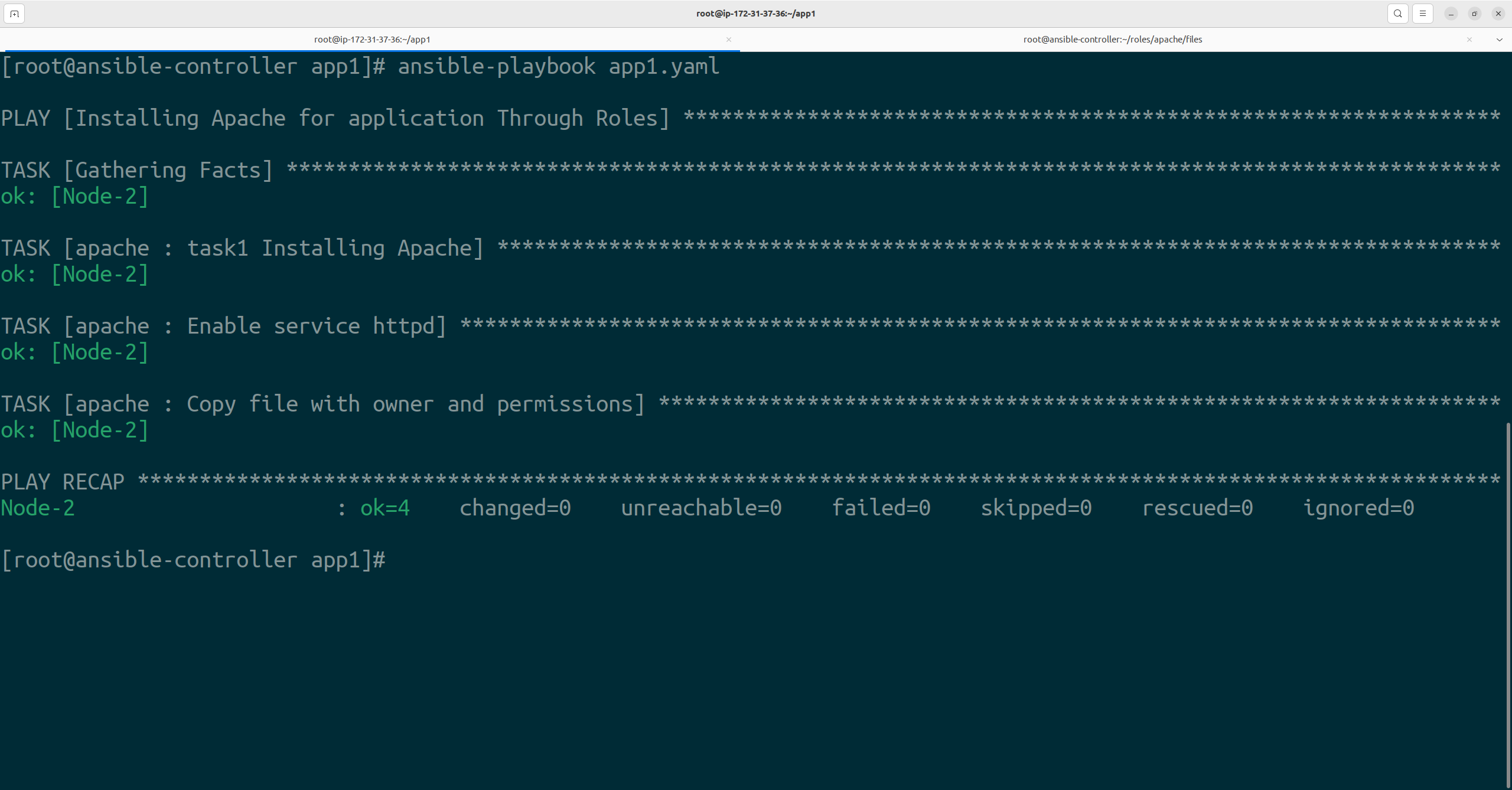
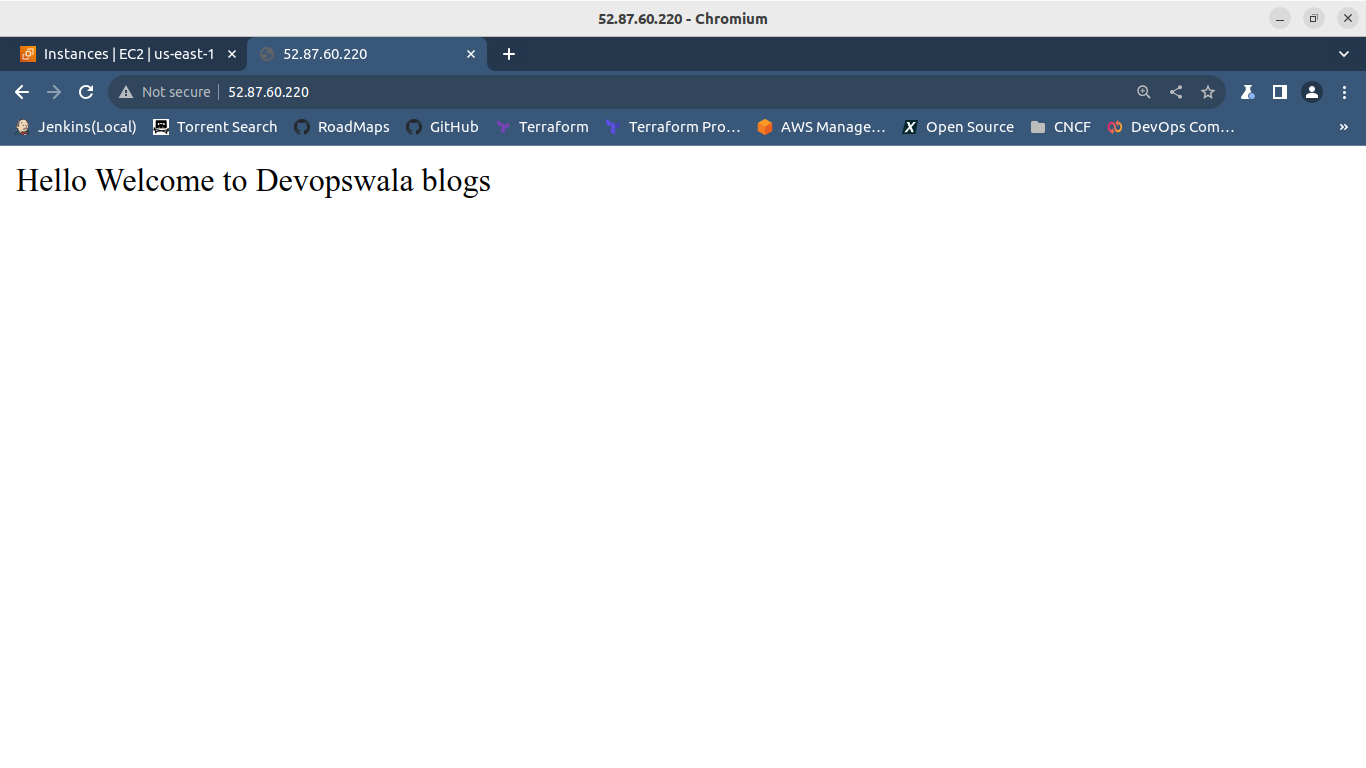
Hence, we saw the use of Roles in the Ansible for the Installation of Apache. Kindly visit my Github profile to check the code for installing Apache.
%[https://github.com/chiragkuk24/Ansible_Learning/blob/main/010_Installing_Apache_via_Ansible.yaml]
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Chirag Kukreja directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Chirag Kukreja
Chirag Kukreja
Working in TSYS