Academic Notes About Visual Sensory
 Mikoto
MikotoTable of contents
Lectures in MIT University
Sensory Systems The Human Brain
Terminology
Membrane - ja: maku Anatomy A thin piece of skin that covers or connects parts of a person's or animal's body: The cornea is the transparent membrane that covers the front of the eye. Engineering A very thin piece of material that covers an opening Biology The outer covering of a cell: A cell membrane
Tissue - ja: saibou soshiki A group of connected cells in an animal or plant that are similar to each other, have the same purpose, and form the stated part of the animal or plant: Human tissue Plant tissue Brain/lung/muscle/fat tissue His face is covered with scar tissue where he was badly burned.
Equation - ja: houteishiki A mathematical statement in which you show that two amounts are equal using mathematical symbols:
Translucent - ja: han-toumei If an object or a substance is translucent, it is almost transparent, allowing some light through it in an attractive way.
Scattur - ja: chirasu To (cause to) move far apart in different directions: The protesters scattered at the sound of gunshots. The soldiers came in and scattered the crowd.
Parmeate - ja: shintou-suru To spread through something and be present in every part of it: Dissatisfaction with the government seems to have permeated every section of society. A foul smell of stale beer permeated the whole building. The table has a plastic coating which prevents liquids from permeating into the wood beneath.
Diffuse - ja: kakusan-suru To (cause something to) spread in many directions: Television is a powerful means of diffusing knowledge. To (cause a gas or liquid to) spread through or into a surrounding substance by mixing with it: Oxygen diffuses from the lungs into the bloodstream. The drop of red dye diffused slowly in the water.
Glow - kagayaki, kirameki To produce a continuous light and sometimes heat: A nightlight glowed dimly in the corner of the children's bedroom. This substance is so radioactive that it glows in the dark. To look attractive because you are happy or healthy, especially with eyes that are shining: The children's faces were glowing with excitement. They came back from their week at the beach, glowing with health.
Anamorphic - ja:na Denoting or relating to a distorted projection or drawing that appears normal when viewed from a particular point or with a suitable mirror or lens. "An anamorphic widescreen image"
Denote - ja: shimesu Be a sign of; indicate. "This mark denotes purity and quality"
Cinematographer - ja: satsuei-kantoku
Steadicam - ja: na A lightweight mounting for a movie camera that keeps it steady for filming when handheld or moving.
Buoyant - ja: furyoku Able to float: Cork is light and buoyant.
Cuspy - ja: togatta Edgy
Payload - ja: na 1 The part of a vehicle's load, especially an aircraft's, from which revenue is derived; passengers and cargo. 2 An explosive warhead carried by a missile. 3 Computing The actual information or message in transmitted data, as opposed to automatically generated metadata.
Subsurce - ja: hika Of, relating to, or situated in an area beneath a surface, especially the surface of the earth or of a body of water.Below the surfacebeneath the surface
Uniform - ja: Uniform: [adjective] having always the same form, manner, or degree : not varying or variable.
Lumen - ja: na Physics The si unit of luminous flux, equal to the amount of light emitted per second in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform source of one candle.
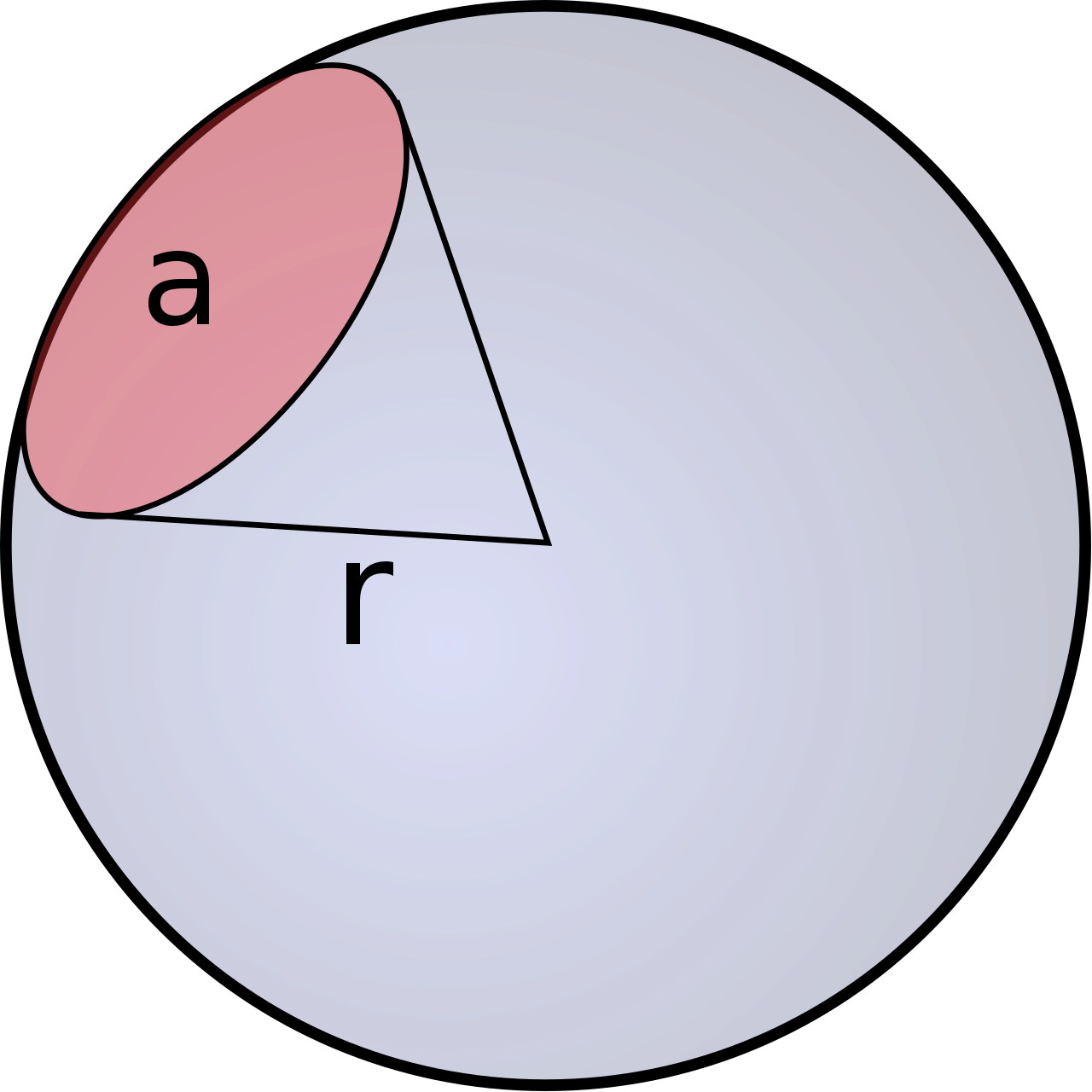
Steradian - ja: na *see the ref pic
Radius - ja: hankei
Illuminance - ja: shoudo In photometry, illuminance is the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It is a measure of how much the incident light illuminates the surface, wavelength-weighted by the luminosity function to correlate with human brightness perception.[1] similarly, luminous emittance is the luminous flux per unit area emitted from a surface. Luminous emittance is also known as luminous exitance. Illuminance = how much intencity of lights comes in to the object Luminous emmitance = how much come out from the object
*calcuration of lumen method: calculate from how much amounts of light needed in the area with uncertain measurement Illuminance(unit:footcandles) = total lumens x light loss factor x coefficient of utilization / area see reference video: Https://www.Youtube.Com/watch?V=wuxwnudgyci Lumen can be calculated with particular condition as difined in si but actual amount of lights will be differed by: Light loss factor, ballast factor, ambient temperature, burnout of the light lifetime, voltage, led
Si (international system of units) The world's most widely used system of measurement.[1]: 123 [9][10] established and maintained[11] by the general conference on weights and measures[j] (cgpm[k]), it is the only system of measurement with an official status[m] in nearly every country in the world,[n] employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. A foot-candle is a non-si unit of illuminance or light intensity. The foot-candle is defined as one lumen per square foot. This unit is commonly used in lighting layouts in parts of the world where united states customary units are used, mainly the united states. Nearly all of the world uses the corresponding si derived unit lux, defined as one lumen per square meter. *100 lumen / square foot (=foot-candle) = 100 lumen / square meter (=lux)
Derive - ja: hasei-suru Obtain something from (a specified source).
Afterimage - ja: zanzou
Negative afterimages Negative afterimages are caused when the eye's photoreceptors, primarily known as rods and cones, adapt to overstimulation and lose sensitivity. Negative afterimages exhibit inverted lightness levels, or colours complementary to, those of the stimulus and are usually brought on by prolonged viewing of a stimulus. They are best seen against a brightly light background. They occur (as least in part) because some cells (cones) on the retina do not respond to the present stimulation because they have been desensitised by looking at a previous stimulus.
Positive afterimages Positive afterimages, by contrast, appear the same color as the original image. They are often very brief, lasting less than half a second. The cause of positive afterimages is not well known, but possibly reflects persisting activity in the brain when the retinal photoreceptor cells continue to send neural impulses to the occipital lobe.
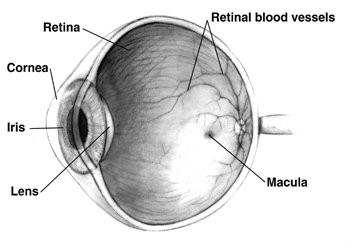
- See the ref pic: Rod cells Photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells.
Retina The innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs.
Photoreceptor cell A specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction.
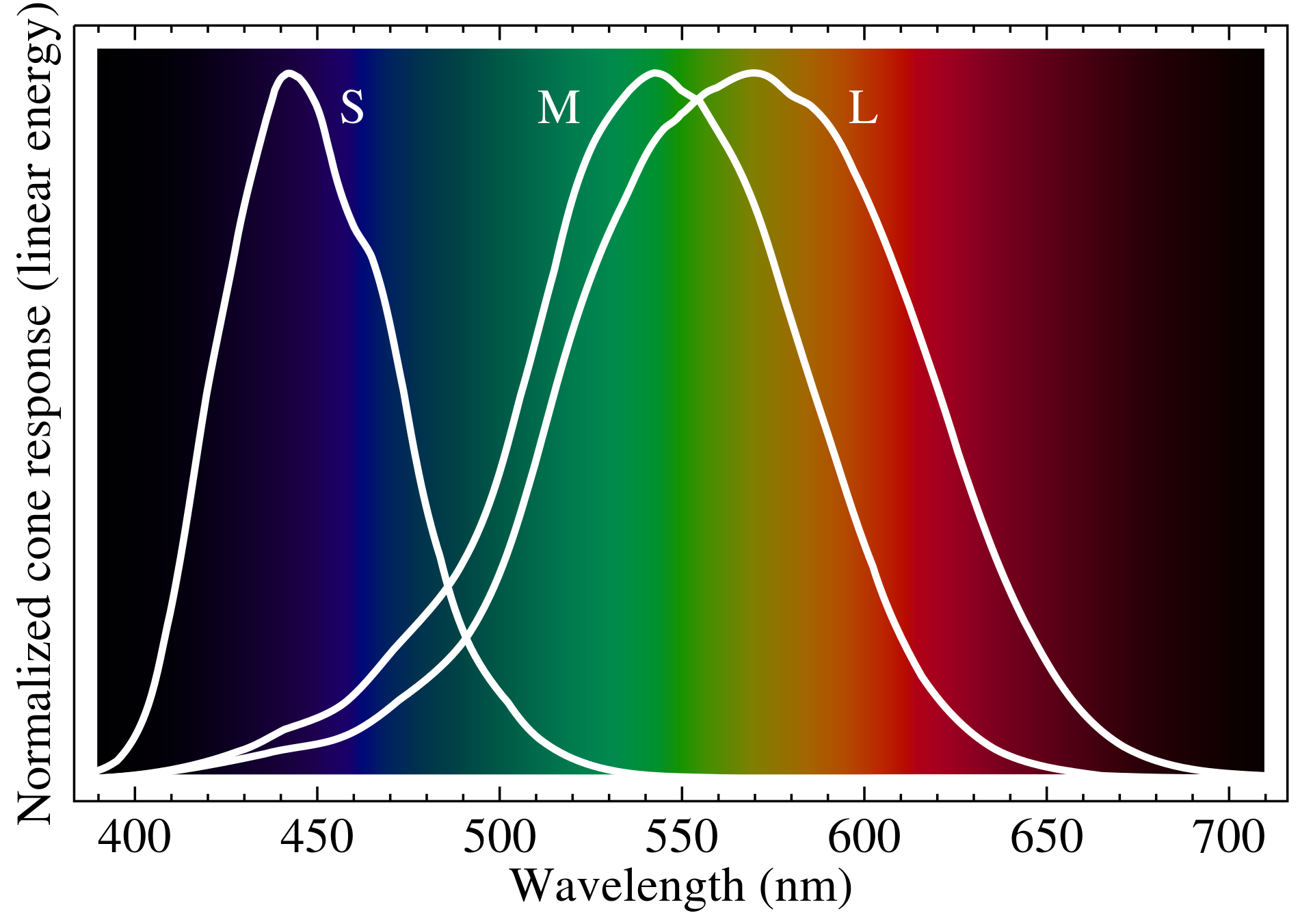
Cone cells Photoreceptor cells in the retinas of vertebrate eyes including the human eye.[citation needed] they respond differently to light of different wavelengths, and the combination of their responses is responsible for color vision. Cones function best in relatively bright light, called the photopic region, as opposed to rod cells, which work better in dim light, or the scotopic region.
Transduciton The transfer of genetic material from one cell to another. The act of leading or carrying over.The act of conveying over.
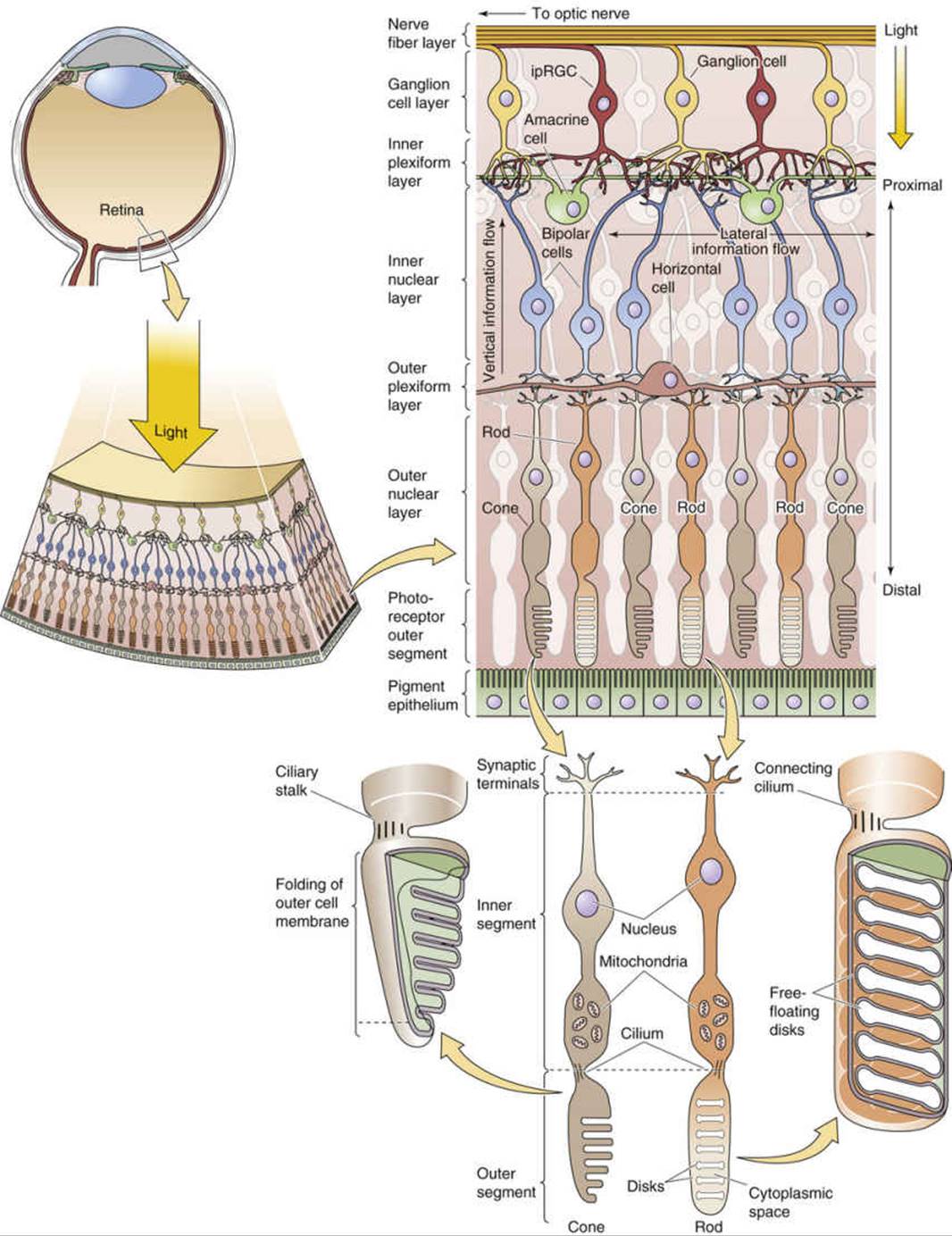
Sensory transduciton in eyes *see the reference pic
Reference Pictures
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mikoto directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mikoto
Mikoto
2025年はイマーシブ空間職人になる