Understanding the Basics of Cloud Computing
 Halliru Musa Halliru
Halliru Musa HalliruTable of contents
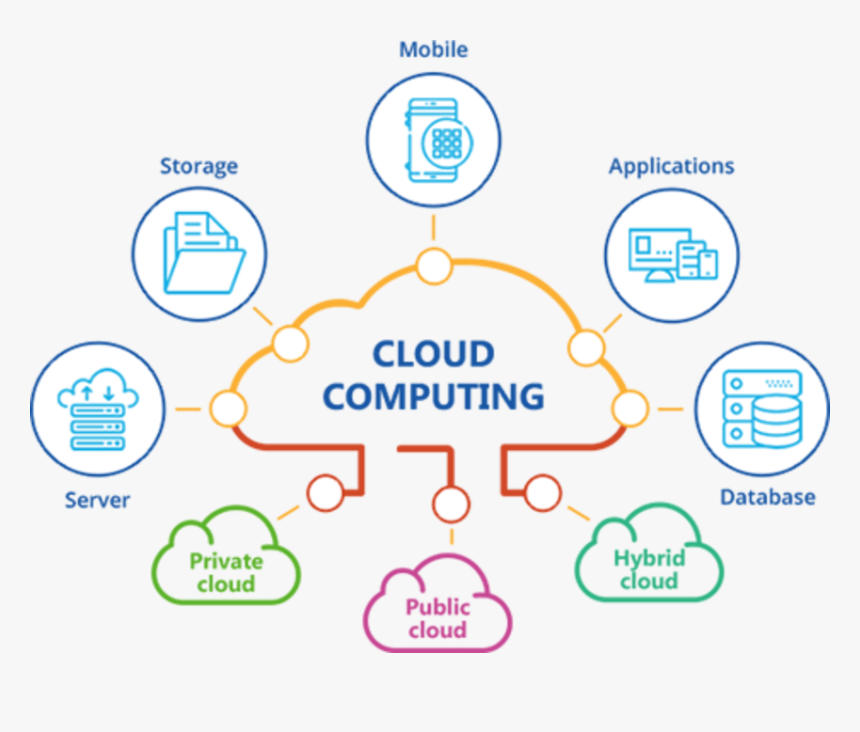
Introduction:
In today's digital age, cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access and manage data, applications, and services over the internet. This technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, transforming the way we store, process, and share information. In this blog post, we will delve into the fundamentals of cloud computing, exploring its definition, key components, advantages, and popular service models.
Defining Cloud Computing:
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of various computing services – including storage, databases, servers, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence – over the internet ("the cloud") to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Unlike traditional computing methods that rely on local servers or personal computers, cloud computing enables users to access resources remotely through the internet.
Key Components of Cloud Computing:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing users to rent virtual machines, storage, and networking components on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It provides tools, libraries, and services for application development.
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications via web browsers, eliminating the need for manual installations and updates.
Advantages of Cloud Computing:
Scalability: Cloud computing allows businesses to scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without over-provisioning.
Cost-Efficiency: Cloud services eliminate the need for investing in and maintaining physical hardware, reducing capital expenditures. Users pay only for the resources they consume.
Flexibility and Mobility: Users can access cloud services from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting collaboration and flexibility in work environments.
Automatic Updates: Cloud service providers handle software updates and security patches, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and protection against vulnerabilities.
Popular Cloud Computing Service Models:
Amazon Web Services (AWS): A comprehensive cloud computing platform offered by Amazon, providing a wide range of services for computing power, storage, and databases.
Microsoft Azure: Microsoft's cloud computing service, offering solutions for building, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google's suite of cloud computing services that provides a variety of tools and services for computing, storage, machine learning, and data analytics.
Conclusion:
Cloud computing has redefined the way businesses operate, fostering innovation, agility, and efficiency. By understanding its core concepts, components, advantages, and popular service providers, individuals and organizations can harness the power of the cloud to propel their digital initiatives forward.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Halliru Musa Halliru directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
