All about Heaps in DSA
 Sawan Badhwar
Sawan Badhwar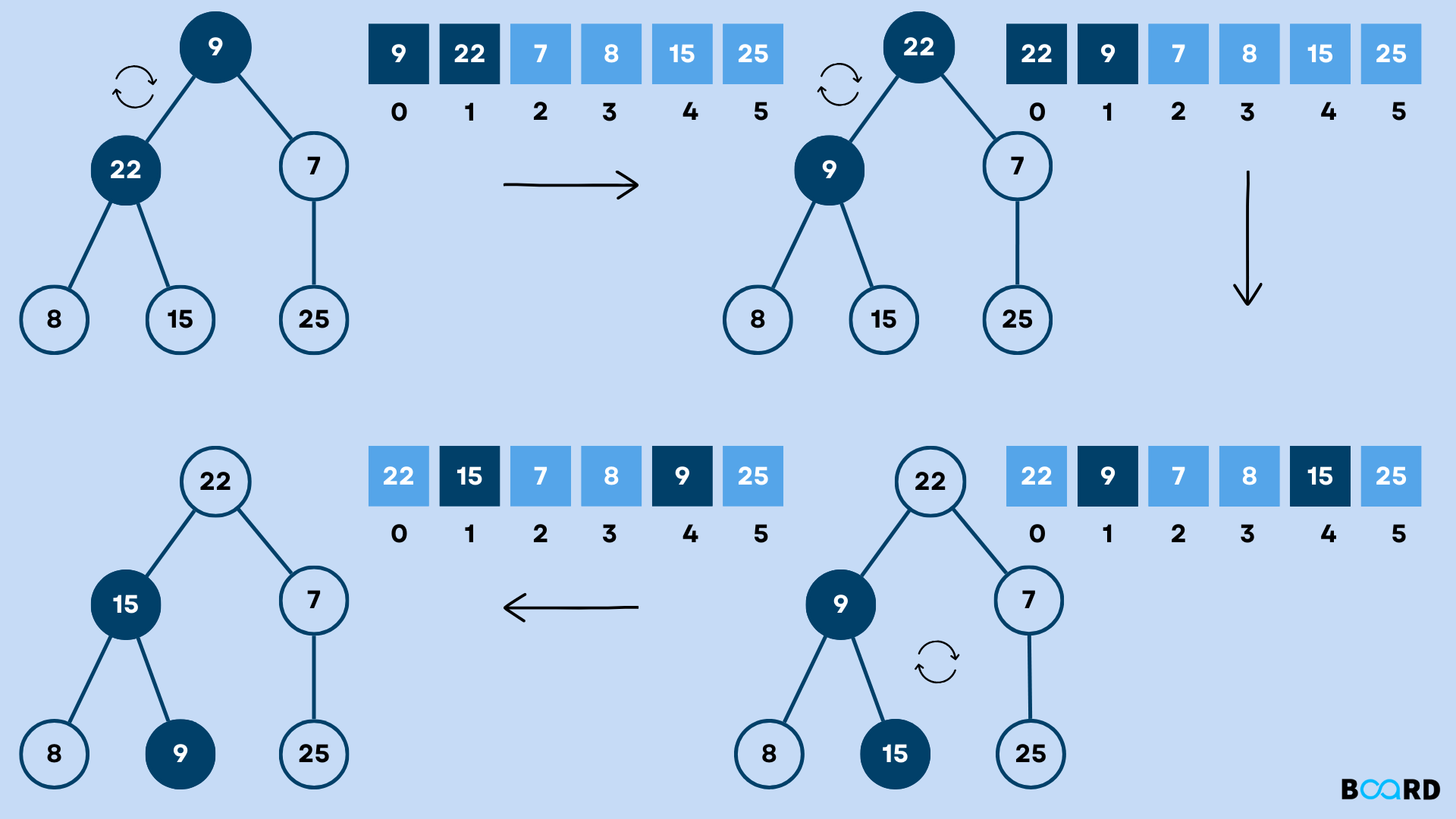
I am having fun on my DSA journey of the 100-Day challenge. Today, I encountered an interesting topic i.e. Heaps. Heaps are nothing different but the Complete Binary Tree that comes with the heap order property. In this concept, I studied the insertion and deletion operations of the heap and their algorithms.
I also came across the term Heapify Algorithm i.e. the major concern behind the execution of sorting of a heap. Heapify positions the element at its correct position depending on the type of heap, that we're performing.
//left and right children when starting index = 0
// int left = 2*i + 1;
// int right = 2*1 + 2;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class heap {
public:
int arr[100];
int size;
heap(){
arr[0] = -1;
size = 0;
}
void insert(int val){
size = size + 1;
int index = size;
arr[index] = val;
while (index > 1)
{
int parent = index/2;
if(arr[parent] < arr[index]){
swap(arr[parent], arr[index]);
index = parent;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
void print(){
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}cout << endl;
}
void remove(){
if(size == 0){
cout << "Underflow" << endl;
return;
}
//put last element at root node
arr[1] = arr[size];
//remove last element
size--;
//take root node to its correct position by comparing with neighbouring elements
int i = 1;
while (i < size)
{
int leftChild = 2*i;
int rightChild = 2*i + 1;
if(leftChild < size && arr[i] < arr[leftChild]){
swap(arr[i], arr[leftChild]);
i = leftChild;
}
else if(rightChild < size && arr[rightChild]){
swap(arr[i], arr[rightChild]);
i = rightChild;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
};
void max_heapify(int arr[], int n, int i){
int largest = i;
//left and right children when starting index = 1
int left = 2*i;
int right = 2*1 + 1;
if(left <= n && arr[largest] < arr[left]){
largest = left;
}
if(right <= n && arr[largest] < arr[right]){
largest = right;
}
if (largest != i)
{
swap(arr[largest], arr[i]);
max_heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
void min_heapify(int arr[], int n, int i){
int smallest = i;
int left = 2*i;
int right = 2*1 + 1;
if(left <= n && arr[smallest] > arr[left]){
smallest = left;
}
if(right <= n && arr[smallest] > arr[right]){
smallest = right;
}
if (smallest != i)
{
swap(arr[smallest], arr[i]);
min_heapify(arr, n, smallest);
}
}
void heapsort(int arr[], int n){
int size = n;
while(size > 1){
//step 1
swap(arr[size], arr[1]);
//step 2
size--;
//step 3
heapsort(arr, size);
}
}
int main(){
heap h;
h.insert(50);
h.insert(55);
h.insert(53);
h.insert(52);
h.insert(54);
h.print();
h.remove();
h.print();
int arr[6] = {-1, 54, 53, 55, 52, 50};
int n = 5;
for (int i = n/2; i > 0; i--)
{
max_heapify(arr, n, i);
}
cout << "Heapify Algorithm... Max Heap : ";
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = n/2; i > 0; i--)
{
min_heapify(arr, n, i);
}
cout << "Heapify Algorithm... Min Heap : ";
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
heapsort(arr, n);
cout << "Heap Sort : ";
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
In this above code, you have come across: -
Insertion in heap
Deletion in heap
Heapify Algorithm
Heap Sort
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sawan Badhwar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
