Usage of JavaScript array methods
 Saiful Alam
Saiful AlamTable of contents
- List of Array methods
- How we can create an array in JavaScript?
- The concat() method
- The copyWithin() method
- The entries() method
- The every() method
- The fill() method
- The filter() method
- The find() method
- The findIndex() method
- The forEach() method
- The from() method
- The includes() method
- The indexOf() method
- The isArray() method
- The join() method
- The keys() method
- The lastIndexOf() method
- The map() method
- The flat() method
- The flatMap() method
- The pop() method
- The push() method
- The reduce() method
- The reduceRight() method
- The reverse() method
- The shift() method
- The slice() method
- The some() method
- The sort() method
- The splice() method
- The toString() method
- The unshift() method
- The valueOf() method
- Conclusion
- Further reading
In JavaScript, an array is a data structure that contains a collection of elements. Arrays are very useful because you can store, access, and manipulate multiple elements in a single array. In this article, we will discuss the usage of JavaScript array methods.
List of Array methods
concat() - Joins two or more arrays, and returns a copy of the joined arrays
copyWithin() - Copies array elements within the array, to and from specified positions
entries() - Returns a key/value pair Array Iteration Object
every() - Checks if every element in an array passes a test
fill() - Fill the elements in an array with a static value
filter() - Creates a new array with every element in an array that passes a test
find() - Returns the value of the first element in an array that passes a test
findIndex() - Returns the index of the first element in an array that passes a test
forEach() - Calls a function for each array element
from() - Creates an array from an object
includes() - Check if an array contains the specified element
indexOf() - Search the array for an element and returns its position
isArray() - Checks whether an object is an array
join() - Joins all elements of an array into a string
keys() - Returns a Array Iteration Object, containing the keys of the original array
lastIndexOf() - Search the array for an element, starting at the end, and returns its position
map() - Creates a new array with the result of calling a function for each array element
flat() - Creates a new array with all sub-array elements concatenated into it recursively up to the specified depth.
flatMap() - Creates a new array with the result of calling a function for each array element, and flattening the result into a new array.
pop() - Removes the last element of an array, and returns that element
push() - Adds new elements to the end of an array, and returns the new length
reduce() - Reduce the values of an array to a single value (going left-to-right)
reduceRight() - Reduce the values of an array to a single value (going right-to-left)
reverse() - Reverses the order of the elements in an array
shift() - Removes the first element of an array, and returns that element
slice() - Selects a part of an array, and returns the new array
some() - Checks if any of the elements in an array pass a test
sort() - Sorts the elements of an array
splice() - Adds/Removes elements from an array
toString() - Converts an array to a string, and returns the result
unshift() - Adds new elements to the beginning of an array, and returns the new length
valueOf() - Returns the primitive value of an array
How we can create an array in JavaScript?
There are two ways to create an array in JavaScript. The first way is to use the array literal syntax, which is a comma-separated list of elements inside square brackets.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
The second way is to use the Array constructor function with the new operator.
const fruits = new Array('Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange');
How we can access an array element?
You can access an array element by using the index of the element. The index of the first element is 0, the index of the second element is 1, and so on.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits[0]); // Apple
console.log(fruits[1]); // Banana
console.log(fruits[2]); // Orange
How we can get the length of an array?
You can use the length property to get the length of an array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.length); // 3
Okay enough of the basics, let's dive into the usage of JavaScript array methods.
The concat() method
The concat() method is used to join two or more arrays. This method does not change the existing arrays, but instead returns a new array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const vegetables = ['Tomato', 'Potato', 'Cabbage'];
const fruitsAndVegetables = fruits.concat(vegetables);
console.log(fruitsAndVegetables);
// ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Tomato", "Potato", "Cabbage"]
The copyWithin() method
The copyWithin() method copies array elements within the array, to and from specified positions.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Tomato', 'Potato', 'Cabbage'];
fruits.copyWithin(2, 0);
console.log(fruits);
// ["Apple", "Banana", "Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Tomato"]
The entries() method
The entries() method returns a key/value pair Array Iteration Object.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const f = fruits.entries();
console.log(f.next().value); // [0, "Apple"]
console.log(f.next().value); // [1, "Banana"]
console.log(f.next().value); // [2, "Orange"]
The every() method
The every() method checks if every element in an array passes a test.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const isFruit = (fruit) => {
return fruit === 'Apple';
};
console.log(fruits.every(isFruit)); // false
The fill() method
The fill() method fills the elements in an array with a static value.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
fruits.fill('Kiwi');
console.log(fruits);
// ["Kiwi", "Kiwi", "Kiwi"]
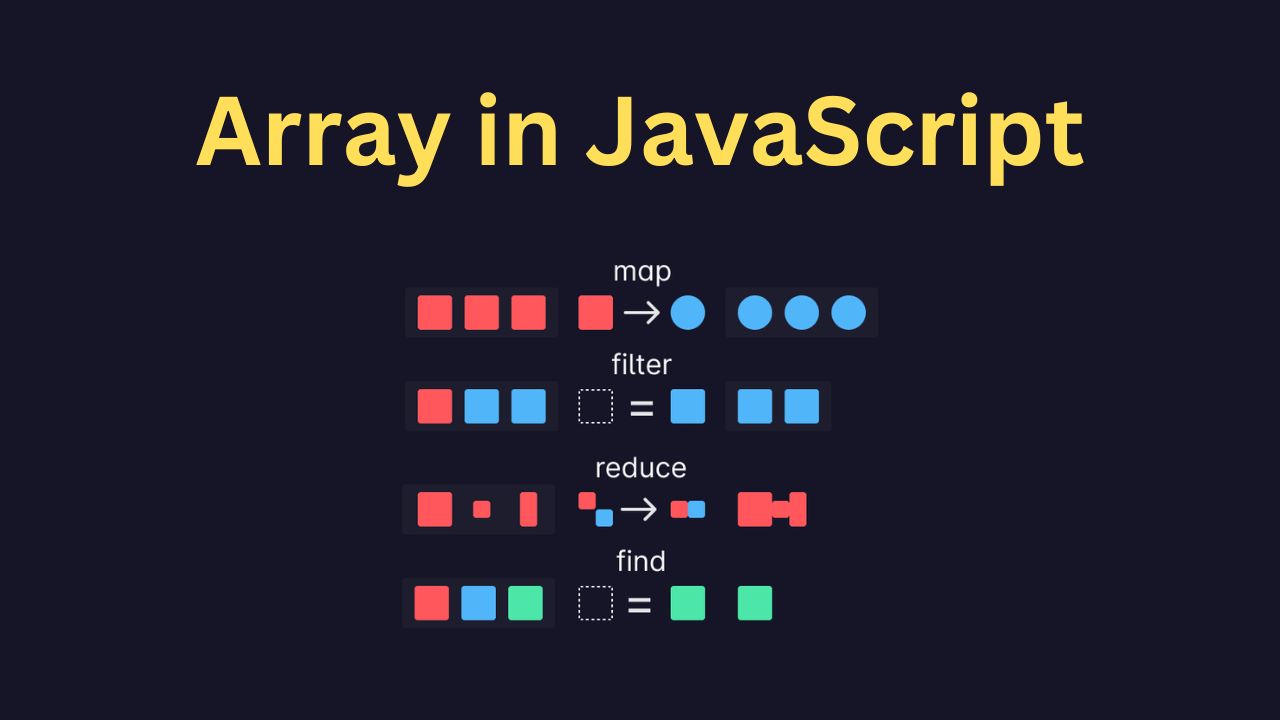
The filter() method
The filter() method creates a new array with every element in an array thapassesss a test.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const isFruit = (fruit) => {
return fruit === 'Apple';
};
const filteredFruits = fruits.filter(isFruit);
console.log(filteredFruits);
// ["Apple"]
The find() method
The find() method returns the value of the first element in an array that passes a test.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const isFruit = (fruit) => {
return fruit === 'Apple';
};
const fruit = fruits.find(isFruit);
console.log(fruit);
// "Apple"
The findIndex() method
The findIndex() method returns the index of the first element in an array that passes a test.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const isFruit = (fruit) => {
return fruit === 'Orange';
};
const index = fruits.findIndex(isFruit);
console.log(index);
// 2
The forEach() method
The forEach() method calls a function for each array element.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
fruits.forEach((fruit) => {
console.log(fruit);
});
// Apple
// Banana
// Orange
The from() method
The from() method creates an array from an object.
const fruits = Array.from('Apple');
console.log(fruits);
// ["A", "p", "p", "l", "e"]
The includes() method
The includes() method checks if an array contains the specified element.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.includes('Banana')); // true
console.log(fruits.includes('Kiwi')); // false
The indexOf() method
The indexOf() method searches the array for an element and returns its position.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.indexOf('Banana')); // 1
console.log(fruits.indexOf('Kiwi')); // -1
The isArray() method
The isArray() method checks whether an object is an array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(Array.isArray(fruits)); // true
console.log(Array.isArray('Apple')); // false
console.log(Array.isArray({name: 'The Alchemist'})) // false
The join() method
The join() method joins all elements of an array into a string.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.join()); // Apple,Banana,Orange
console.log(fruits.join('')); // AppleBananaOrange
console.log(fruits.join('-')); // Apple-Banana-Orange
console.log(fruits.join(' ')); // Apple Banana Orange
The keys() method
The keys() method returns a Array Iteration Object, containing the keys of the original array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const f = fruits.keys();
console.log(f.next().value); // 0
console.log(f.next().value); // 1
console.log(f.next().value); // 2
The lastIndexOf() method
The lastIndexOf() method searches the array for an element, starting at the end, and returns its position.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Apple'];
console.log(fruits.lastIndexOf('Apple')); // 3
console.log(fruits.lastIndexOf('Kiwi')); // -1
The map() method
The map() method creates a new array with the result of calling a function for each array element.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const toUpperCase = (fruit) => {
return fruit.toUpperCase();
};
const upperCaseFruits = fruits.map(toUpperCase);
console.log(upperCaseFruits);
// ["APPLE", "BANANA", "ORANGE"]
The flat() method
The flat() method creates a new array with all sub-array elements concatenated into it recursively up to the specified depth.
const fruits = ['Apple', ['Banana', 'Orange'], 'Kiwi'];
console.log(fruits.flat());
// ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Kiwi"]
The flatMap() method
The flatMap() method creates a new array with the result of calling a function for each array element and flattening the result into a new array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const toUpperCase = (fruit) => {
return fruit.toUpperCase();
};
const upperCaseFruits = fruits.flatMap(toUpperCase);
console.log(upperCaseFruits);
// ["APPLE", "BANANA", "ORANGE"]
The pop() method
The pop() method removes the last element of an array and returns that element.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.pop()); // Orange
console.log(fruits); // ["Apple", "Banana"]
The push() method
The push() method adds new elements to the end of an array, and returns the new length.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.push('Kiwi')); // 4
console.log(fruits); // ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Kiwi"]
The reduce() method
The reduce() method reduces the values of an array to a single value (going left-to-right).
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => {
return accumulator + currentValue;
};
console.log(fruits.reduce(reducer)); // AppleBananaOrange
The reduceRight() method
The reduceRight() method reduces the values of an array to a single value (going right-to-left).
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => {
return accumulator + currentValue;
};
console.log(fruits.reduceRight(reducer)); // OrangeBananaApple
The reverse() method
The reverse() method reverses the order of the elements in an array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.reverse()); // ["Orange", "Banana", "Apple"]
The shift() method
The shift() method removes the first element of an array and returns that element.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.shift()); // Apple
console.log(fruits); // ["Banana", "Orange"]
The slice() method
The slice() method selects a part of an array, and returns the new array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.slice(1)); // ["Banana", "Orange"]
console.log(fruits.slice(1, 2)); // ["Banana"]
The some() method
The some() method checks if any of the elements in an array pass a test.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
const isFruit = (fruit) => {
return fruit === 'Apple';
};
console.log(fruits.some(isFruit)); // true
The sort() method
The sort() method sorts the elements of an array.
const fruits = ['Jelly', 'Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.sort()); // ["Apple", "Banana", "Jelly", "Orange"]
The splice() method
The splice() method adds/removes elements from an array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
fruits.splice(1, 0, 'Kiwi');
console.log(fruits); // ["Apple", "Kiwi", "Banana", "Orange"]
The toString() method
The toString() method converts an array to a string and returns the result.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.toString()); // Apple,Banana,Orange
The unshift() method
The unshift() method adds new elements to the beginning of an array and returns the new length.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.unshift('Kiwi')); // 4
console.log(fruits); // ["Kiwi", "Apple", "Banana", "Orange"]
The valueOf() method
The valueOf() method returns the primitive value of an array.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'];
console.log(fruits.valueOf()); // ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange"]
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the usage of JavaScript array methods. You can find a complete list of JavaScript array methods on the MDN web docs.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to reach out to me on Twitter or from here
Happy coding!
Further reading
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Saiful Alam directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Saiful Alam
Saiful Alam
An Expert software engineer in Laravel and React. Creates robust backends and seamless user interfaces. Committed to clean code and efficient project delivery, In-demand for delivering excellent user experiences.