Maximizing Efficiency with Composer Scripts
 Sandip Shrestha
Sandip Shrestha
In the ever-evolving landscape of software development, optimizing workflows and streamlining processes is crucial. One powerful tool that often goes underutilized is Composer scripts. Composer, the dependency manager for PHP, allows developers to define and run custom scripts that enhance project automation and improve overall development efficiency.
In this blog post, we'll learn about composer scripts and explore real-world scenarios where leveraging Composer scripts can bring substantial benefits to developers.
How to write and run composer scripts
To write and run Composer scripts, we need to use the "scripts" section in our project's composer.json file. Within this section, you define custom scripts that can be executed using the composer command.
For instance, let's consider a scenario where you want to create a script to clear your Laravel project's cache. In your composer.json file, you can add the following:
"scripts": {
"cache:clear": "php artisan cache:clear"
}
In this example, the script named cache-clear is defined to execute the Laravel command php artisan cache:clear. To run this script, open your terminal and navigate to your project's root directory, then execute the following command:

Below are some of the examples where we can use composer script in our development process.
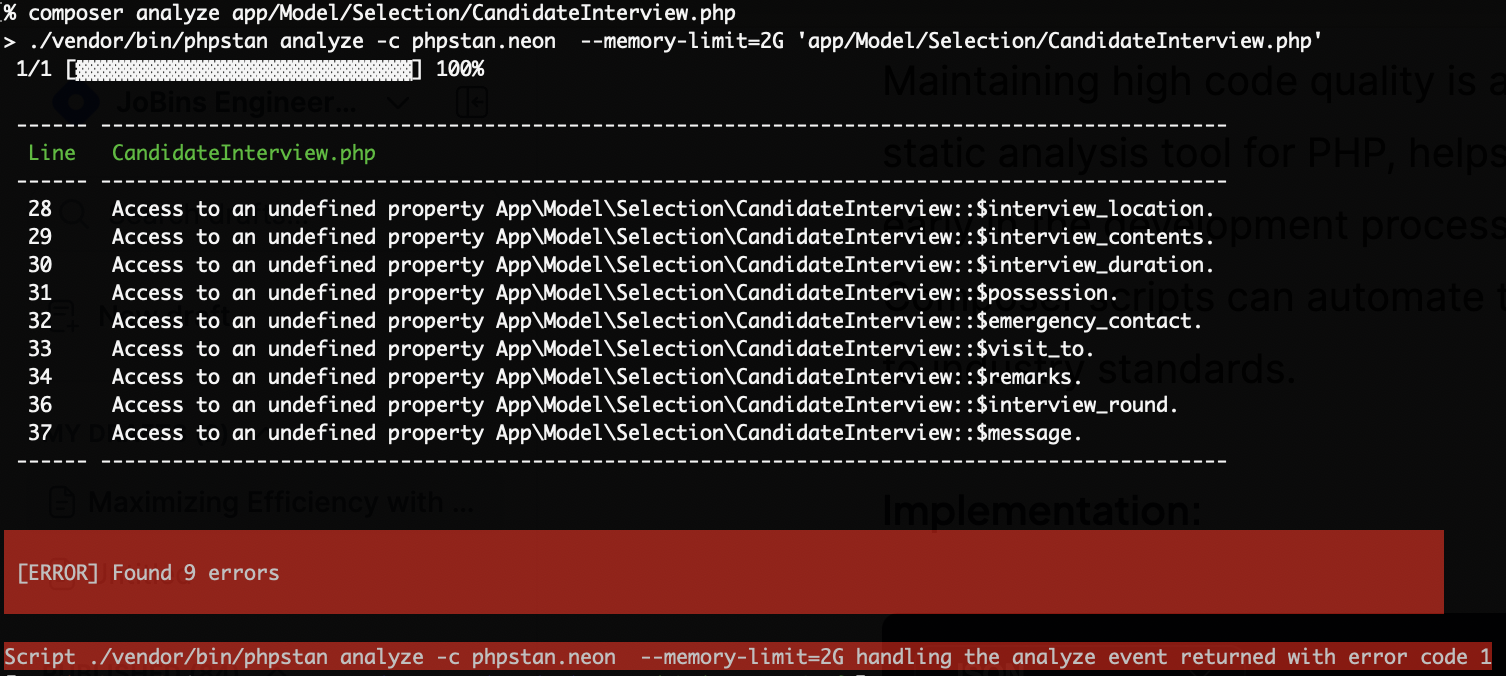
1. Code Quality Assurance with PHPStan
Maintaining high code quality is a top priority for any development team. PHPStan, a static analysis tool for PHP, helps in achieving this by uncovering potential issues early in the development process. Integrating PHPStan into your workflow using Composer scripts can automate the analysis and ensure that the codebase adheres to industry standards.
Implementation:
"scripts": {
"analyze": "./vendor/bin/phpstan analyze src -c phpstan.neon --memory-limit=2G"
}
With this simple script, running composer analyze will trigger PHPStan to analyze the src directory, providing instant feedback on potential issues such as undefined variables, incorrect types, or unused code.
2. Automated Testing with PHPUnit
Writing tests is a fundamental aspect of modern software development. PHPUnit is a widely adopted testing framework for PHP, and integrating it with Composer scripts can significantly enhance the testing process. Automating test execution allows for quick feedback during development and ensures that new features or changes don't introduce regressions.
Implementation:
"scripts": {
"test": "./vendor/bin/phpunit tests"
}
Now, developers can execute tests with a simple composer test command, promoting a testing culture within the team and reducing the chance of releasing buggy code.
3. Continuous Integration and Deployment
For larger projects with multiple contributors, maintaining a robust CI/CD pipeline is crucial. GitLab CI, paired with Composer scripts, can automate the testing and deployment processes seamlessly.
Implementation:
"scripts": {
"test": "phpunit",
"deploy": [
"@test",
"echo 'Deploying to production...'",
"php artisan migrate --force"
]
}
In this example, the composer deploy command triggers PHPUnit tests first and, if successful, proceeds with the deployment process. Integrating this script into GitLab CI allows for automatic testing and deployment on each merge to the main branch.

4. Health Check Automation
Composer scripts and a dedicated health check package like "spatie/laravel-health," can automate the testing and health verification processes seamlessly.
Implementation:
"scripts": {
"health-check": [
"php artisan health:check",
"echo 'Health check passed successfully.'"
]
}
In this example, the composer health-check command utilizes the Laravel Health package to perform a comprehensive health check on the application. If the health check succeeds, it signals that the application is in good health.
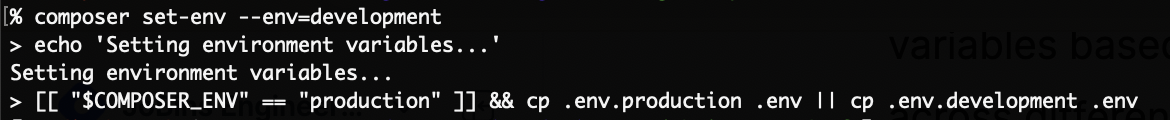
5. Custom Environment Configuration
Managing environment-specific configurations is a common challenge in development. Composer scripts can be used to dynamically set environment variables based on the current environment, ensuring consistent configurations across different stages.
Implementation:
"scripts": {
"set-env": [
"echo 'Setting environment variables...'",
"[[ \"$COMPOSER_ENV\" == \"production\" ]] && cp .env.production .env || cp .env.development .env"
]
}
With this script, running composer set-env --env=production or composer set-env --env=development will set the appropriate environment variables, making it easier to switch between environments.
Conclusion
These examples showcase the flexibility of Composer scripts in addressing real-world challenges faced by top-level engineers. Whether it's streamlining CI/CD, managing environment configurations, or automating database tasks, Composer scripts can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a development team. By incorporating these practices into your workflow, you can achieve a higher level of efficiency and maintainability in your Laravel and PHP projects. Happy coding!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sandip Shrestha directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
Sandip Shrestha
Sandip Shrestha
I am a Full stack Software Engineer and also a hobbyist writer who writes about Software Development and its allied intricacies. I hold on to my methods loosely, embrace flexibility & modularity and believe we can always grow.