Controller Area Network (CAN) Frames
 BHAKTI KHANVILKAR
BHAKTI KHANVILKARFrame Types:
1.Data Frame:
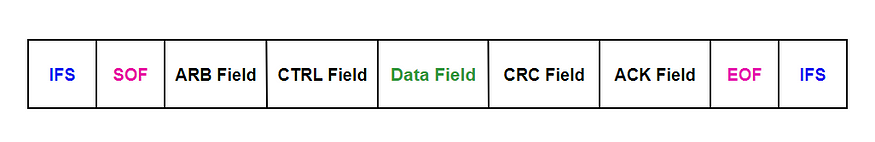
a)Standard Frame/ Base Frame Format
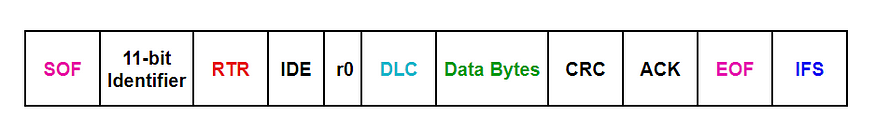
>SOF : Start of Frame: Dominant(0)
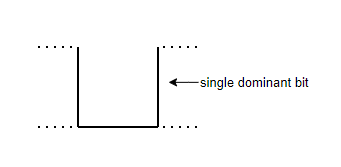
> Identifier : 11-bit unique Identifier , also represents message priority.Low-valued IDs always have higher priority to access the bus,because dominant(0) wins over recessive(1).
>RTR : Remote Transmisssion Request : Dominant(0) = Data Frame Recessive(1) = Remote Frame
>IDE : Identifier Extension: Dominant(0) = 11bit ID
>ro: Reserve bit for future
>DLC: Data Length Code — 4 bit size , Represents number of bytes of data being transmitted.
>Data Bytes: 8 bytes maximum
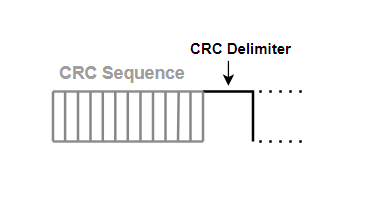
>CRC: Cyclic Redundancy Check Field : 15 bits checksum and a CRC Delimiter (Recessive).
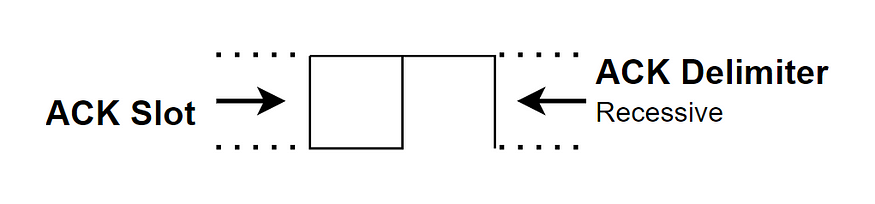
>Acknowledge Field : All CAN nodes that receive any error-free transfer do send Dominant bit as ACK slot, If no one receives frame correctly then ACK slot stays recessive.
>EOF: End of Frame: 7 conescutive recessive bits.
b)Extended Frame Format
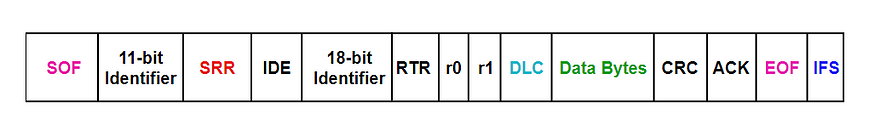
Extended Frame Format
>SRR: Substitute Remote Request : Substitute RTR bit for Extended Data Frames
>IDE : Identifier Extension: Recessive(1) = 29bit ID
>ro,r1: Reserve bit for future
2. Remote Frame:
\>Similar to data frame , sent by the receiver to request data from transmitter.
\>Doesn’t contain any data field.
>RTR : Remote Transmisssion Request : Recessive(1) = Remote Frame
Data Frame wins arbitration if both are ready to transmit at same time, because RTR bit of data frame is dominant.
3.Error Frame:
If transmitting or reciving nodes detect an error, it will immediately stop transmission and send an error frame consisting error flag with 6 dominant bits and 8 recessive bits error flag delimitter
4.Overload Frame
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from BHAKTI KHANVILKAR directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
