Godot Post-Processing Outline Shader
 Caleb Doise
Caleb Doise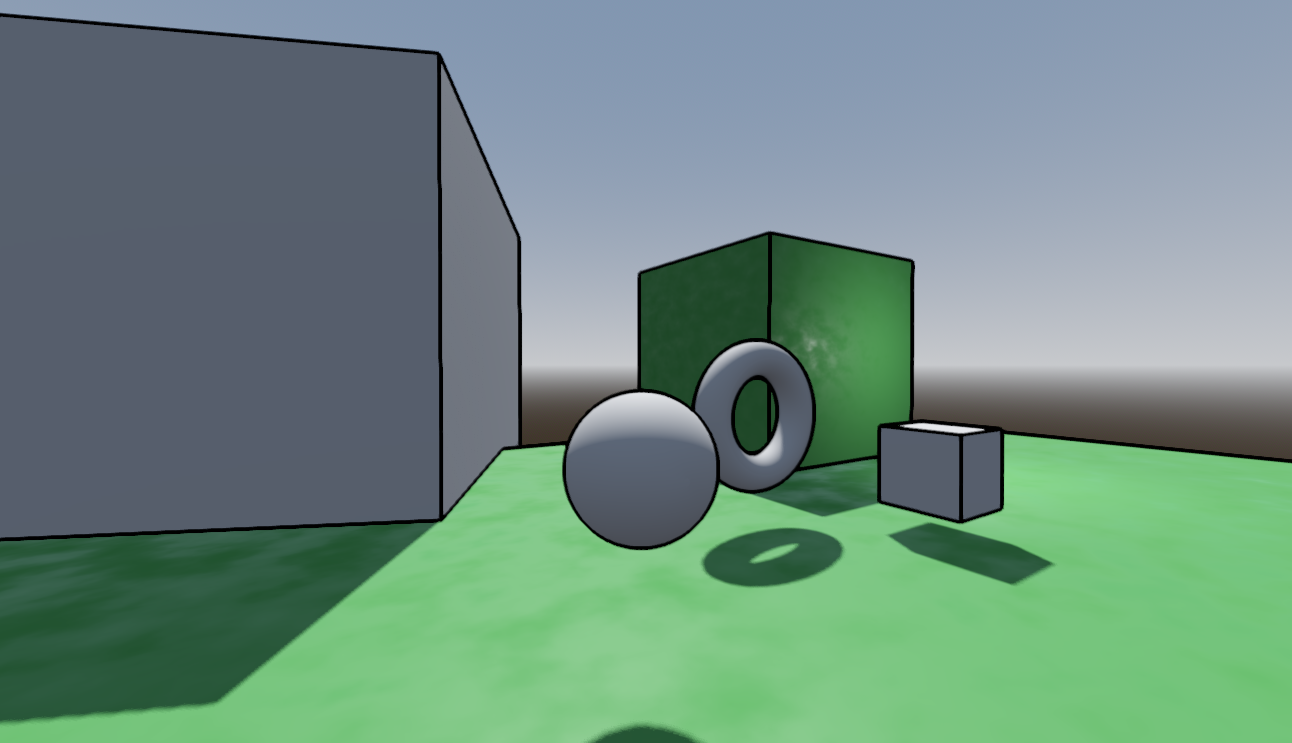
Changes in depth and normal vectors can be used to draw outlines around objects in a rendered scene. I've posted an example of one such method here:
GitHub Repo: https://github.com/Vortex-Basis-LLC/Godot-VBG-Samples-Shaders
Specific Shader: https://github.com/Vortex-Basis-LLC/Godot-VBG-Samples-Shaders/blob/main/shaders/post_process_edge_detection.gdshader
For each pixel and a set of neighboring pixels, the depth value is sampled from the depth buffer and if the difference exceeds a certain threshold, we apply the outline color over the original color. We do the same for normals since at the corner of a cube, the pixels will all be similar distances from the camera but the direction they face will be different.
One problem that I ran into at first was an inability to get a consistent outline thickness at both near and far distances. This issue is likely due to the limited precision of the depth buffer and the fact that it stores depths in a non-linear fashion. My solution was to use the stored depth values as-is near the camera but to use linearized depth values after a certain depth cutoff (see linear_depth_cutoff in the shader code). There is likely a way to automatically calibrate the linear_depth_cutoff from the projection matrix and near/far-z clip values, but I chose to keep it simple and let the user adjust the value.
Here's the full source of the shader, but I'd recommend viewing the source file on github to make sure you are seeing the latest version:
shader_type spatial;
render_mode skip_vertex_transform, unshaded;
uniform sampler2D screen_texture: hint_screen_texture, filter_nearest;
uniform sampler2D normal_texture: hint_normal_roughness_texture, filter_nearest;
uniform sampler2D depth_texture: source_color, hint_depth_texture, filter_nearest;
// Adjust approximate line width by changing how far apart pixel samples are.
uniform int line_width = 2;
// See usage below. Adjust to taste.
uniform float depth_diff_scalar = 1000.0;
uniform float depth_diff_power = 2.0;
// See usage below. Adjust to taste.
uniform float normal_diff_scalar = 20.0;
uniform float normal_diff_power = 3.0;
// Depth at which linear depth is no longer used and we revert to using the
// depth values straight from the depth buffer due to precision issues.
uniform float linear_depth_cutoff = 7.0;
void vertex(){
// Place the post-processing mesh surface directly in front of the camera.
// The coordinates of the mesh should already be in NDC space.
POSITION = vec4(VERTEX, 1.0);
}
float get_linear_depth(ivec2 pixel_coord, mat4 inv_proj_matrix, vec2 pixel_size) {
vec2 uv = vec2(pixel_coord) * pixel_size;
float depth = texelFetch(depth_texture, pixel_coord, 0).r;
vec3 ndc = vec3(uv * 2.0 - 1.0, depth);
vec4 view = inv_proj_matrix * vec4(ndc, 1.0);
view.xyz /= view.w;
float linear_depth = -view.z;
return linear_depth;
}
void fragment() {
vec2 pixel_size = 1.0 / VIEWPORT_SIZE;
// The original final color of the rendered pixel.
vec3 original_color = texture(screen_texture, SCREEN_UV).rgb;
// Normal of the pixel relative to the camera position, but values range
// from 0 to 1. Multiply xyz component by 2.0 and subtract 1.0 to get the
// actual direction. The w component is the roughness.
vec4 normal_color = texture(normal_texture, SCREEN_UV);
float depth_value = texture(depth_texture, SCREEN_UV).x;
float linear_depth_value = get_linear_depth(ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy), INV_PROJECTION_MATRIX, pixel_size);
// Calculate difference amount based on depth.
float depth_diff_total = 0.0;
float depth;
float delta_diff_scaled;
if (linear_depth_value > linear_depth_cutoff) {
depth = texelFetch(depth_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(-line_width, 0), 0).r;
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - depth_value);
depth = texelFetch(depth_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(line_width, 0), 0).r;
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - depth_value);
depth = texelFetch(depth_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(0, -line_width), 0).r;
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - depth_value);
depth = texelFetch(depth_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(0, line_width), 0).r;
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - depth_value);
delta_diff_scaled = pow(depth_diff_total * depth_diff_scalar * depth_value, depth_diff_power);
}
else {
depth = get_linear_depth(ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(-line_width, 0), INV_PROJECTION_MATRIX, pixel_size);
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - linear_depth_value);
depth = get_linear_depth(ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(line_width, 0), INV_PROJECTION_MATRIX, pixel_size);
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - linear_depth_value);
depth = get_linear_depth(ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(0, -line_width), INV_PROJECTION_MATRIX, pixel_size);
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - linear_depth_value);
depth = get_linear_depth(ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(0, line_width), INV_PROJECTION_MATRIX, pixel_size);
depth_diff_total += abs(depth - linear_depth_value);
// We don't apply scaling to the values near the camera.
delta_diff_scaled = depth_diff_total;
}
delta_diff_scaled = delta_diff_scaled <= 0.9 ? 0.0 : delta_diff_scaled;
// Calculate difference amount based on normals.
float normal_diff_total = 0.0;
vec3 other_normal_color, normal_diff;
other_normal_color = texelFetch(normal_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(-line_width, 0), 0).rgb;
normal_diff = (normal_color.rgb - other_normal_color);
normal_diff_total += dot(normal_diff, normal_diff);
other_normal_color = texelFetch(normal_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(line_width, 0), 0).rgb;
normal_diff = (normal_color.rgb - other_normal_color);
normal_diff_total += dot(normal_diff, normal_diff);
other_normal_color = texelFetch(normal_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(0, -line_width), 0).rgb;
normal_diff = (normal_color.rgb - other_normal_color);
normal_diff_total += dot(normal_diff, normal_diff);
other_normal_color = texelFetch(normal_texture, ivec2(FRAGCOORD.xy) + ivec2(0, line_width), 0).rgb;
normal_diff = (normal_color.rgb - other_normal_color);
normal_diff_total += dot(normal_diff, normal_diff);
float normal_diff_scaled = pow(normal_diff_total * normal_diff_scalar, normal_diff_power);
// Determine which diff value to use.
float diff_total_to_use = max(delta_diff_scaled, normal_diff_scaled);
ALBEDO = mix(original_color, vec3(0.0), clamp(diff_total_to_use, 0.0, 1.0));
}
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Caleb Doise directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
