2-Tier Application Deployment with Docker-Compose
 Sagar Shah
Sagar Shah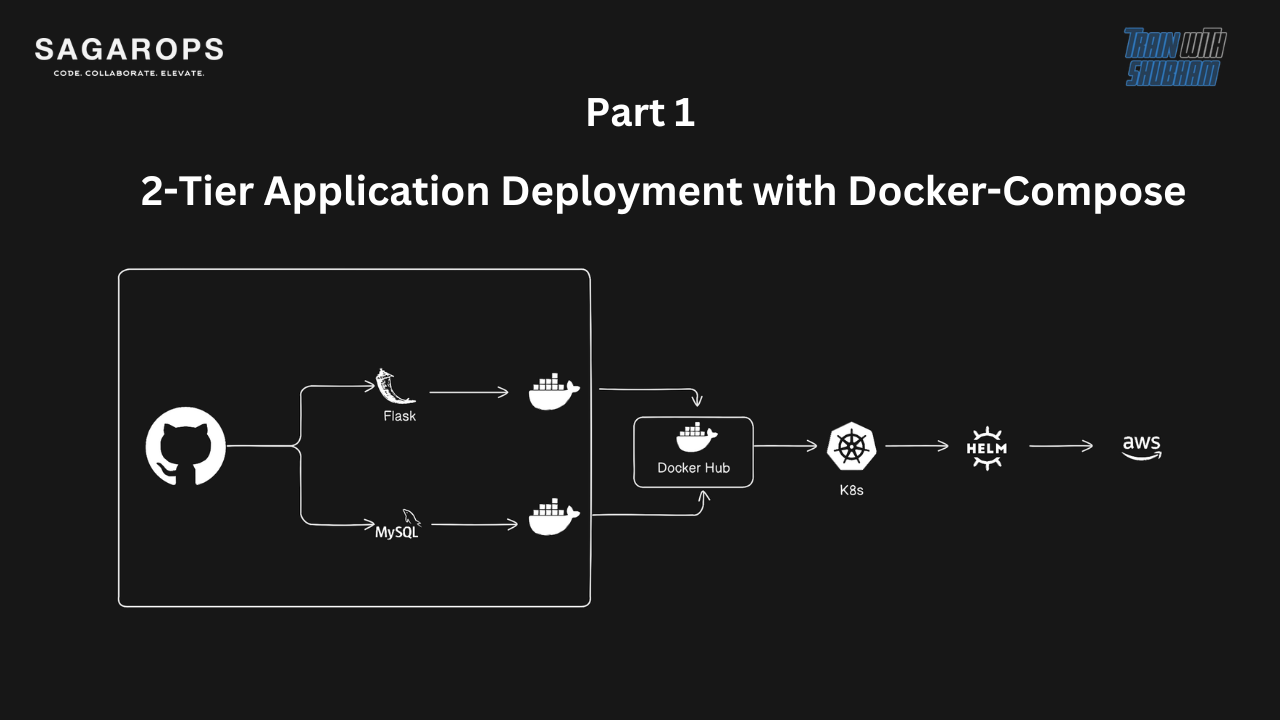
Introduction:
🌐 In the ever-evolving landscape of DevOps, containerization has become a key player in streamlining the deployment process. Docker, a leading containerization platform, and Docker Compose, a tool for defining and managing multi-container Docker applications, offer a powerful combination for deploying applications with ease. In this guide, we'll walk through the steps to set up a simple two-tier application using Docker Compose on an Ubuntu server.
Step 1: Set Up an Ubuntu Server
🚀 Start by creating a new Ubuntu server instance. You can use a cloud provider like AWS, Azure, or DigitalOcean, or set up a local virtual machine. Ensure that your server has a stable internet connection.
Step 2: Install Docker and Docker Compose
🔧 To install Docker and Docker Compose, follow the instructions outlined in this link. This will guide you through the process of installing both Docker and Docker Compose on your Ubuntu server.
Step 3: Clone the Project
👥 Once Docker and Docker Compose are installed, clone the Docker Compose project onto your server. Use the following command to clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/SagarOps/two-tier-flask-app.git
Replace the URL with the actual URL of your Docker Compose project.
Step 4: docker-compose.yml 📝
version: '3'
services:
backend:
build:
context: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
environment:
MYSQL_HOST: mysql
MYSQL_USER: admin
MYSQL_PASSWORD: admin
MYSQL_DB: myDb
networks:
- twotier
depends_on:
- mysql
mysql:
image: mysql:5.7
ports:
- "3306:3306"
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
MYSQL_DATABASE: myDb
MYSQL_USER: admin
MYSQL_PASSWORD: admin
networks:
- twotier
volumes:
- ./message.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/message.sql # Mount sql script into container's /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d directory to get table automatically created
- mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql # Mount the volume for MySQL data storage
volumes:
mysql-data:
networks:
twotier:
name: custom_twotier
This Docker Compose file defines a multi-container application composed of two services:
backendandmysql. Let's break down the main components of the Docker Compose file:version: '3':
- Specifies the version of the Docker Compose file format being used. In this case, it's version 3.
services:
- This section defines the individual services or containers that make up the application.
backend:
This is a service named "backend."
build:
- Specifies the build context as the current directory (
.). This means theDockerfilefor building thebackendservice is expected to be in the same directory as thedocker-compose.ymlfile.
- Specifies the build context as the current directory (
ports:
- Maps port 5000 on the host to port 5000 on the container, allowing external access to the
backendservice.
- Maps port 5000 on the host to port 5000 on the container, allowing external access to the
environment:
- Sets environment variables that the
backendservice expects. For example, it configures the MySQL connection details such as host, user, password, and database.
- Sets environment variables that the
networks:
- Connects the
backendservice to the custom network named "twotier."
- Connects the
depends_on:
- Specifies that the
backendservice depends on themysqlservice. This ensures that themysqlservice is started before thebackendservice.
- Specifies that the
mysql:
This is a service named "mysql."
image:
- Specifies the Docker image to be used, in this case,
mysql:5.7.
- Specifies the Docker image to be used, in this case,
ports:
- Maps port 3306 on the host to port 3306 on the container, allowing external access to the MySQL service.
environment:
- Sets environment variables for configuring the MySQL instance, such as the root password, database name, user, and password.
networks:
- Connects the
mysqlservice to the custom network "twotier."
- Connects the
volumes:
Mounts two volumes:
./message.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/message.sql: This mounts an SQL script into the container's initialization directory. This script will be automatically executed, creating tables or initializing the MySQL database.mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql: This mounts a volume for persistent storage of MySQL data.
volumes:
- Defines a volume named "mysql-data" that can be used for persistent storage.
networks:
- Defines a custom network named "custom_twotier" that both the
backendandmysqlservices are connected to. This allows these services to communicate with each other using the network alias.
- Defines a custom network named "custom_twotier" that both the
In summary, this Docker Compose file sets up a two-tier application with a backend service and a MySQL (mysql) service. The services are connected to a custom network, and dependencies between services are defined to ensure proper initialization. Persistent storage for MySQL data is handled using volumes, and an SQL script is executed during MySQL initialization.
Step 5: Configure Security Group and Enable Ports
🔒 If you are using a cloud provider, navigate to the security group settings and open the necessary ports based on your project requirements. In this example, we are exposing ports 5000 and 3306. Adjust the ports according to your project.
Step 6: Run Docker Compose
🏃 Navigate to the project directory and run the following command to start the containers in detached mode:
sudo docker-compose up -d
This command reads the docker-compose.yml file and builds the specified services. The -d flag runs the containers in the background.
Step 7: Explore Docker Networks
🕸️ To view the Docker networks created by your project, use the following commands:
sudo docker network ls
sudo docker network inspect custom_twotier
This provides insights into the networks and their configurations.
Step 8: Stop Everything
⛔ When you're done testing or need to stop the containers, use the following command:
sudo docker-compose down
This will stop and remove the containers, networks, and volumes defined in your Docker Compose file.
Conclusion:
🛠️ Docker Compose simplifies the deployment process by allowing you to define, configure, and manage multi-container applications effortlessly. Following these steps will help you set up a two-tier application quickly on an Ubuntu server, showcasing the power and simplicity of Docker Compose in your DevOps toolkit.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sagar Shah directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Sagar Shah
Sagar Shah
🚀 Sagar Shah 🚀 💻 DevOps Engineer 💡 🌐 Automating the digital universe, one script at a time ⚙️ 📚 Passionate learner and tech enthusiast 🤓 ☁️ Cloud explorer, making servers dance in the cloud 🌥️ 🛠️ Building bridges between development and operations 🌉 📖 Sharing insights and knowledge on all things DevOps 📢 🌟 Let's transform the world of IT together! ✨