An In-Depth Exploration of the Technical Processes Involved in Using Google's Search Engine
 Blain Muema
Blain Muema
Typing "https://www.google.com" into your browser and pressing Enter triggers a series of intricate processes. These processes work together to deliver the Google search engine to your screen. In this article we look at the technical details of this processes. We combine insights from various sources, to unveil the complexity behind this simple action. Let's dig in.
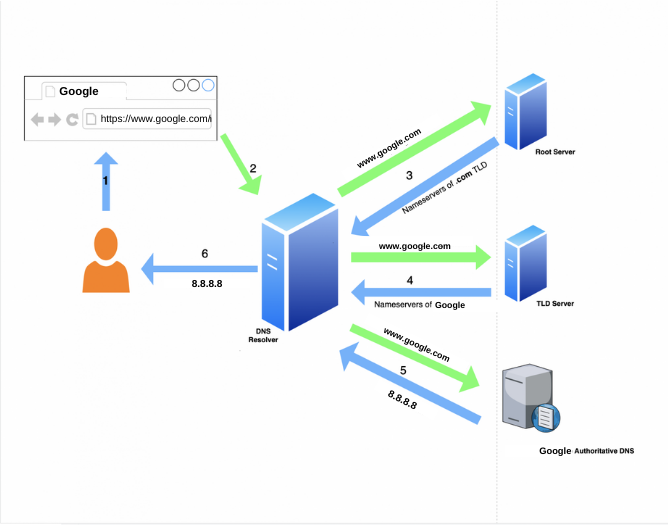
DNS Resolution
As you type the URL, the first step is a DNS request. The Domain Name System translates the human-readable address into an IP address. This address is (www.google.com). Your browser initiates this process, starting with a request to your local DNS resolver. Your Internet Service Provider provides this DNS resolver.
If the IP address is not in the cache, the request travels through these 3 servers. First is the root DNS servers, then the TLD servers, and finally, the authoritative DNS server. The DNS server then responds with the IP address of the server hosting the website. TLD nameservers maintain info for all the domain names that share a common domain extension.
TCP/IP Connection
Armed with the IP address, your browser establishes a TCP/IP connection with Google's web server. This involves the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). A TCP protocol works on top of the IP protocol to guarantee dependable packet transfer. It ensures reliable data exchange between the Internet Protocol (IP) routing the data between networks.
Firewall
Before the connection is established, it must pass through a firewall. A firewall is a security mechanism monitoring and controlling network traffic. It forms the wall that separates a private internal network from the open Internet at its most basic level. The firewall checks the incoming request for legitimacy. This ensures the incoming request doesn't pose a security threat to the network.
HTTPS/SSL
Once the connection is established, your browser sends an HTTP request to the web server. Google's web server responds using the secure HTTPS/SSL protocol. HTTPS, or HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure, is an acronym that shows up in the URL of a website that is secured by an SSL certificate.
Only the letters HTTP, or without the S for Secure, will show up in place of an SSL certificate. Additionally, a padlock icon will show up in the URL address box. This protocol encrypts data to prevent eavesdropping and tampering during transmission.
Load-Balancer
Before reaching your browser, the webpage passes through a load-balancer server. This server distributes incoming network traffic across many servers to prevent overloading. Load-balancers enhance performance by directing traffic to the most available and responsive server.
Web Server
The processed webpage then moves through Google's web server. A web server is a computer program that handles incoming requests and sends back responses. A web server's software consists of many components that regulate how web users can access hosted content. This is, at the very least, an HTTP server. The web server retrieves the webpage from a database, processing it to generate HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Files in these 3 languages form a large percentage of most webpages on the internet.
Application Server
For web pages requiring more complex processing, the request is forwarded to an application server. A server can create a dynamic, personalized response to a client request with the help of this server. The web server and application server work together to provide a dynamic, personalized response to a client request. This server processes application logic and retrieves data from databases. The server then generates dynamic content, such as search results or personalized recommendations.
Database and Database Servers
The application server fetches necessary data from a database, a structured electronic storage. The database contains information vital for generating content. This content can be search results or product listings. Computers connected to a network and used only for database storage and data retrieval are known as database servers. An essential part of a client/server computer environment is the database server. It houses the databases as well as the database management system (DBMS).
Conclusion
In conclusion, a symphony of technologies—DNS requests, TCP/IP communication, firewalls, HTTPS/SSL encryption, load-balancers, web servers, application servers, and databases—are involved in the process of typing "https://www.google.com" and accessing Google's search engine.
You can access Google's search engine and the information you're looking for thanks to these integrated technologies. They guarantee the efficient delivery of requested content to your browser.
Please feel free to leave a remark below with your opinions!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Blain Muema directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
