Importing Data From Multiple MS Access Files To SQL Server
 mortylen
mortylen
In this brief article, I aim to share my approach to importing data from MS Access files into SQL Server. With the task of importing data from hundreds of files with identical structures into SQL Server tables, I've distilled this guide to focus on a simplified scenario involving only a few files. Specifically, I demonstrate the process of importing data from a few single-table files into a corresponding table on the SQL Server.
Design description
The structure is as follows: a collection of files is placed in a single directory and a list of their names is stored in a table on the SQL Server. I go through this table row by row, and in each iteration I take the data from the corresponding Access file and insert it into the SQL Server table.
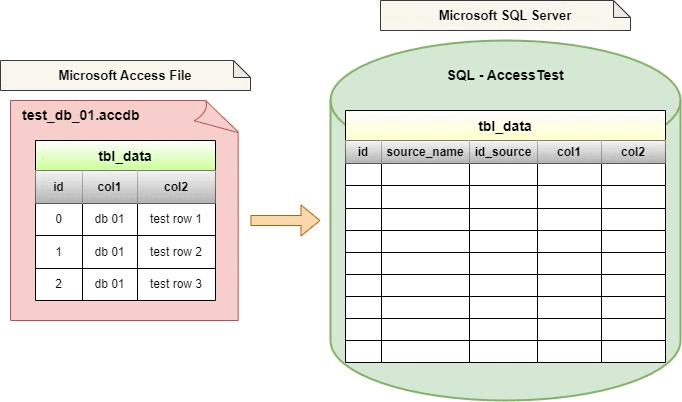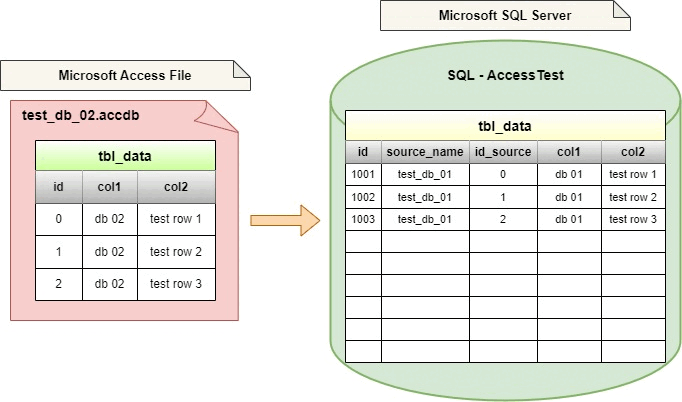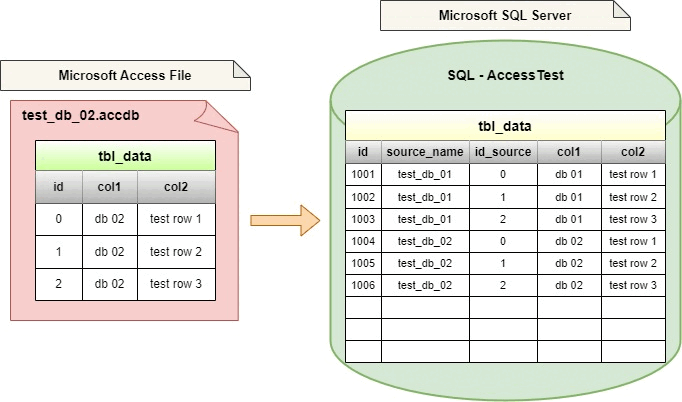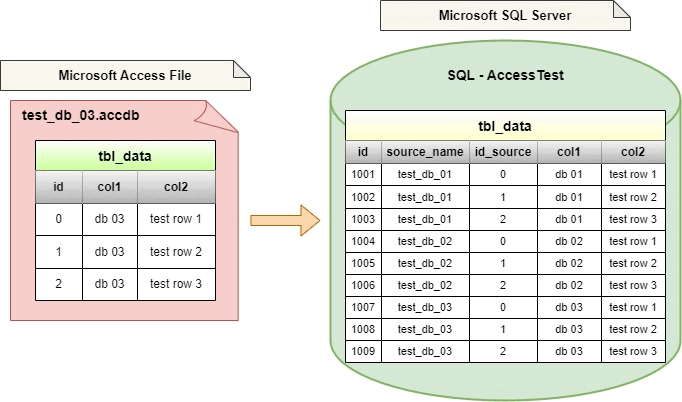
Let's assume that the directory structure / list of Access files will look like this. The access_files directory will contain the files we want to import into SQL Server.
C:\Data\access_files\
- test_db_01.accdb
- test_db_02.accdb
- test_db_03.accdb
Each database *.accdb file will contain a table called tbl_data.
- test_db_01.accdb
| id | col1 | col2 |
|----|-------|------------|
| 0 | db 01 | test row 1 |
| 1 | db 01 | test row 2 |
| 2 | db 01 | test row 3 |
- test_db_02.accdb
| id | col1 | col2 |
|----|-------|------------|
| 0 | db 02 | test row 1 |
| 1 | db 02 | test row 2 |
| 2 | db 02 | test row 3 |
- test_db_03.accdb
| id | col1 | col2 |
|----|-------|------------|
| 0 | db 03 | test row 1 |
| 1 | db 03 | test row 2 |
| 2 | db 03 | test row 3 |
And on the SQL Server side we will have a database called AccessTest and two tables in it. The one called dbo.file_names will contain the list of files we want to import. The second table named dbo.data_content will store all the data from the imported Access files.
- AccessTest.dbo.file_names
| file_name |
|------------------|
| test_db_01.accdb |
| test_db_02.accdb |
| test_db_03.accdb |
- AccessTest.dbo.data_content
| id | source_name | id_source | col1 | col2 |
|----|-------------|-----------|------|------|
What all we need?
I chose the OPENROWSET function to connect to the remote Access files *.accdb. According to the documentation, it is a one-time, ad hoc method of connecting and accessing remote data using OLE DB. The syntax is documented as follows:
OPENROWSET
( { 'provider_name'
, { 'datasource' ; 'user_id' ; 'password' | 'provider_string' }
, { <table_or_view> | 'query' }
} )
provider_name: Is a string that represents name (or PROGID) of the OLE DB provider as specified in the registry. I used
Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.16.0to access the*.accdbfiles.datasource: This string includes the name of the database file, the name of a database server, or a name that the provider understands to locate the database or databases. In this case, for example
C:\Data\access_files\test_db_01.accdbuser_id and password: Contains the user name and password for accessing the remote data source. In this case, I don't need to authenticate to the Access database, so these arguments will be empty.
table_or_view or query: I simply use
table_or_viewas the name of the table, since I want to import it all. Of course it is also possible to use thequeryoption, in this case it is enough to specify aSELECTquery as argument.
Distributed queries using OPENROWSET are disabled by default, so you need to enable them:
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1
RECONFIGURE
GO
EXEC sp_configure 'ad hoc distributed queries', 1
RECONFIGURE
GO
What will the whole thing look like?
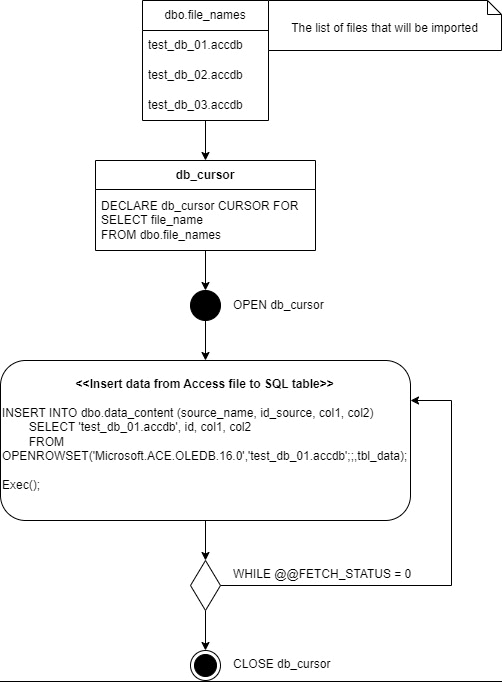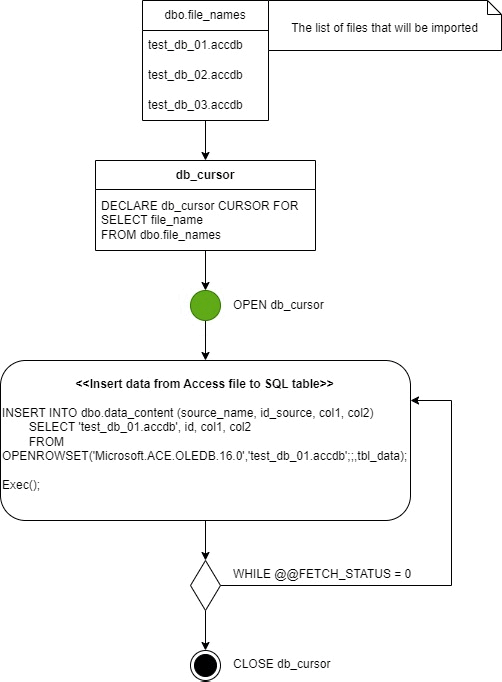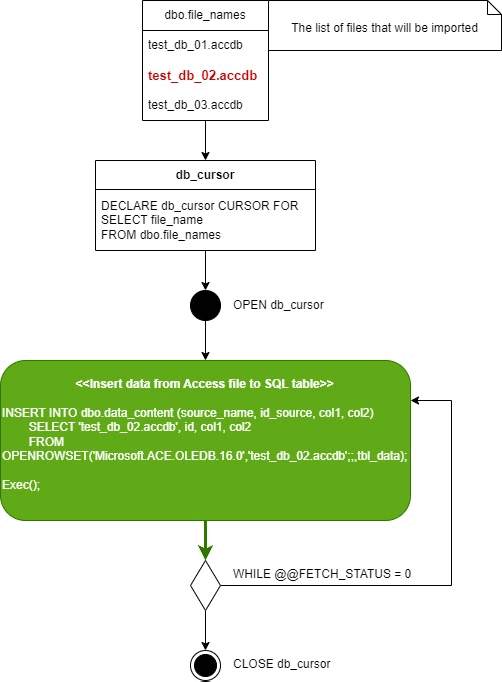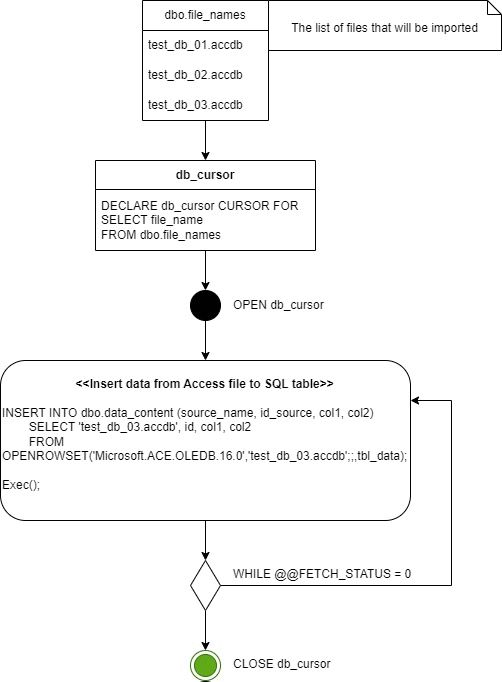
--Enable ad hoc distributed queries
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1
RECONFIGURE
GO
EXEC sp_configure 'ad hoc distributed queries', 1
RECONFIGURE
GO
USE AccessTest
GO
DECLARE @filename NVARCHAR(50)
DECLARE @root_file_path NVARCHAR(200)
DECLARE @full_file_path NVARCHAR(255)
DECLARE @sql NVARCHAR(MAX)
SET @root_file_path = N'C:\Data\access_files\'
DECLARE db_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT file_name
FROM dbo.file_names
OPEN db_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @filename
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
SET @full_file_path = @root_file_path + @filename
SET @sql = 'INSERT INTO dbo.data_content
(source_name, id_source, col1, col2)
SELECT ' + '''' + @filename + '''' + ' as source_name, id, col1, col2
FROM OPENROWSET(''Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.16.0'',
' + '''' + @full_file_path + '''' + ';;,tbl_data);'
Exec(@sql)
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @filename
END
CLOSE db_cursor
DEALLOCATE db_cursor
--Disable ad hoc distributed queries
EXEC sp_configure 'ad hoc distributed queries', 0
RECONFIGURE
GO
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 0
RECONFIGURE
GO
I'll explain a little bit
First I enabled show advanced options and ad hoc distributed queries.
Next, I defined a few variables.
@filename: will store the current file name from thetbl_file_namestable.@root_file_path: is a constant that stores the path to the files.@full_file_path: is the concatenation of the two variablesfilenameandroot_file_path.
Next, we declare a CURSOR named db_cursor over the dbo.file_names table. This cursor will step through the individual rows in the table. Then open the cursor and start going through the single row records.
You may have noticed that I don't use OPENROWSET directly, but I put the whole SQL query into a text variable and execute the query using Exec(@sql). This is because OPENROWSET does not allow to insert data from variables and I need to point it to a different data source, which I have stored in the full_file_path variable. So instead of a simple command:
INSERT INTO dbo.data_content
(source_name, id_source, col1, col2)
SELECT @filename as source_name, id, col1, col2
FROM OPENROWSET('Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.16.0',@full_file_path;;,tbl_data);
I have to use a little hack and magic with quotes:
SET @sql = 'INSERT INTO dbo.data_content
(source_name, id_source, col1, col2)
SELECT ' + '''' + @filename + '''' + ' as source_name, id, col1, col2
FROM OPENROWSET(''Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.16.0'',
' + '''' + @full_file_path + '''' + ';;,tbl_data);'
Exec(@sql)
What does this query actually do? It is a simple INSERT INTO that inserts data from the source defined in the OPENROWSET into the dbo.data_content table on the SQL Server. This query is executed in a loop for each file individually. The list of these files is stored in the dbo.file_names table.
That's all, finally we just close CURSOR and disable ad hoc distributed queries again.
Conclusion
We have shown how it is possible to import data from many MS Access *.accdb; *.mdb files to SQL Server. Of course it is also possible to import data from other sources, for example from MS Excel, just edit the datasource in OPENROWSET: OPENROWSET('Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.16.0', 'Excel 12.0 Xml;Database=C:\Data\excel_files\data.xlsx;', Sheet1$)
For use in the real world, I recommend adapting the code to your own needs. It would also be useful to log the result of the import to make sure we have all the data we want. Hopefully I have inspired someone and you don't get lost in the data :)
If you found this useful, consider supporting me:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from mortylen directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

mortylen
mortylen
By day, I work on enterprise and industrial systems; by night, I experiment with modern technologies. I’m committed to lifelong learning and continuously exploring new ideas.