Aws Introduction Day 1
 Vipul Chaudhary
Vipul Chaudhary
Index
What is Cloud
Traditional IT Overview
What are the Servers Composed of?
Problems with the Traditional IT approach
Deployment Model of the Cloud
Different Types of Cloud Computing
AWS Shared Responsibility Model
Pricing of the Cloud
Conclusion
What is Cloud
On-demand service of Compute power, database storage, application, and other IT resources
Its features are Pay-as-you-go Provisions for the right and required size of Computing resource that you need. You can access as many Resources as you need, almost Instantly. A simple way to access server, storage, database, and a set of application services
Traditional IT Overview
How the website works
Client -> Network -> Servers
It's just like a letter-sending process that has the address in the form of the IP address.
What are the Servers Composed of?
1)Compute=CPU
2)Memory = RAM
3)Storage = Data
4)Database = Store data in a structured way
5)Network = Router, Switch, DNS Server
Problems with the Traditional IT approach.
1)Pay for the rent for the data center
2)Pay for power supply, cooling, and maintenance.
3)Scaling is limited. Adding and replacing hardware takes time.
4)The deployment model of the Cloud.
Deployment Model of the Cloud
| Private | Public | Hybrid |
| It is a cloud service used by a single organization, not exposed to the public people. | It us a Cloud resource owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider and delivered over the Internet. | Hybrid Cloud Keep some servers on your premises and extend some capabilities to the Cloud. |
| We have the Complete Control over it | Least Control | Control over sensitive assets in your private infrastructure. |
| Meet specific business needs. | Public Usage | Meet specific business needs. |
| Example: Rackspace | AWS, AZURE, GOOGLE CLOUD | Example: AWS AND On-Premises Servers |
Characteristics of the Cloud
1)On-Demand Self Service.
2)Broad Network access.
3)Multi-Tenancy and Resource Pooling.
4)Rapid elasticity and scalability.
5)Measured Service.
Different Types of Cloud Computing
1) Infrastructure As A Service
IAAS(EC2 Elastic Cloud Compute)
Building block of the IT Infrastructure.
Have access to networking, computing, and data storage classes.
Highest level of flexibility.
2) Platform As A Service
PAAS(Elastic Beanstalk)
Remove the need for your organization to manage the underlying structure.
Focus on the deployment and management of your application.
3) Software As A Service
SAAS(Rekogintion)
Complete Product that is run and managed by AWS.
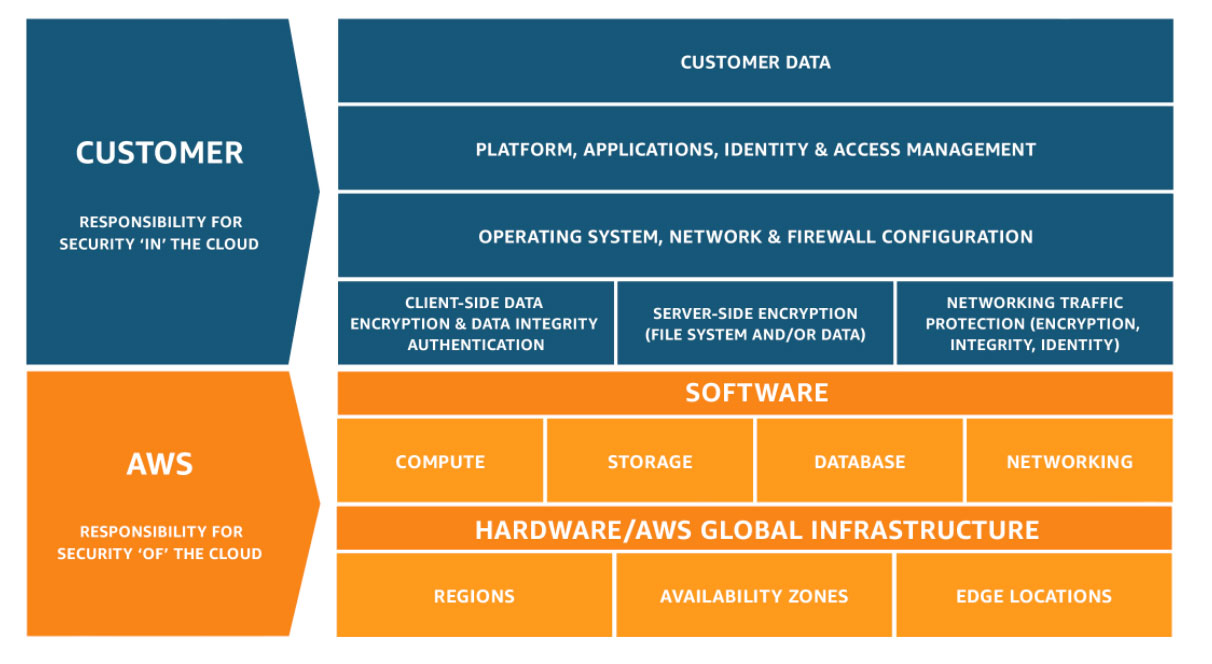
AWS Shared Responsibility Model:
Define the responsibility of the user and AWS of the service
Pricing of the Cloud
AWS has 3 pricing fundamentals
Following the pay-as-you-go pricing model
1)Compute: Pay for the Compute time.
2)Storage: Pay for the data stored in the Cloud.
3)Data transfer OUT of the Cloud: Data transfer in the cloud is free
Conclusion:
Cloud computing is a pay-as-you-go, quickly scalable, on-demand service that offers a variety of IT resources. Traditional IT has drawbacks such as high expenses and constrained scalability. There are three types of cloud deployment models: private, public, and hybrid. Broad network access, multi-tenancy, and on-demand self-service are all features of the cloud. Software as a Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) are two examples of cloud kinds. Pricing for AWS is determined by computation time, data storage, and outbound data transfer. The company uses a shared responsibility approach.
I appreciate you reading this blog, please check back for more posts soon, and don't forget to follow for such informative content.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Vipul Chaudhary directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Vipul Chaudhary
Vipul Chaudhary
Passionate AWS Certified Professional with expertise in Competitive Programming and Network Building. Strong problem-solving skills, technical proficiency, and proven leadership in team management as a president.