Using FabricRestClient To Make Fabric REST API Calls
 Sandeep Pawar
Sandeep PawarAccessing Fabric REST endpoints in Fabric notebooks was already easy but it became easier and straightforward with semantic-link version 0.4.0. You can use the FabricRestClient class from sempy to set up a REST client and call the APIs. Authentication is automatically managed for you.
#sempy version 0.4.0 or higher
!pip install semantic-link --q
import pandas as pd
import sempy.fabric as fabric
#Instantiate the client
client = fabric.FabricRestClient()
Refer to the official documentation for API details. To call an API, you only need to pass the below portion of the URL.
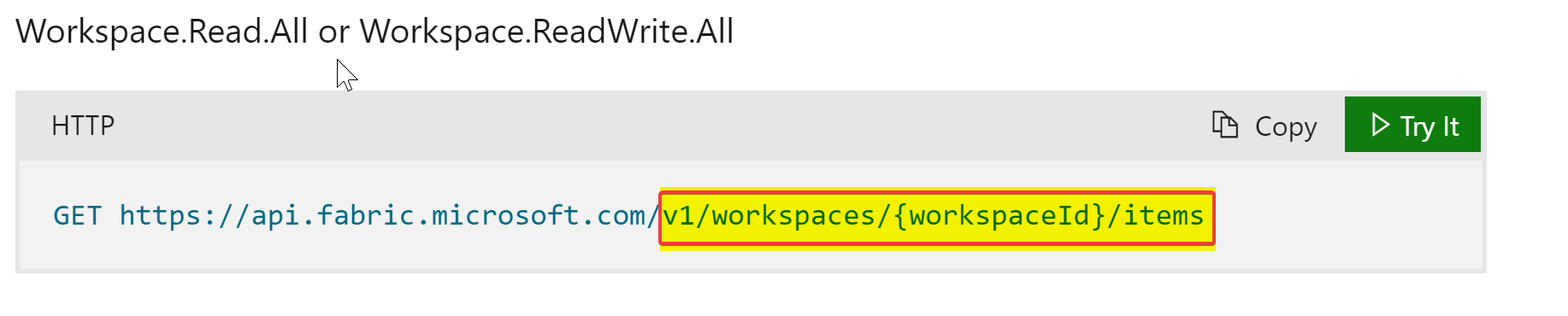
#example usage
url = "v1/workspaces/<workspaceId>/items"
result = client.get(url)
This approach is not substantially different from using requests to make API calls, but there are a few advantages:
You don't have to generate and pass the authentication token. sempy uses the environment details to authenticate the user automatically.
This approach is similar to using
requests.Session()to maintain a persistent connection, keeping the session open longer. This is particularly beneficial if you plan to call multiple REST endpoints within the same session.sempy has a few nice utilities and functions for exception handling and getting workspace/lakehouse ids.
Example
In this simple example, I will get a list of Fabric items from a workspace. I will show how some of the utilities can help make this even easier and robust.
#instantiate the client
client = fabric.FabricRestClient()
#get a list of items from a workspace
workspaceId = "<workspaceid>"
client.get(f"/v1/workspaces/{workspaceId}/items")
In this example, I manually provided the workspace ID. However, we can obtain the notebook's workspace ID automatically without needing to define it.
#instantiate the client
import pandas as pd
client = fabric.FabricRestClient()
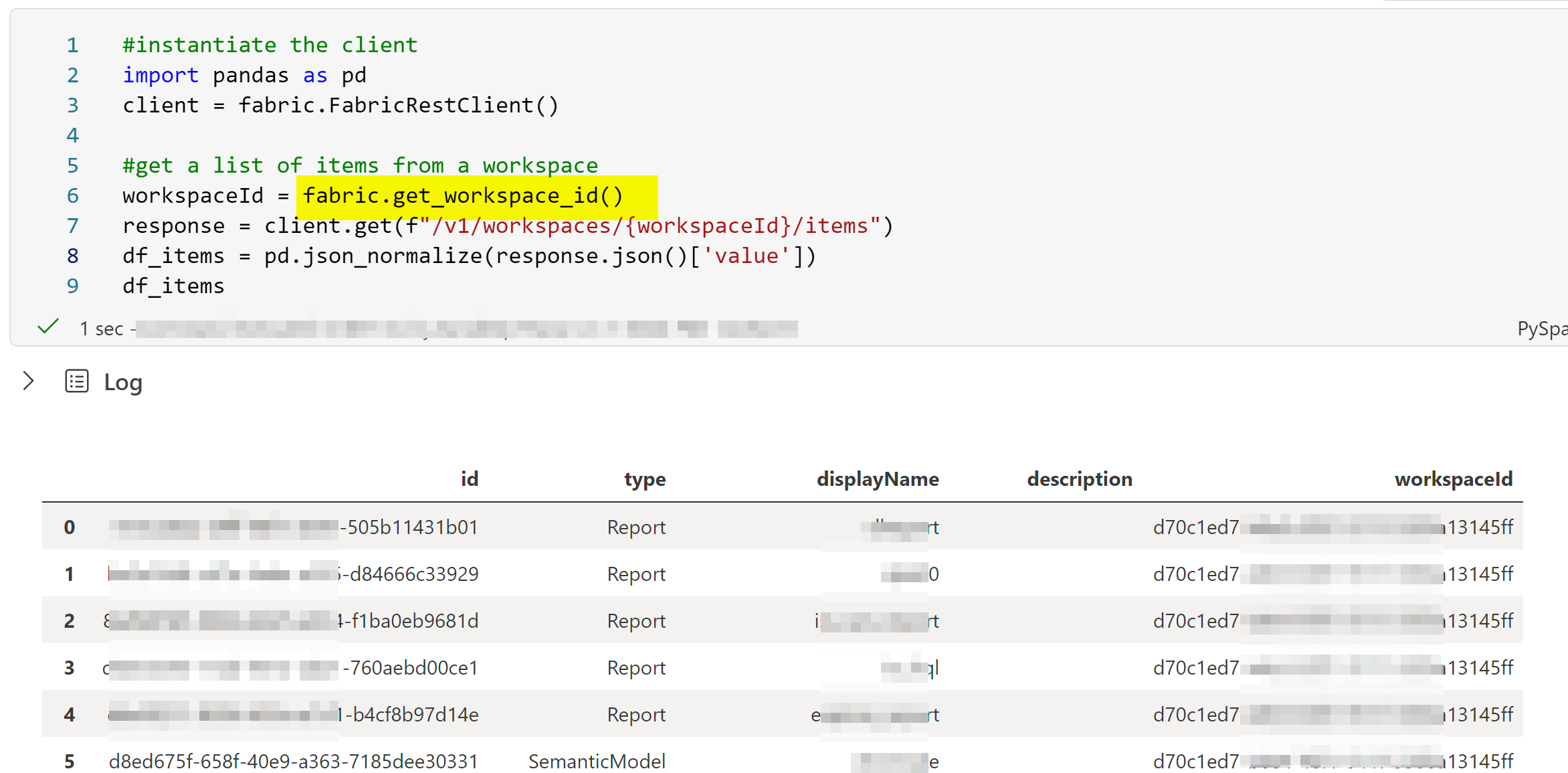
#get the default workspace id of the notebook
workspaceId = fabric.get_workspace_id()
#get a list of items from a workspace
response = client.get(f"/v1/workspaces/{workspaceId}/items")
df_items = pd.json_normalize(response.json()['value'])
df_items
For production use cases you will need to include exception handling. sempy provides a few nice utilities, see an example below:
import sempy.fabric as fabric
from sempy.fabric.exceptions import FabricHTTPException, WorkspaceNotFoundException
import pandas as pd
client = fabric.FabricRestClient()
def get_workspace_items(workspace=None):
"""
Sandeep Pawar | fabric.guru
Get a list of workspace items using FabricRestClient
"""
df_items = None
if workspace is None:
workspaceId = fabric.get_workspace_id()
else:
try:
workspaceId = fabric.resolve_workspace_id(workspace)
response = client.get(f"/v1/workspaces/{workspaceId}/items")
# Check the status code of the response for this endpoint
# Use 200 if operation is completed, 201 if item is created
if response.status_code != 200:
raise FabricHTTPException(response)
df_items = pd.json_normalize(response.json()['value'])
except WorkspaceNotFoundException as e:
print("Caught a WorkspaceNotFoundException:", e)
except FabricHTTPException as e:
print("Caught a FabricHTTPException. Check the API endpoint, authentication.")
return df_items
get_workspace_items("<dataflow name or id>")
In the above example:
workspace is optional. If no workspace name/id is passed,
fabric.get_workspace_id()will use the workspace id of the default workspace. Similarly, you can usefabric.get_lakehouse_id()to get the id of the default lakehouse attached to the notebook.All APIs require using workspace id. With
fabric.resolve_workspace_id(workspace)you can get the id of a workspace if the user enters workspace nameWorkspaceNotFoundException,FabricHTTPExceptionhelp catch workspace and REST endpoint exceptions.
Update: 1/21/2024
Making a POST Request
A redear asked how to make a POST request using the FABRICRestClient. Below is te example where I create a lakehouse using a POST request.
import sempy.fabric as fabric
from sempy.fabric.exceptions import FabricHTTPException, WorkspaceNotFoundException
client = fabric.FabricRestClient()
def create_lakehouse(payload:dict, workspace=None):
"""
Sandeep Pawar | fabric.guru
Create a lakehouse using POST request
"""
if workspace is None:
workspaceId = fabric.get_workspace_id()
else:
workspaceId = fabric.resolve_workspace_id(workspace)
try:
response = client.post(f"/v1/workspaces/{workspaceId}/items",json= payload)
if response.status_code != 201:
raise FabricHTTPException(response)
except WorkspaceNotFoundException as e:
print("Caught a WorkspaceNotFoundException:", e)
except FabricHTTPException as e:
print("Caught a FabricHTTPException. Check the API endpoint, authentication.")
return
#payload/body for the POST request as a dict
#example; create a lakehouse named "mylh" in the default workspace
payload = {
"displayName": "mylh",
"type": "Lakehouse"
}
#workspace name or id is optional. If None, default workspace is used.
create_lakehouse(payload=payload, workspace=None)
Thanks to Markus Cozowicz for answering my questions and for his input.
Update: 3/23/2025
Follow-up blog on using SPN authentication : Using Service Principal Authentication With FabricRestClient
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sandeep Pawar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Sandeep Pawar
Sandeep Pawar
Principal Program Manager, Microsoft Fabric CAT helping users and organizations build scalable, insightful, secure solutions. Blogs, opinions are my own and do not represent my employer.