Intro to Neo4j
 Nikhil Akki
Nikhil AkkiTable of contents
Introduction
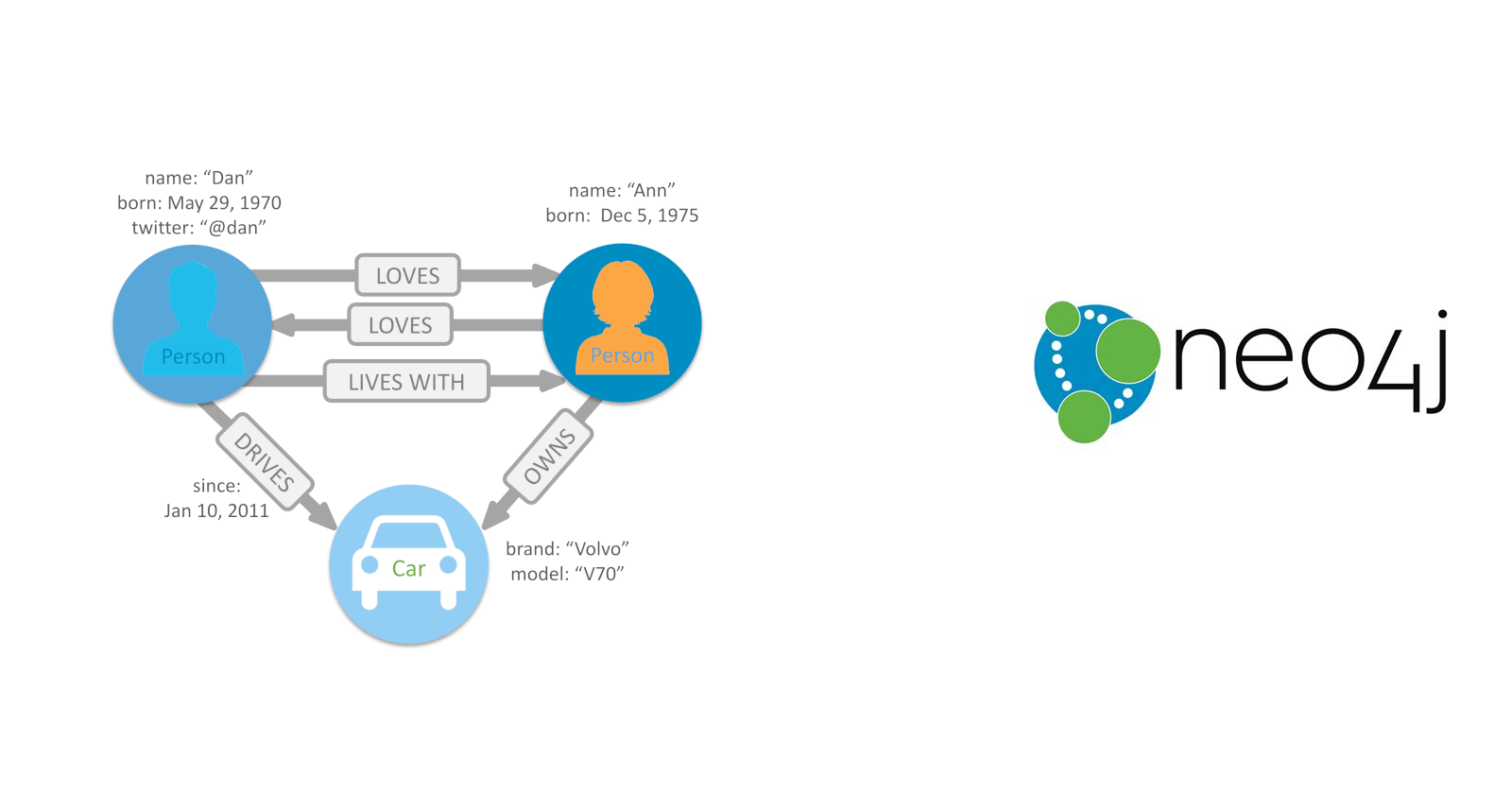
Neo4j is a graph database that allows you to efficiently store, query, and analyze network and connected data. With its native graph storage and processing capabilities, Neo4j shines for working with highly connected data.
Neo4j stores data in nodes and relationships instead of tables like traditional databases. This graph structure mirrors many real-world relationships, making it easy to model networks. Querying is done via the Cypher query language, optimized specifically for graphs.
At its core, Neo4j manages connections. It excels at revealing insights from linked data that are very difficult to determine with non-graph technologies. Questions like finding the shortest path between two points or detecting fraud rings emerge easily from a Neo4j graph database.
Use cases
Fraud detection: Identify suspicious patterns and connections in financial transactions
Identity and access management: Manage user identities and permissions based on connections
Recommendation engines: Provide personalized recommendations based on product relationships
Master data management: Maintain a consistent view of master data entities and hierarchy
Network and IT operations: Model computer networks to understand connectivity and dependencies
Knowledge graphs: Encode knowledge as an interconnected semantic graph to enable knowledge applications
Social network analysis: Analyze social relationships and interactions between individuals
IoT and time series: Ingest sensor data and analyze relationships across time and devices
Real-time analytics: Conduct fast graph queries to deliver real-time analytic insights
Cypher is Neo4j’s graph query language. Its declarative nature allows you to focus on what you want from the graph, not how to retrieve it.
MATCH (p:Person)-[:KNOWS]->(friends)
RETURN friends
Returns All Person nodes and connect friends nodes
MATCH p=shortestPath((p1:Person)-[:KNOWS*]-(p2:Person)) WHERE p1.name = "Arun" AND p2.name="Nisha" RETURN p
Returns the shortest path between Arun and Nisha
MATCH (account:Account)-[:TRANSFERRED_TO]->(externalAccount)
WHERE account.balance < 0
RETURN account, externalAccount
Surfaces suspicious money transfers
MATCH (movie:Movie)<-[r:RATED]-(user)
RETURN movie.title AS recommendation, count(r) AS score
ORDER BY score DESC LIMIT 10
Recommends movies based on highest ratings
MATCH (user:User)-[:CLICKED]->(article:Article)
RETURN user.name AS user, collect(article.title) AS recommendations
Recommends articles based on a user's clicks
Conclusion
In summary, Neo4j provides a powerful way to work with highly connected data by representing relationships as first-class citizens. Its graph data model and Cypher query language empower users to analyze data in new ways.
References:
https://neo4j.com/developer/cypher-query-language/ - Introduction to Cypher
https://neo4j.com/use-cases/ - Neo4j use cases
https://neo4j.com/developer/guide-data-modeling/ - Data modeling in Neo4j
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nikhil Akki directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nikhil Akki
Nikhil Akki
I am a Full Stack Solution Architect at Deloitte LLP. I help build production grade web applications on major public clouds - AWS, GCP and Azure.