Unleashing the Potential of Kubernetes: Day 01
 Vedant Adhe
Vedant AdheTable of contents
Introduction : Welcome to Day 01 of the #30DaysOfKubernetes challenge! In this journey, we’ll explore Kubernetes, the open-source container orchestration engine that’s transforming the world of application deployment and management. Let’s dive right in ! .
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration engine designed for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. This open-source project is hosted by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
Understanding of Kubernetes and Docker
Okay, so if you want to get the hang of Kubernetes, it's like this: first, you gotten know your way around Docker. Think of Docker as the place where we put our apps, neatly tucked away in these things called containers.
Now, in Kubernetes, it's like taking things up a notch. Instead of just handling a couple of containers, we're talking about dealing with a whole bunch of them, sometimes even thousands! It all depends on how much traffic your app is getting. So, in a nutshell, Docker is like the cozy home for your apps, and Kubernetes is the wizard that manages this bustling neighborhood of containers, making sure everything runs smoothly. Cool, huh?
Visualizing Docker and Kubernetes
In Docker, imagine a ship containing containers.
Now, in Kubernetes, picture that same ship, but this time, it has a steering wheel. Just like a captain operates the ship’s wheel to make decisions about its course, Kubernetes acts as the “ship wheel” for managing containers.
Kubernetes is an open-source platform, meaning its source code is freely available for anyone to use, modify, and redistribute.
What are Monolithic Architecture and Microservices Architecture?
Monolithic Architecture:
Imagine a restaurant where everything happens in one big kitchen. This kitchen handles taking orders, cooking food, and serving customers all in a single place.
In this scenario, if the kitchen gets too crowded or if there’s a problem with one part of the kitchen, it can affect the entire restaurant’s operation. If the chef is sick, the entire kitchen may come to a halt, impacting the entire dining experience.
Microservices Architecture:
Now, consider a food delivery service like Zomato or Swiggy. Instead of one big kitchen, they have a network of different restaurants, each specializing in a specific type of regional food or cuisine.
When you place an order, it’s not prepared in a single kitchen rather, each restaurant (microservice) prepares its own portion of the order. These portions are then assembled and delivered to you.
If one restaurant has an issue, it doesn’t necessarily impact the others. For example, if the burger place is busy, it won’t affect the rolls restaurant’s ability to fulfill orders.
Key Differences:
Monolithic architecture is like a single kitchen handling all tasks, while microservices architecture is like multiple specialized restaurants working together.
Monoliths are typically easier to set up and manage initially, while microservices offer more flexibility and scalability.
Monoliths can have a single point of failure, while microservices are more fault-tolerant because a failure in one microservice doesn’t necessarily affect the others.
In the end, Kubernetes helps to achieve microservice-based architecture which is good for business aspects, etc.
Why do we need Kubernetes?
After Docker came into the Picture, the deployment of the applications was very easy on the containers because containers are lightweight. But after some time, there were a lot of issues arose such as managing the huge amount of containers in the Production environment where Containers getting failed leading to huge Business losses.
After Kubernetes came, it automates many tasks such as:
Autoscaling of Containers according to the peak or normal hours.
Load balancing of multiple containers.
Automatically deployment of containers to the available nodes in the cluster.
Self-healing if containers fail.
Kubernetes Origins and Open Source:
Kubernetes was created by Google in 2013 in Golang. Initially, Kubernetes was not open source but in 2014, google introduced Kubernetes open source and donated to CNCF.
Languages Supported by Kubernetes
Kubernetes supports both YAML and JSON for configuration.
Features of Kubernetes
AutoScaling: Kubernetes supports two types of autoscaling horizontal and vertical scaling for large-scale production environments which helps to reduce the downtime of the applications.
Auto Healing: Kubernetes supports auto healing which means if the containers fail or are stopped due to any issues, with the help of Kubernetes components(which will talk in upcoming days), containers will automatically repaired or heal and run again properly.
Load Balancing: With the help of load balancing, Kubernetes distributes the traffic between two or more containers.
Platform Independent: Kubernetes can work on any type of infrastructure whether it’s On-premises, Virtual Machines, or any Cloud.
Fault Tolerance: Kubernetes helps to notify nodes or pods failures and create new pods or containers as soon as possible
Rollback: You can switch to the previous version.
Health Monitoring of Containers: Regularly check the health of the monitor and if any container fails, create a new container.
Orchestration: Suppose, three containers are running on different networks (On-premises, Virtual Machines, and On the Cloud). Kubernetes can create one cluster that has all three running containers from different networks.
Alternatives of Kubernetes
Docker Swarm
Apache Mesos
Openshift
Nomad, etc
We don’t need to know the other alternative in depth except Docker Swarm as our main focus is Kubernetes.
Difference between Docker Swarm and Kubernetes
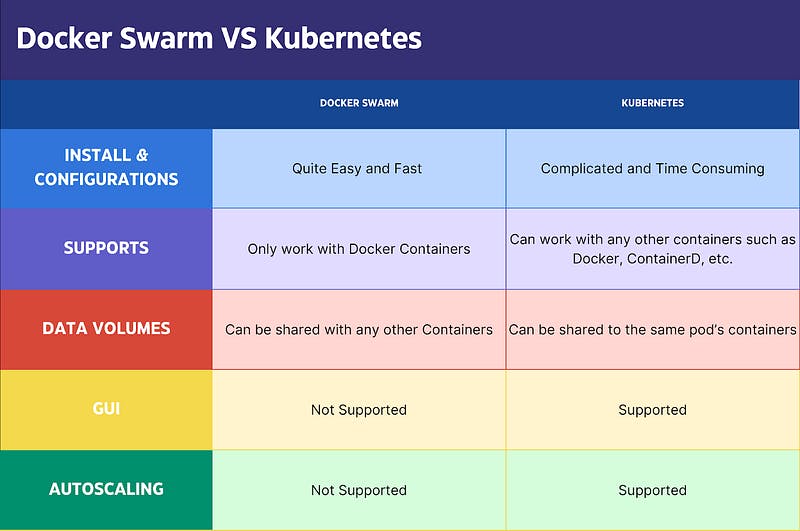
Differences
Master-Slave/ Client-Server Architecture in Kubernetes
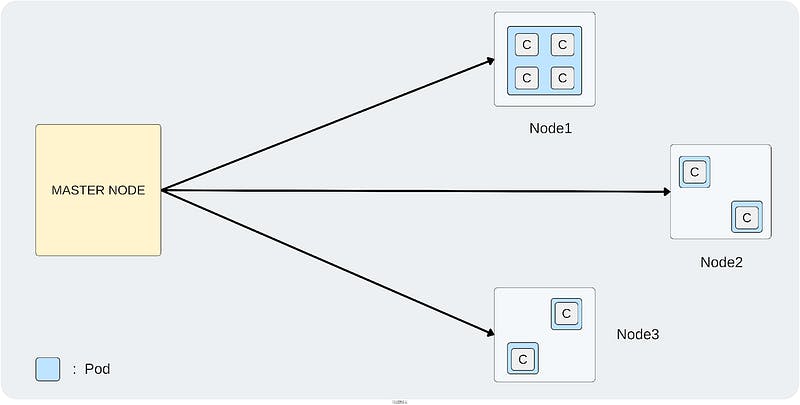
Architecture
This is the glimpse only. We will discuss Kubernetes Architecture in the detailed blog.
Conclusion:
And there you have it — a glimpse into the fascinating world of Kubernetes. We’ve covered the basics, understanding its roots, and how it compares to Docker. In the days to come, we’ll dive deeper into the inner workings of Kubernetes, exploring its features, architecture, and much more.
If you’re as excited as we are to embark on this #30DaysOfKubernetes challenge, you’re in for an incredible learning journey! Stay tuned for daily posts that will unravel the mysteries of Kubernetes and empower you to become a skilled practitioner.
I am a passionate DevOps enthusiast with a strong foundation in Linux, containerization, orchestration, automation, and cloud technologies. My goal is to continuously learn and implement DevOps best practices to streamline development and operations processes.
LinkedIn linkedin.com/in/vedant-adhe
GitHub (github.com/VedantAdhe)
Connect Vedantadhe04@gmail.com
!!!!!Thank you for reading !!!!!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Vedant Adhe directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
