Proxy Design Patterns
 MUKUL JHA
MUKUL JHA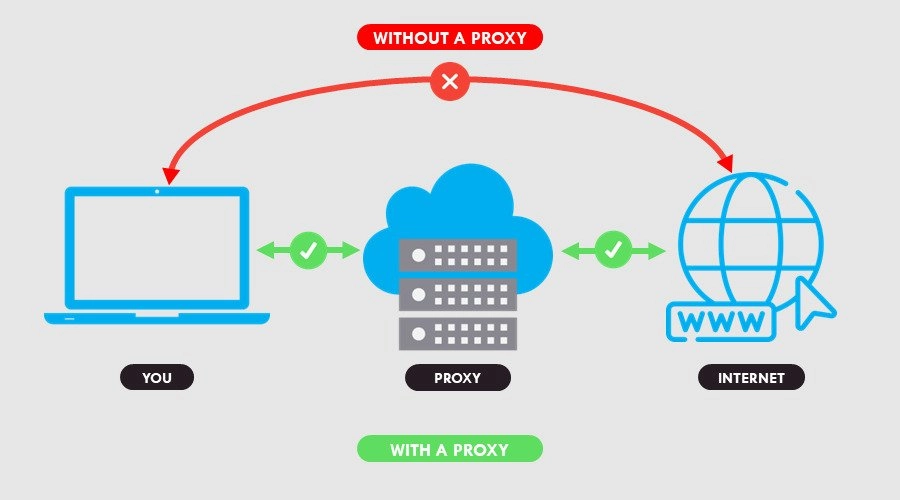
Proxy is a structural design pattern. The proxy design pattern will help to hide implementation and expose the proxy to the client.
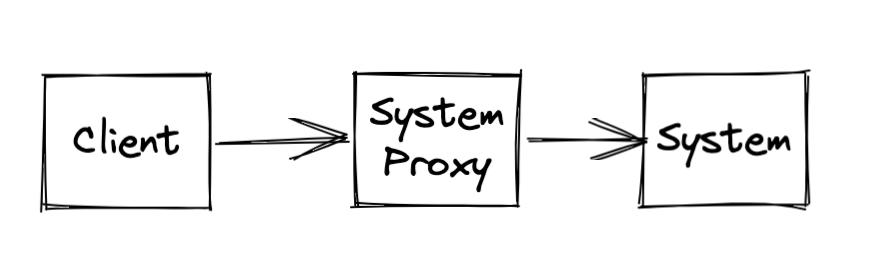
The client doesn’t have any idea or implementation knowledge of the system.
System proxy works on behalf of the System.
Real-Time uses of proxy design pattern.
Hibernate uses a proxy design
Hibernate always returns a proxy object whenever we write code to fetch data from a database.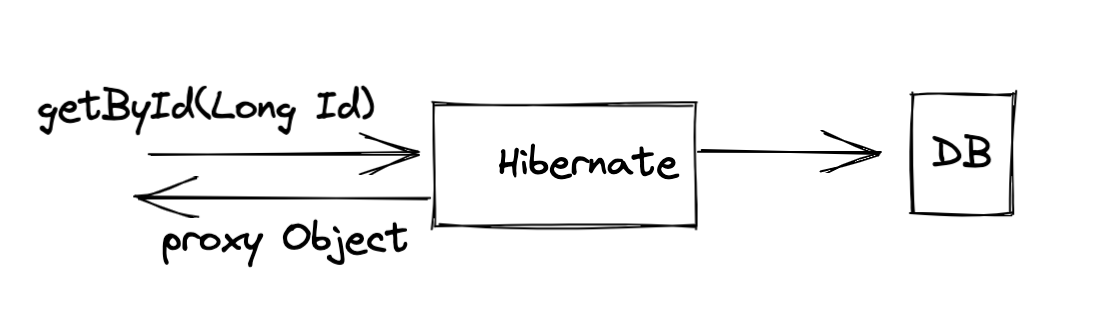
Spring uses proxies for object creation
Proxies are essential for AOP in Spring
Proxy Server
Implementation
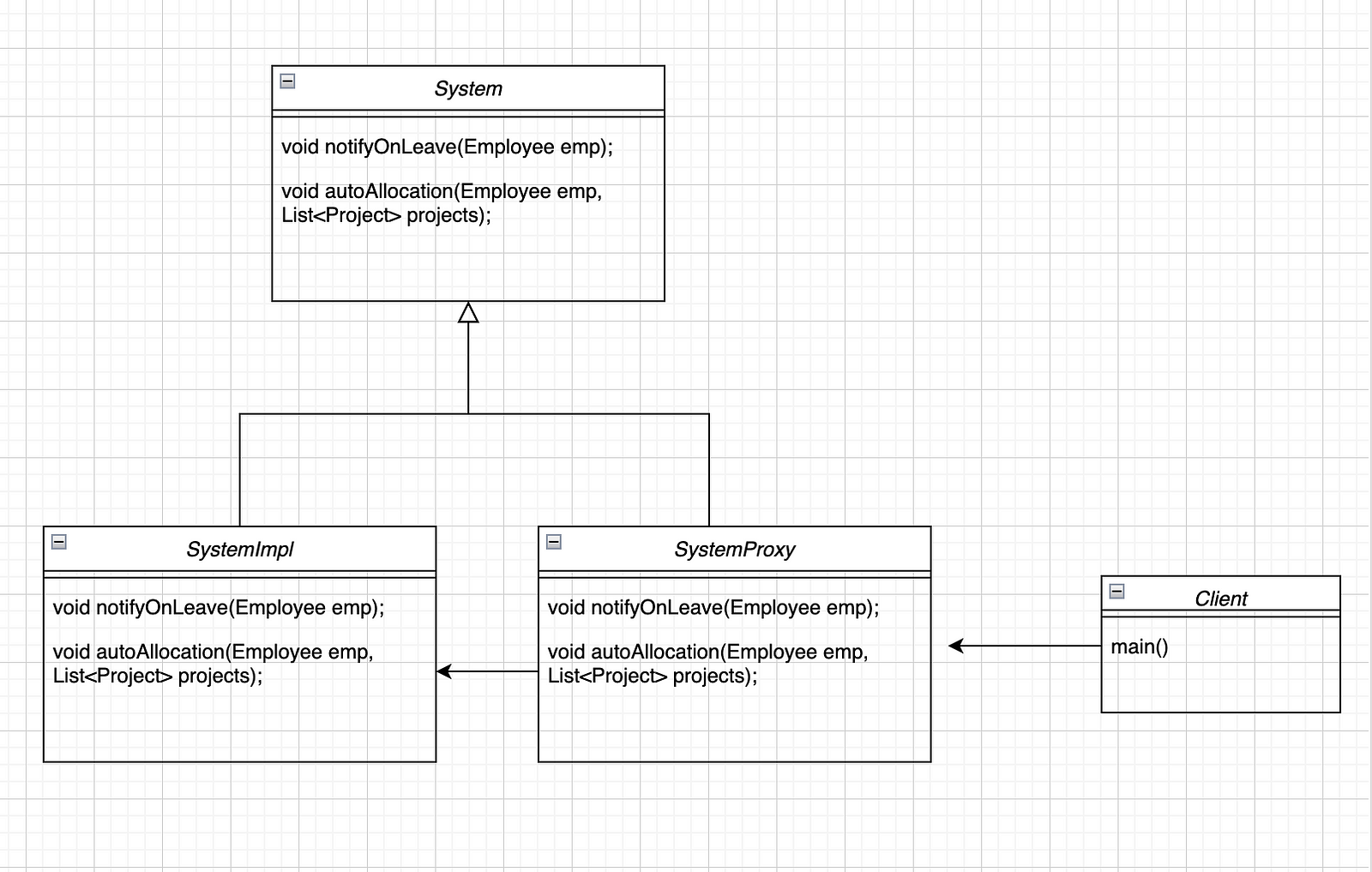
System: is an interface that exposes the functionality available to the clients.
SystemImpl: is a class implementing of system and it is a concrete implementation that needs to be hidden behind a proxy.
The client should not interact with SystemImpl directly. They have to interact with SystemProxy
SystemProxy: hides the real object by extending it and clients communicate to the real object via this proxy object. Usually, frameworks create this proxy object when the client requests the real object.
The system interface has two methods
notifyOnLeave: Notify Employee on leave
autoProjectAllocation: It should be authenticated and auto-project allocation access should be restricted to internal use cases.
Project class
Now implement the methods from the System class and always remember System implementation class(SystemImpl) should be protected so no one gets direct access to the System class rather than SystemProxy.
Let’s create a proxy class.
Now client interacts with the proxy, not with the implementation class.
Let’s test sending notifications to employees about leave.
Employee emp = new Employee(1, "Mukul");
// Using SystemProxy instead of SystemImpl
System system = new SystemProxy();
system.notifyOnLeave(emp);
Output: sending leave notification to emp Mukul
Auto allocates project to employee request from the client.
Employee emp1 = new Employee(2, "Rahul");
List<Project> projects = new ArrayList<>();
projects.add(new Project(1, "IBM", "Bangalore"));
projects.add(new Project(2, "Google", "Bangalore"));
System system = new SystemProxy();
system.autoProjectAllocation(emp, projects);
Output: You can't access auto project allocation.
Hope you enjoyed reading!
Your support means a lot. Feel free to like and share if you find it valuable. Thanks for your time! 🙏
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from MUKUL JHA directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
