Networking For Devopsc
 Mahesh Prasad Khamari
Mahesh Prasad Khamari
NETWORKING BASIC FOR DEVOPS AUTOMATION
IP Addresses and Subnets:
● In an IP network, each device is assigned a unique IP address for identification and communication. An IP address consists of two parts: the network address and the host address. Subnetting involves dividing the host part of the IP address into subparts.
● Subnets divide a larger network into smaller, more manageable segments. A subnet mask is a 32-bit number that divides the IP address into network and host portions. It uses a combination of binary ones (1) to represent the network bits and binary zeros (0) to represent the host bits. The subnet mask helps devices determine whether a destination IP address is on the same subnet or a different one.
POPULAR PROTOCOLS
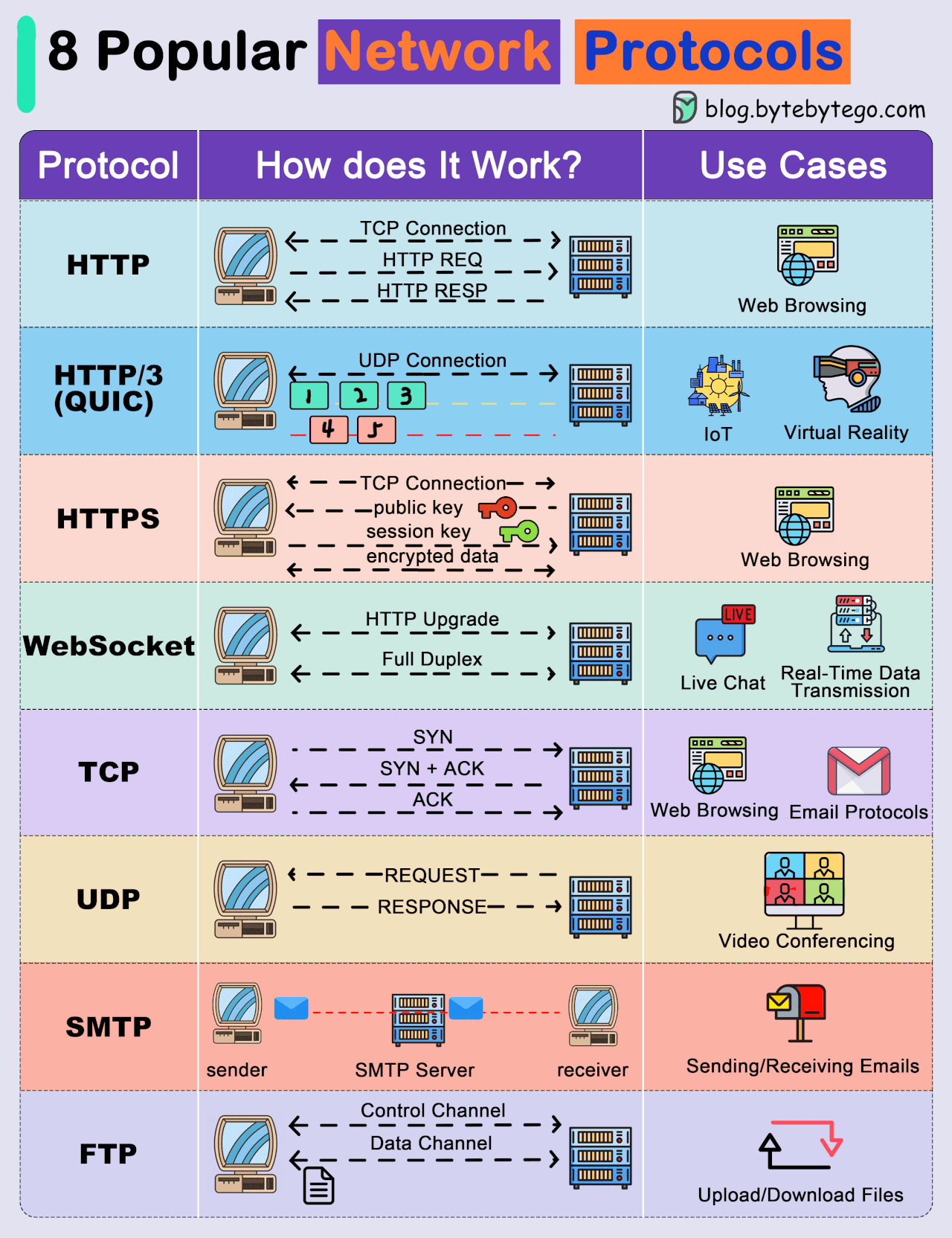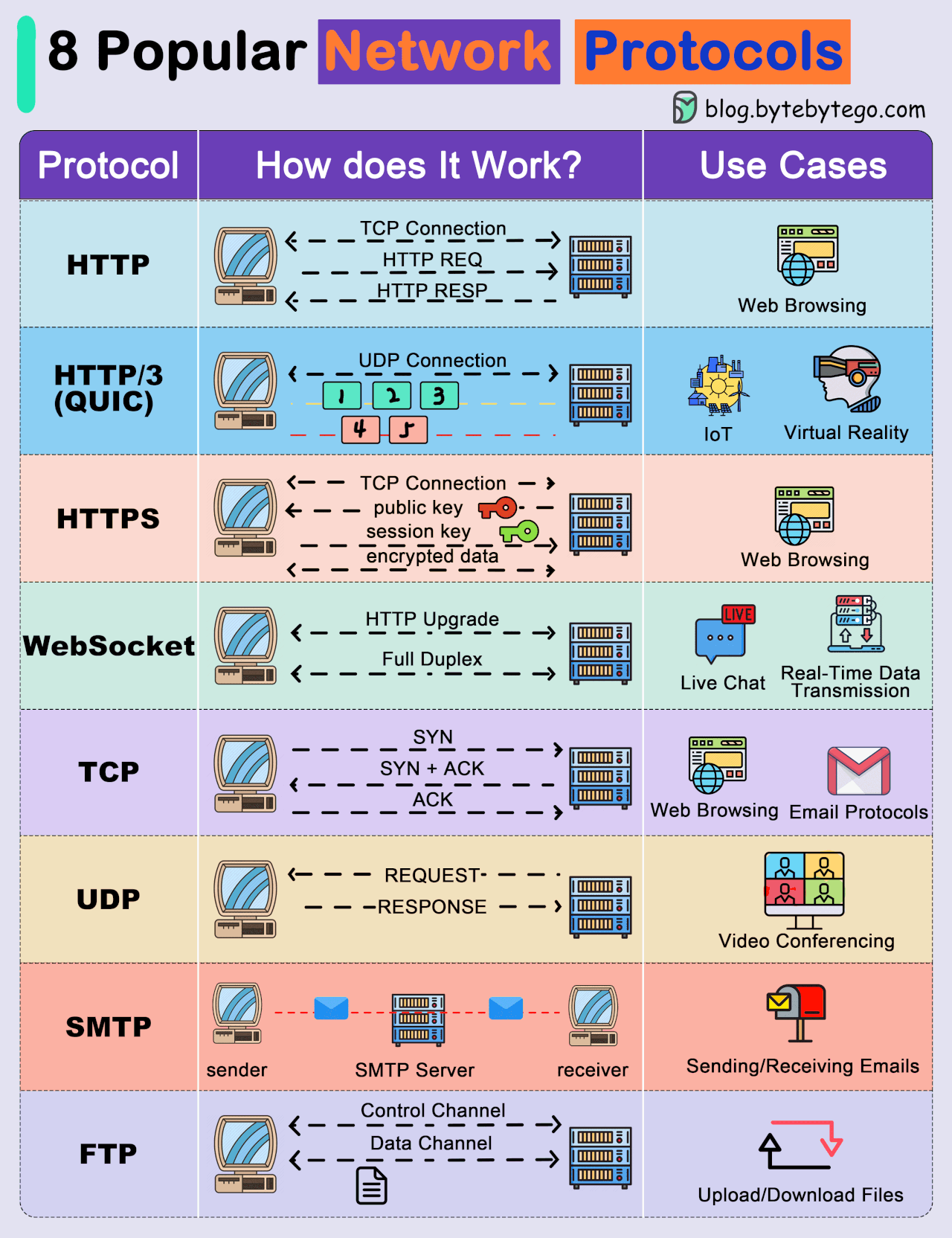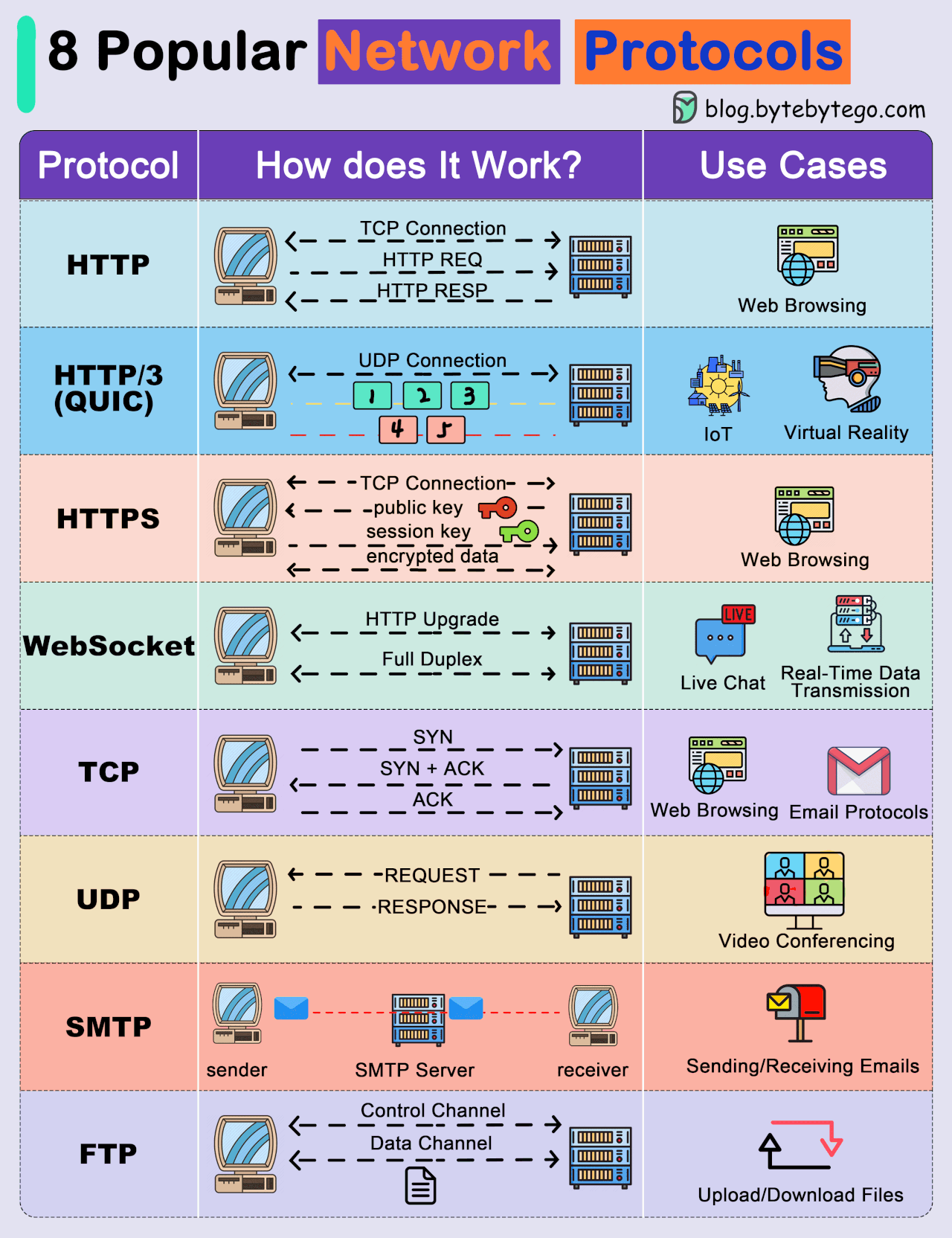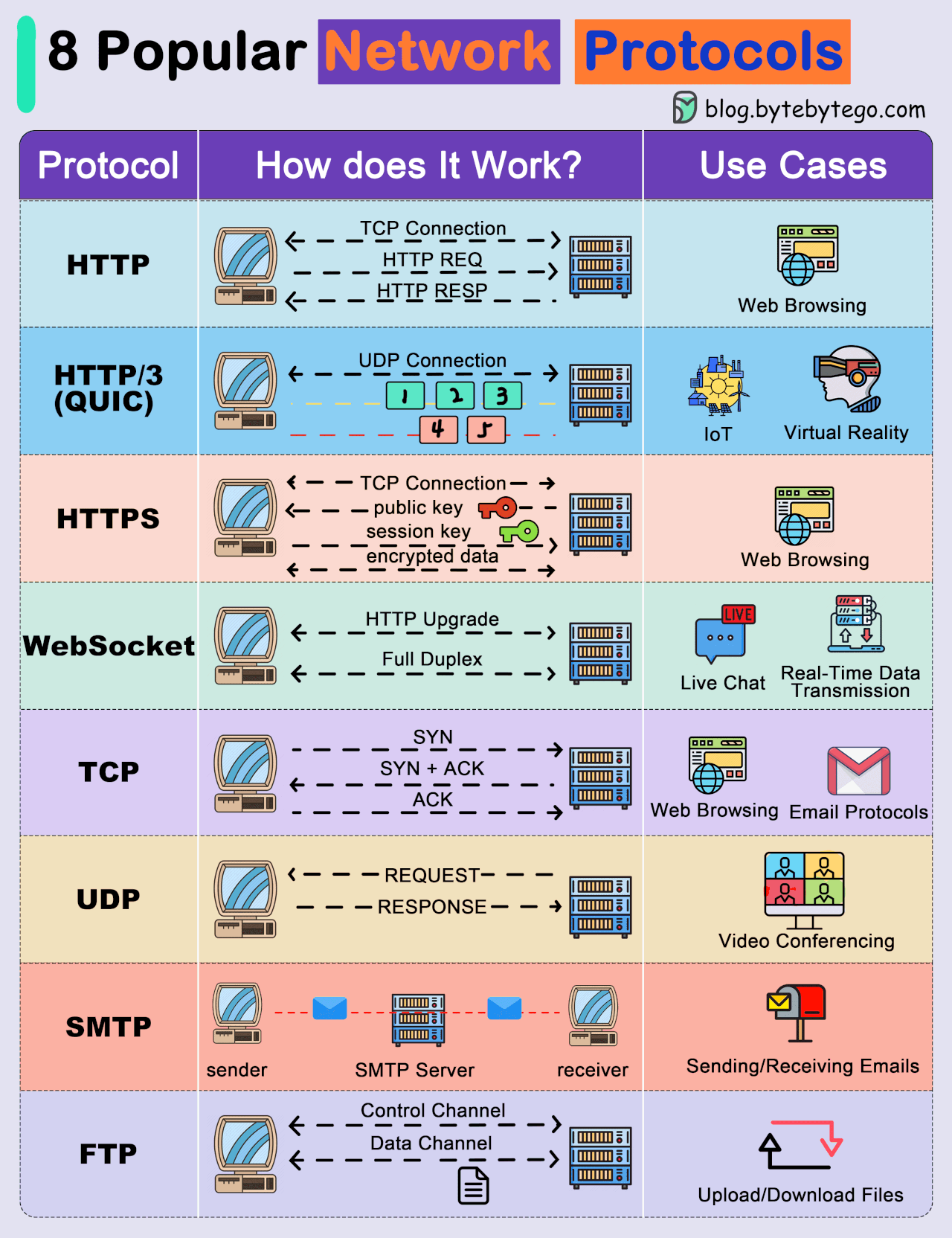
● Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): TCP is a connection-oriented protocol that provides reliable and ordered delivery of data. It establishes a connection between two devices before transmitting data, ensuring that data is received accurately and in the correct order.
● User Datagram Protocol (UDP): UDP is a connectionless protocol that offers faster, but less reliable, communication. It does not establish a connection before sending data, making it suitable for scenarios where speed is more critical than data integrity.
● Internet Protocol (IP): IP is a fundamental protocol responsible for addressing and routing data packets between devices on a network. IP is often used in conjunction with TCP or UDP.
● Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP): HTTP is a protocol used for transmitting hypermedia documents, such as HTML. It forms the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web.
● Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS): HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP that uses encryption, typically provided by Transport Layer Security (TLS) or its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), to protect data during transmission.
● File Transfer Protocol (FTP): FTP is a protocol for transferring files between computers on a network. It allows users to upload and download files from servers.
● Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP): SMTP is a protocol for sending email messages between servers. It is a fundamental part of email communication
. ● Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) and Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP): These protocols are used by email clients to retrieve messages from a mail server. IMAP allows messages to be kept on the server, while POP3 typically downloads messages to the client.
● Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS): Facilitate communication between web browsers and servers, with HTTPS adding a layer of encryption for secure transactions.
● Secure Shell (SSH): Enables secure remote access and command execution on networked devices
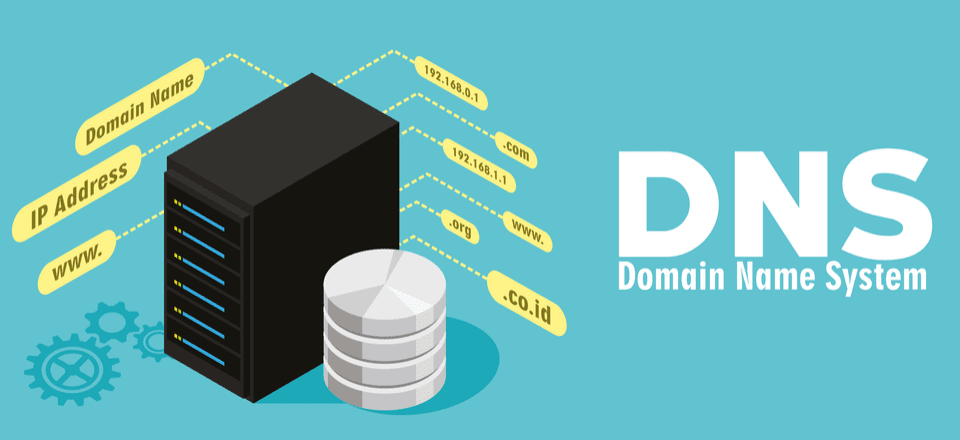
DNS (Domain Name System):
● DNS translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, facilitating easy navigation on the internet.
● In a DevOps environment, understanding DNS is vital for managing server configurations and ensuring seamless interactions between applications.
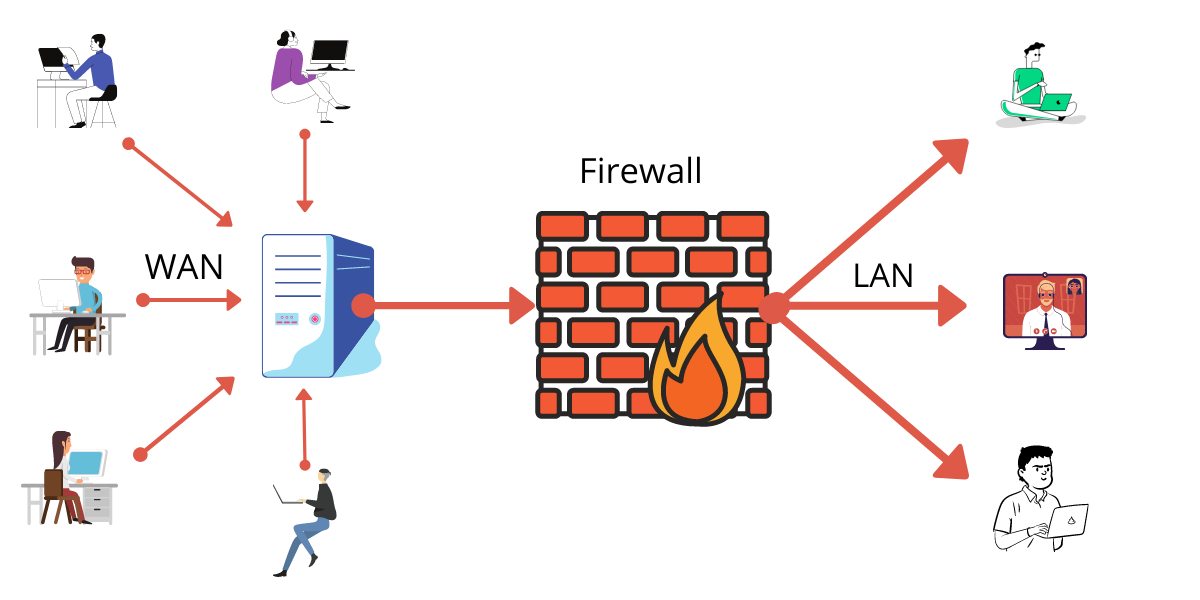
FIREWALL
*Firewalls act as barriers between a secure internal network and untrusted external networks, preventing unauthorized access.
● DevOps teams must configure firewalls to allow necessary traffic while maintaining security.
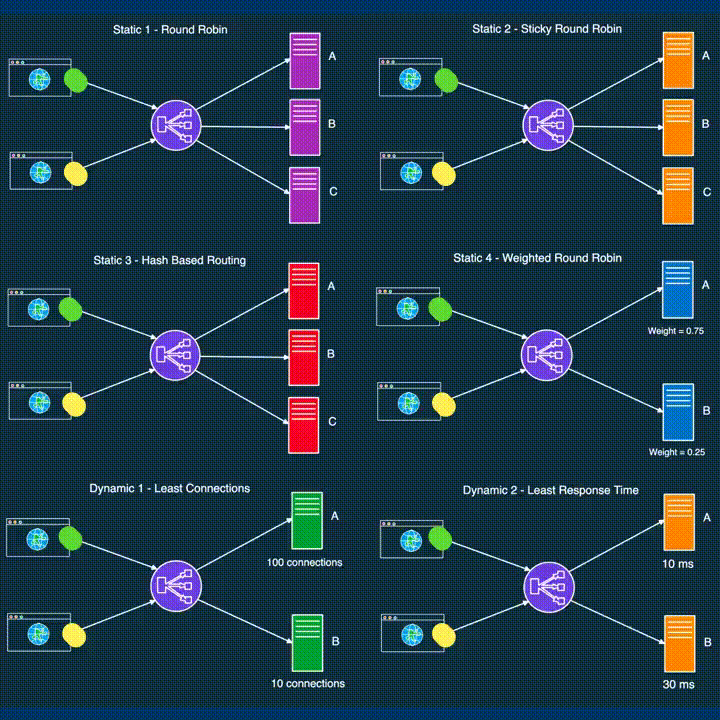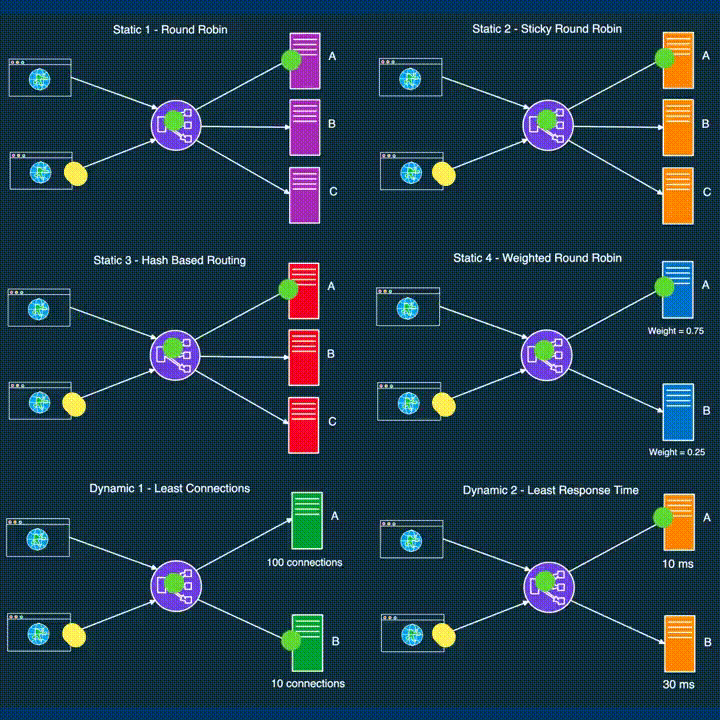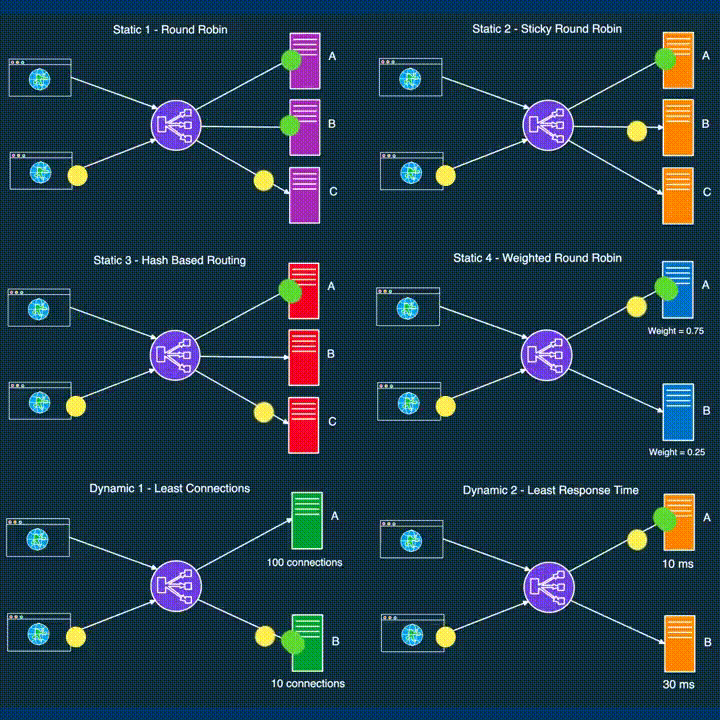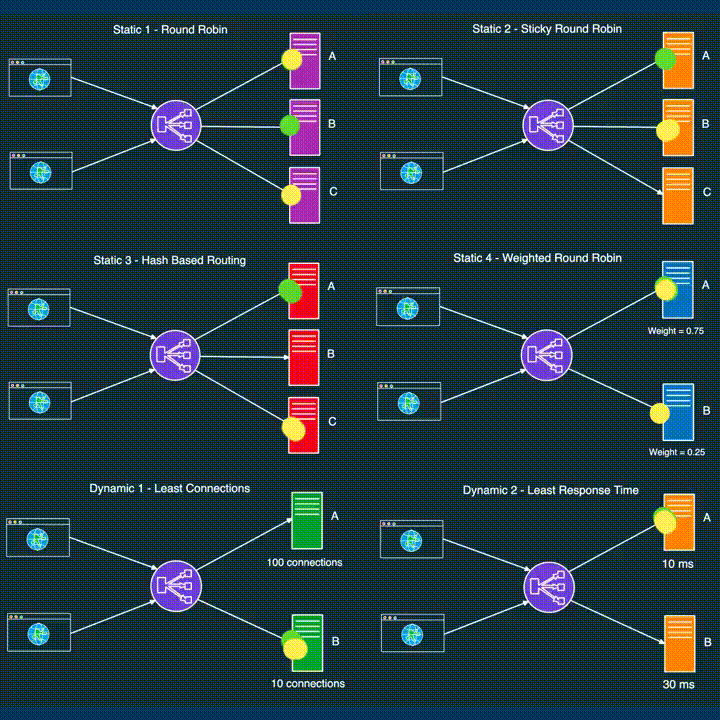
LOAD BALANCING
*Load balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers, ensuring optimal resource utilization and preventing server overload.
● DevOps leverages load balancing to enhance application performance and reliability.
Proxy Servers:

● Proxy servers act as intermediaries between clients and servers, forwarding requests and responses.
● DevOps teams often use proxies for security, monitoring, and content caching purposes.
Integration with DevOps:
1. Infrastructure as Code (IaC):

● IaC involves managing and provisioning infrastructure through code. Networking configurations can be defined alongside application code, ensuring consistency and version control.
● Tools like Terraform and Ansible are commonly used to automate networking tasks.
2. Container Orchestration:

● Container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes provide networking solutions to manage communication between containers and enable efficient scaling.
● Networking considerations are crucial for deploying and connecting containers across distributed environments.
3. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
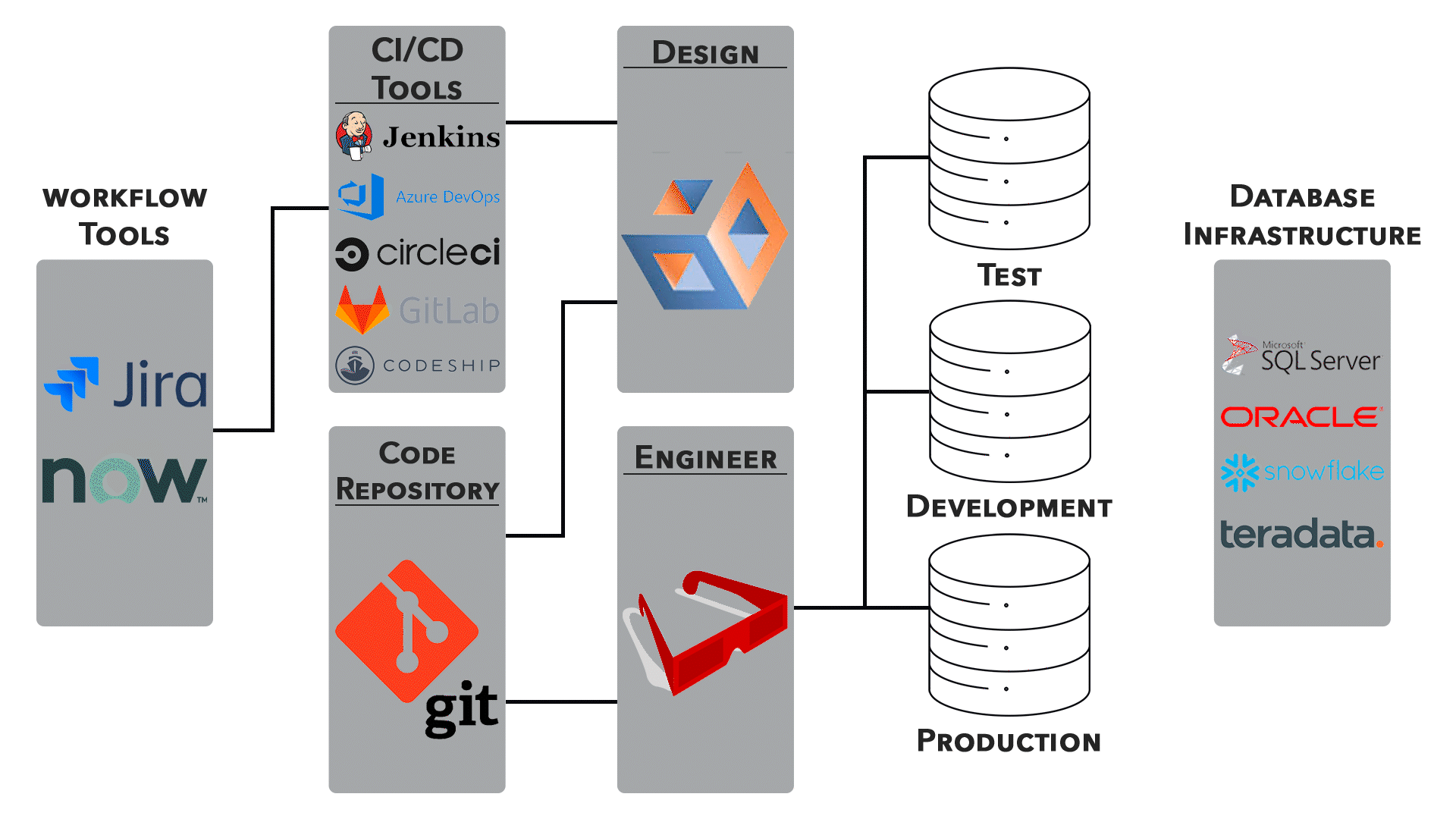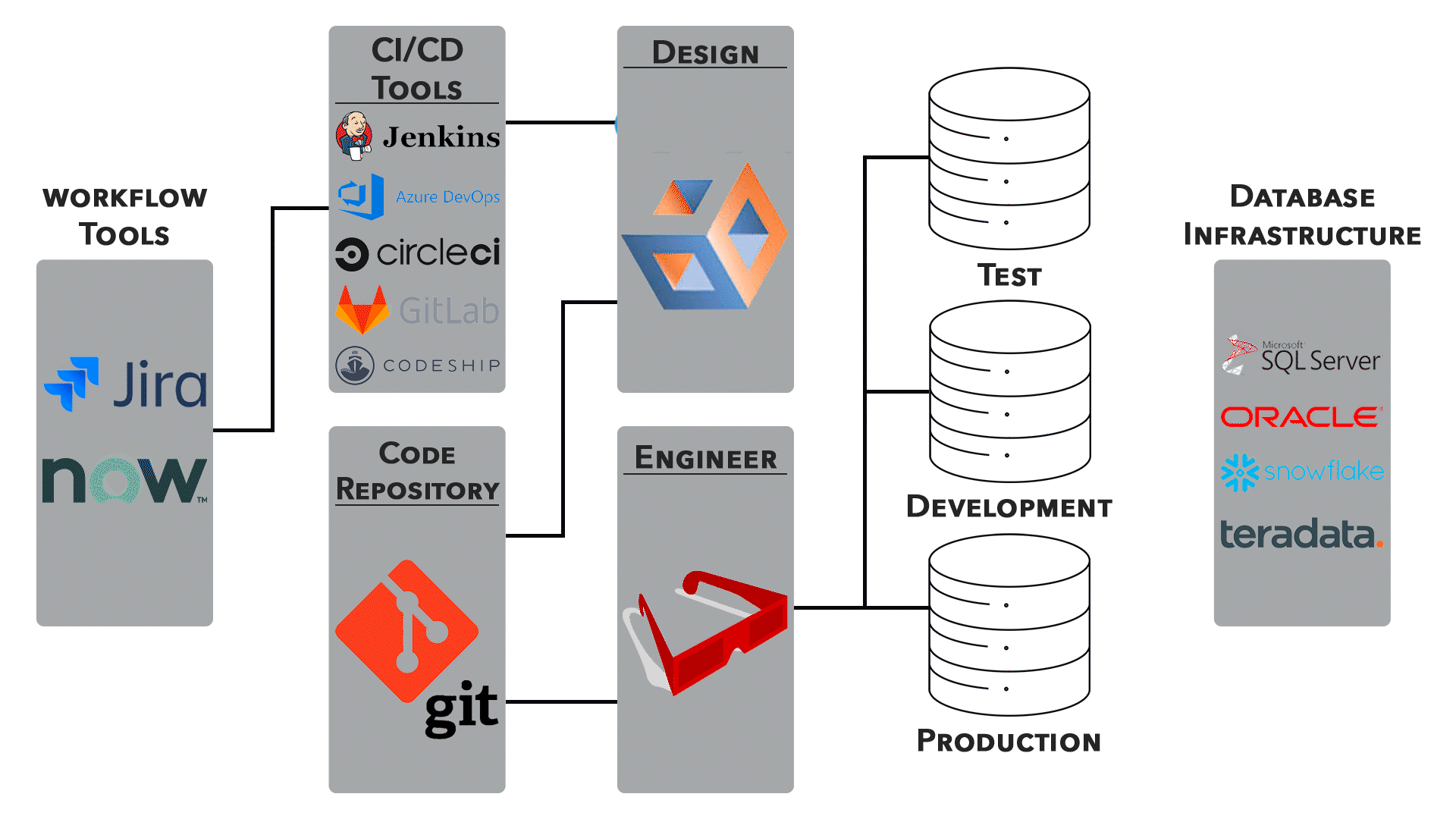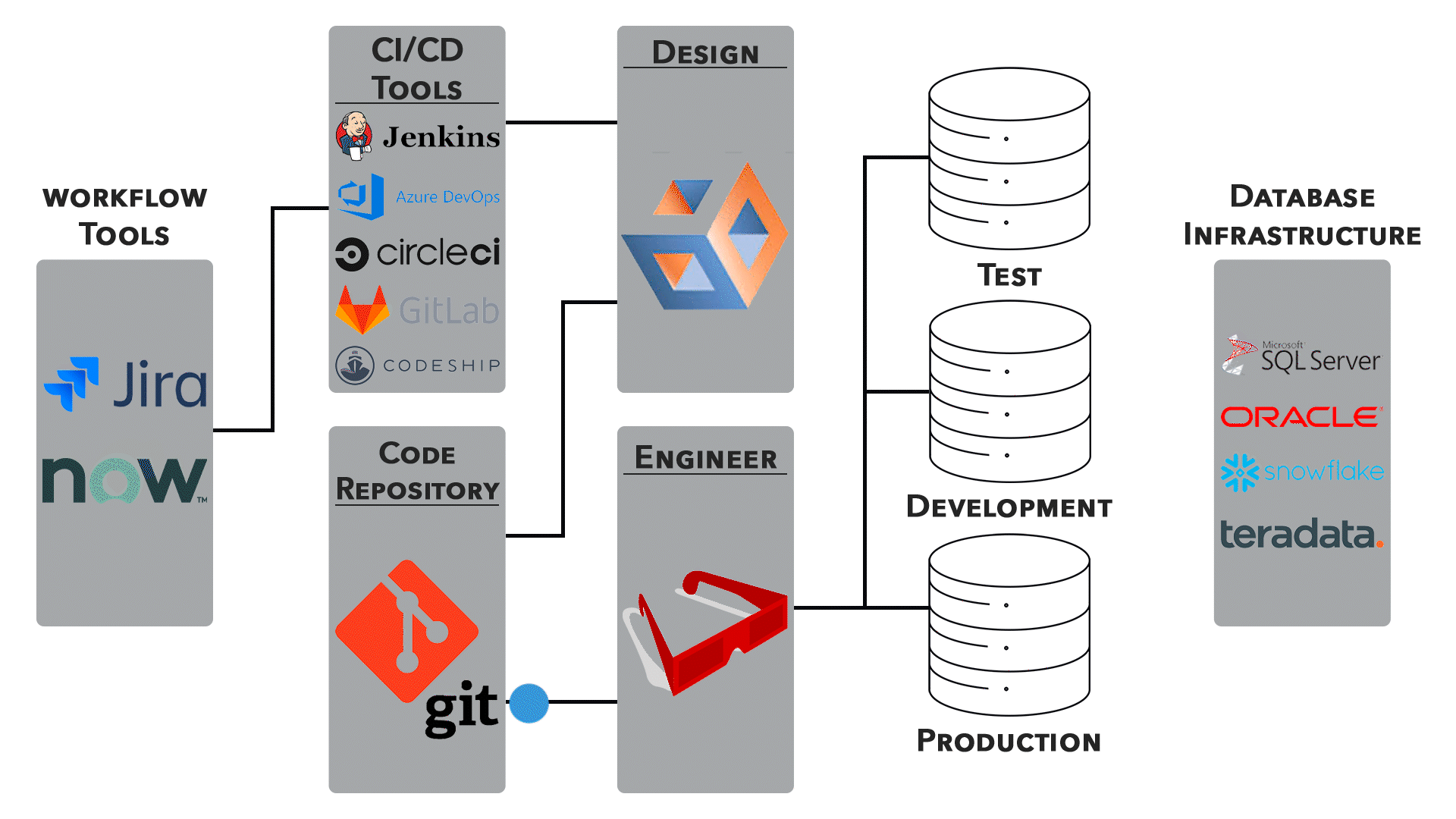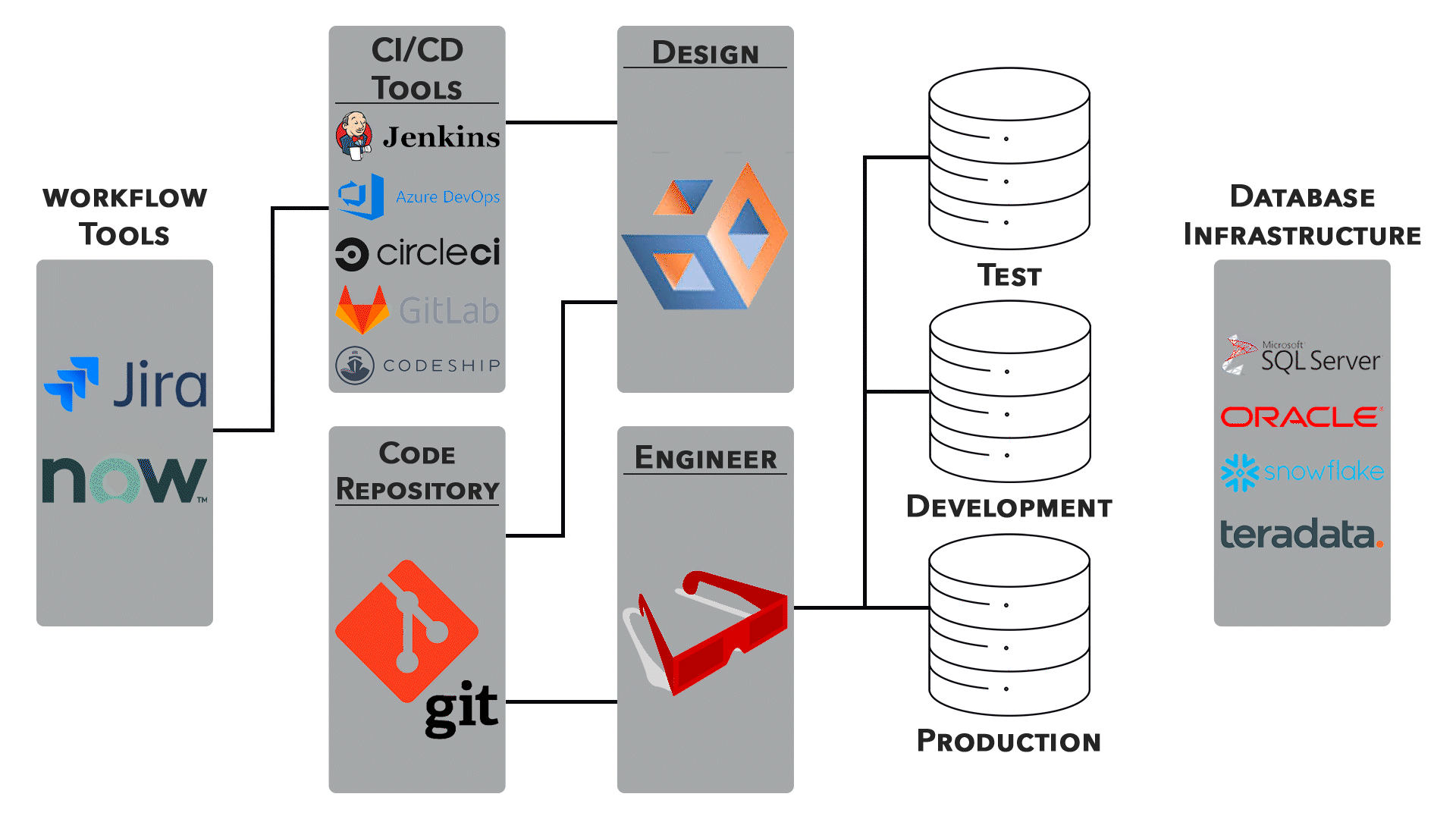
● Networking configurations are an integral part of CI/CD pipelines. Automated testing, deployment, and rollback processes require careful network orchestration.
● Collaboration between development and operations teams is essential for ensuring smooth transitions.
In the DevOps landscape, a solid understanding of networking fundamentals and protocols is indispensable. As DevOps teams strive for faster, more reliable software delivery, the seamless integration of networking principles becomes a cornerstone. By embracing these basics and adopting modern tools and practices, DevOps professionals can build a robust infrastructure that supports agile development and continuous improvement. Networking, when aligned with DevOps principles, becomes an enabler for innovation and efficiency in the ever-evolving world of software development
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mahesh Prasad Khamari directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mahesh Prasad Khamari
Mahesh Prasad Khamari
Hi there! I'm a passionate individual deeply fascinated by the world of cloud computing, DevOps practices, and AWS. My journey in this field is driven by an insatiable curiosity and an unyielding desire to explore and share knowledge with others. As a dedicated cloud enthusiast, I immerse myself in the ever-evolving landscape of cloud technologies, staying up-to-date with the latest trends and advancements. I find immense joy in leveraging the power of cloud platforms, especially AWS, to design scalable and robust solutions that meet modern-day business needs. DevOps has captured my heart with its holistic approach to software development and operations. I firmly believe in the power of collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement to streamline the software delivery process. With my strong foundation in DevOps principles, I strive to bridge the gap between development and operations teams, fostering a culture of efficiency and innovation. One of my greatest passions lies in sharing knowledge with the community. Through blogging and engaging with fellow tech enthusiasts, I aim to demystify complex concepts, provide practical insights, and inspire others to embark on their own cloud and DevOps journeys. I'm a firm believer in the philosophy that knowledge grows when shared, and together we can build a vibrant and supportive community. Join me on this exhilarating expedition as we unravel the intricacies of cloud technologies, dive deep into DevOps practices, and unleash the true potential of AWS. Together, let's explore, learn, and empower one another to thrive in this ever-evolving tech landscape.