Automating Infrastructure with Terraform and Ansible!
 Harish Narnaware
Harish NarnawareIntroduction
This documentation outlines the deployment and configuration process for setting up a basic infrastructure on AWS using Terraform and configuring it with Ansible. The infrastructure includes instances for Nginx, MariaDB, and an Ansible Controller.
you can find all your code in Github
HLD
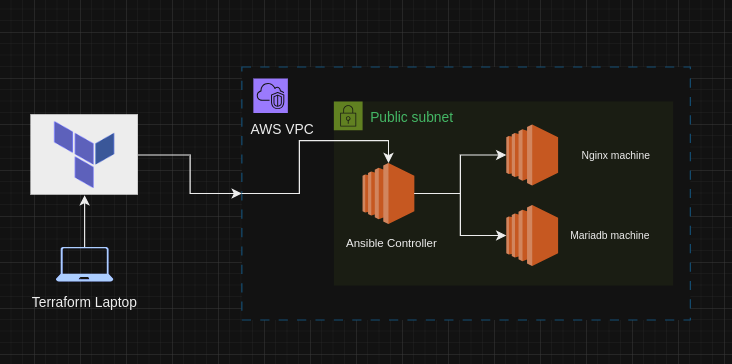
Ansible Script Overview
Ansible Playbook
---
- name: Install Nginx
hosts: all
remote_user: ubuntu
become: true
tasks:
- name: Update apt packages
apt:
update_cache: yes
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Start Nginx service
service:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yes
This ansible playbook script install nginx and run on server machine
Mariadb playbook
---
- name: Install MariaDB
hosts: all
remote_user: ubuntu
become: true
tasks:
- name: Update apt packages
apt:
update_cache: yes
- name: Install MariaDB Server
apt:
name: mariadb-server
state: present
- name: Start MariaDB Service
service:
name: mariadb
state: started
enabled: yes
This playbook install Mariadb server .
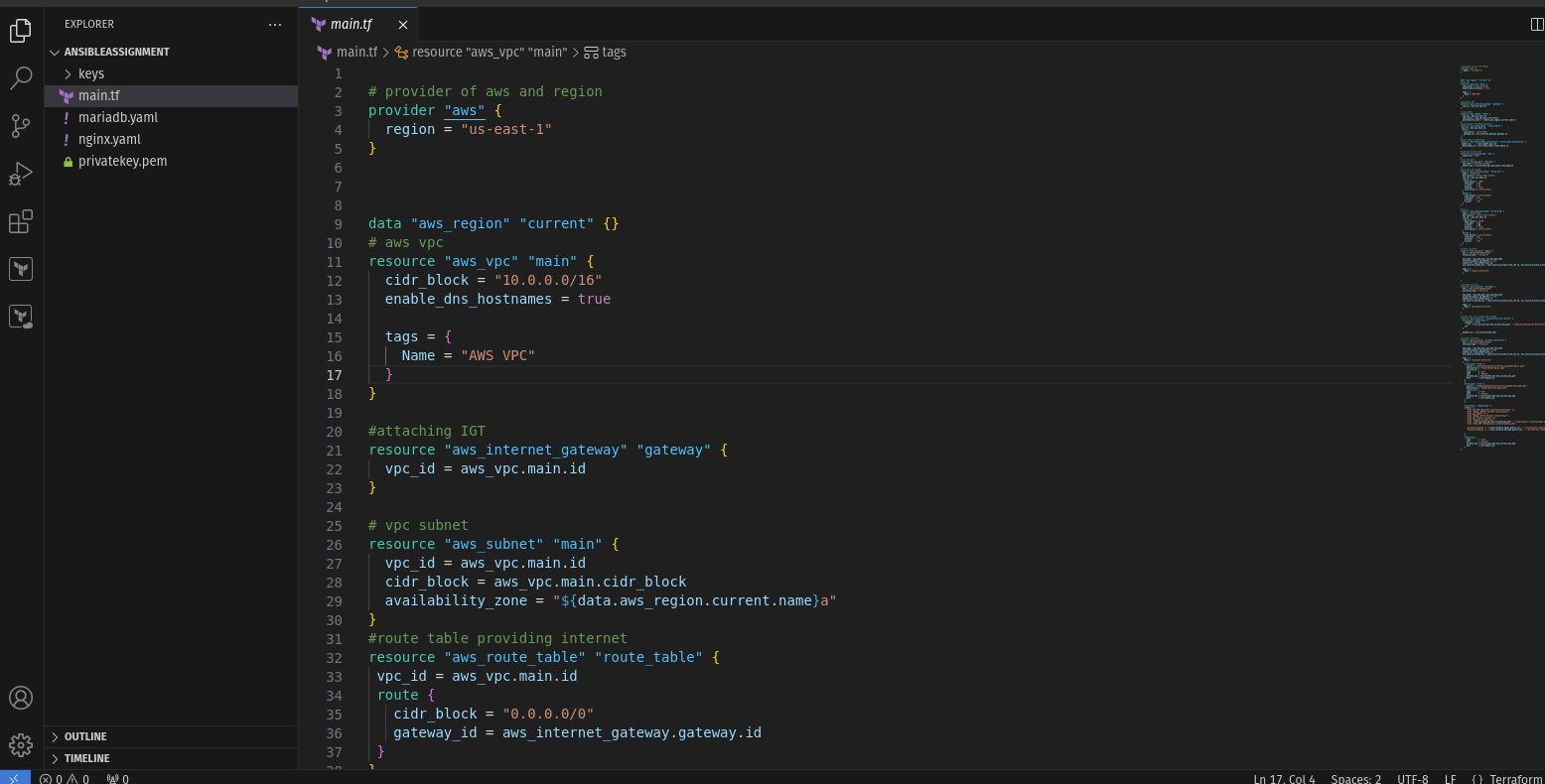
Terraform Script overview
AWS Provider Configuration:
provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" }Specifies that Terraform will be interacting with AWS services.
Sets the AWS region to "us-east-1".
AWS VPC Configuration:
resource "aws_vpc" "main" { cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16" enable_dns_hostnames = true tags = { Name = "AWS VPC" } }Creates an AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with the CIDR block "10.0.0.0/16".
Enables DNS hostnames for instances launched in the VPC.
Adds a tag with the name "AWS VPC" to the VPC.
AWS Internet Gateway Configuration:
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "gateway" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id }- Creates an AWS Internet Gateway and associates it with the VPC created in the previous step.
AWS Subnet Configuration:
resource "aws_subnet" "main" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = aws_vpc.main.cidr_block availability_zone = "${data.aws_region.current.name}a" }Creates a subnet within the VPC, using the VPC's CIDR block.
Associates the subnet with an availability zone based on the current AWS region.
AWS Route Table Configuration:
resource "aws_subnet" "main" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = aws_vpc.main.cidr_block availability_zone = "${data.aws_region.current.name}a" }Creates a route table and associates it with the VPC.
Adds a default route (0.0.0.0/0) pointing to the Internet Gateway for internet access.
AWS Route Table Association Configuration:
resource "aws_route_table_association" "route_table_association" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.main.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.route_table.id }- Associates the previously created route table with the subnet, allowing instances in the subnet to use the specified routes.
TLS Private Key Generation:
resource "tls_private_key" "key" { algorithm = "RSA" }- Generates an RSA private key using Terraform's
tls_private_keyresource.
- Generates an RSA private key using Terraform's
AWS Key Pair Configuration:
resource "aws_key_pair" "aws_key" { key_name = "ansible-ssh-key" public_key = tls_private_key.key.public_key_openssh }Creates an AWS Key Pair named "ansible-ssh-key" for use with SSH access to instances.
Uses the public key generated in the previous step.
AWS Security Group for SSH:
resource "aws_security_group" "allow_ssh" { name = "allow_ssh" description = "Allow SSH traffic" vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id ingress { description = "SSH" from_port = 22 to_port = 22 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } egress { cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] from_port = 0 protocol = "-1" to_port = 0 } }- Creates a security group named "allow_ssh" to allow SSH traffic on port 22 from any source.
AWS Security Group for HTTP:
resource "aws_security_group" "allow_http" { name = "allow_http" description = "Allow HTTP traffic" vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id ingress { description = "HTTP" from_port = 80 to_port = 80 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } egress { cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] from_port = 0 protocol = "-1" to_port = 0 } }- Creates a security group named "allow_http" to allow HTTP traffic on port 80 from any source.
AWS Instances for Nginx and MariaDB:
NGINX EC2 instance
resource "aws_instance" "nginx" { ami = "ami-0c7217cdde317cfec" instance_type = "t2.micro" key_name = aws_key_pair.aws_key.key_name associate_public_ip_address = true subnet_id = aws_subnet.main.id vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.allow_ssh.id, aws_security_group.allow_http.id] tags = { Name = "nginx-controller" } }Mariadb Ec2 instance
# mariadb instance resource "aws_instance" "mariadb" { ami = "ami-0c7217cdde317cfec" instance_type = "t2.micro" key_name = aws_key_pair.aws_key.key_name associate_public_ip_address = true subnet_id = aws_subnet.main.id vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.allow_ssh.id, aws_security_group.allow_http.id] tags = { Name = "mariadb-controller" } }- Launches AWS instances for Nginx and MariaDB with specified AMIs, instance types, key pairs, and security groups.
Local Execution for Private Key Storage:
# local exec for private key storage resource "null_resource" "save_private_key_locally" { provisioner "local-exec" { command = <<-EOT echo '${tls_private_key.key.private_key_pem}' > /home/pc/Desktop/terraform/assignment/keys/ansible.pem EOT } depends_on = [tls_private_key.key] }- Uses a local-exec provisioner to save the private key locally on the machine.
AWS Instance for Ansible Controller:
resource "aws_instance" "ansible_controller" { ami = "ami-0c7217cdde317cfec" instance_type = "t2.micro" key_name = aws_key_pair.aws_key.key_name associate_public_ip_address = true subnet_id = aws_subnet.main.id vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.allow_ssh.id, aws_security_group.allow_http.id] tags = { Name = "ansible-controller" } provisioner "file" { # copying nginx yaml file source = "/home/pc/Desktop/terraform/assignment/nginx.yaml" destination = "/home/ubuntu/nginx.yaml" connection { type = "ssh" user = "ubuntu" private_key = tls_private_key.key.private_key_pem host = self.public_ip } } provisioner "file" { # copying mariadb yaml file source = "/home/pc/Desktop/terraform/assignment/mariadb.yaml" destination = "/home/ubuntu/mariadb.yaml" connection { type = "ssh" user = "ubuntu" private_key = tls_private_key.key.private_key_pem host = self.public_ip } } provisioner "remote-exec" { inline = [ "sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible -y", "echo 'Debug: Before Ansible installation'", "sudo apt update -y ", "echo 'Debug: After Ansible installation'", "sudo apt install ansible -y", "echo 'Copying private key'", "echo '${tls_private_key.key.private_key_pem}' > /home/ubuntu/.ssh/ansiblekey.pem", "sudo chmod 600 /home/ubuntu/.ssh/ansiblekey.pem", "ansible-playbook -i \"${aws_instance.nginx.public_ip},\" --private-key /home/ubuntu/.ssh/ansiblekey.pem --ssh-common-args=\"-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no\" /home/ubuntu/nginx.yaml", "ansible-playbook -i \"${aws_instance.mariadb.public_ip},\" --private-key /home/ubuntu/.ssh/ansiblekey.pem --ssh-common-args=\"-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no\" /home/ubuntu/mariadb.yaml", ] } connection { type = "ssh" user = "ubuntu" private_key = tls_private_key.key.private_key_pem host = self.public_ip } }- Launches an AWS instance for the Ansible Controller with specified configurations.
The subsequent provisioners (file and remote-exec) copy configuration files and execute Ansible commands on the Ansible Controller instance.
File path
before using this project you have to change to change private key file path , nginx file path , mariadb file path.
Command Line
Make sure you have terraform installed in your computer and have AWS configure.
terraform init
Apply terraform files
terraform apply
you will see three instance
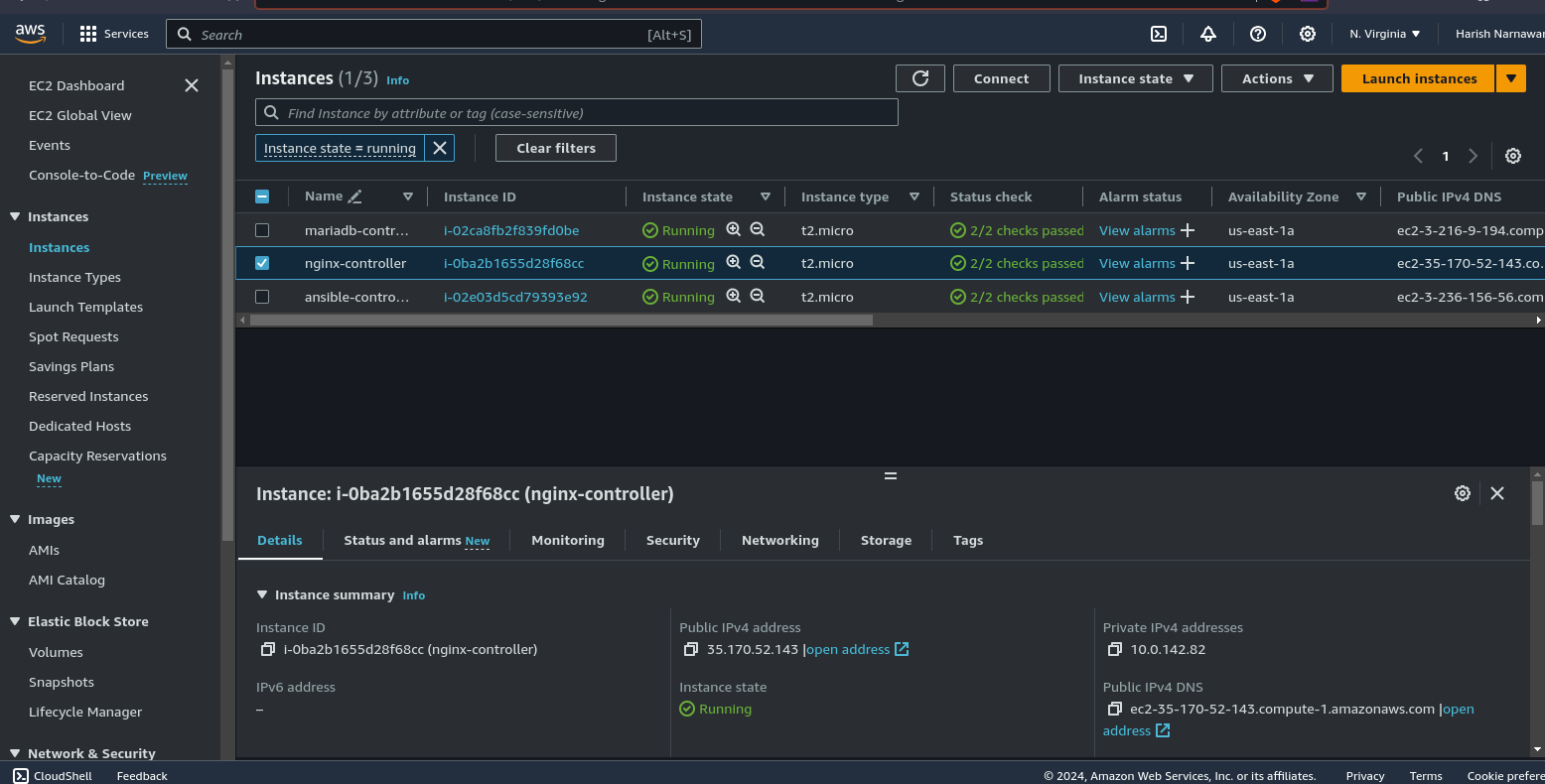
Nginx Instance
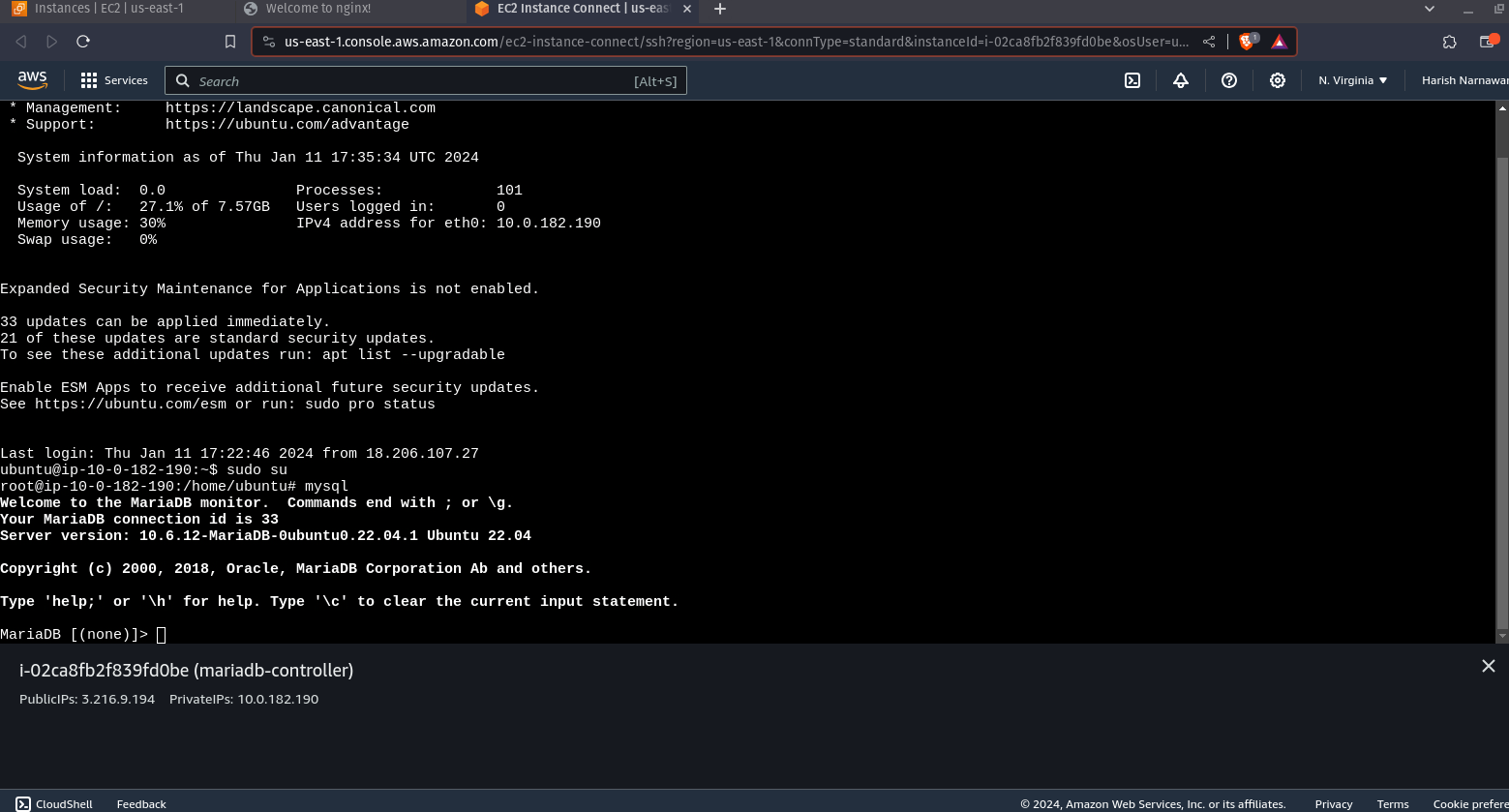
Mariadb Instance
Conclusion
with one click the all infrastructure is created with configuration.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Harish Narnaware directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Harish Narnaware
Harish Narnaware
I am here for giving wonderful knowledge to society