Advanced End-to-End DevSecOps Kubernetes Three-Tier Project using AWS EKS, ArgoCD, Prometheus, Grafana, and Jenkins
 Aman Pathak
Aman PathakTable of contents
- Project Introduction:
- Prerequisites:
- Step 1: We need to create an IAM user and generate the AWS Access key
- Step 2: We will install Terraform & AWS CLI to deploy our Jenkins Server(EC2) on AWS.
- Step 3: Deploy the Jenkins Server(EC2) using Terraform
- Step 4: Configure the Jenkins
- Step 5: We will deploy the EKS Cluster using eksctl commands
- Step 6: Now, we will configure the Load Balancer on our EKS because our application will have an ingress controller.
- Step 7: We need to create Amazon ECR Private Repositories for both Tiers (Frontend & Backend)
- Step 8: Install & Configure ArgoCD
- Step 9: Now, we have to configure Sonarqube for our DevSecOps Pipeline
- Step 10: Install the required plugins and configure the plugins to deploy our Three-Tier Application
- Setup 11: We will set up the Monitoring for our EKS Cluster. We can monitor the Cluster Specifications and other necessary things.
- Step 11: We will deploy our Three-Tier Application using ArgoCD.
- Conclusion:
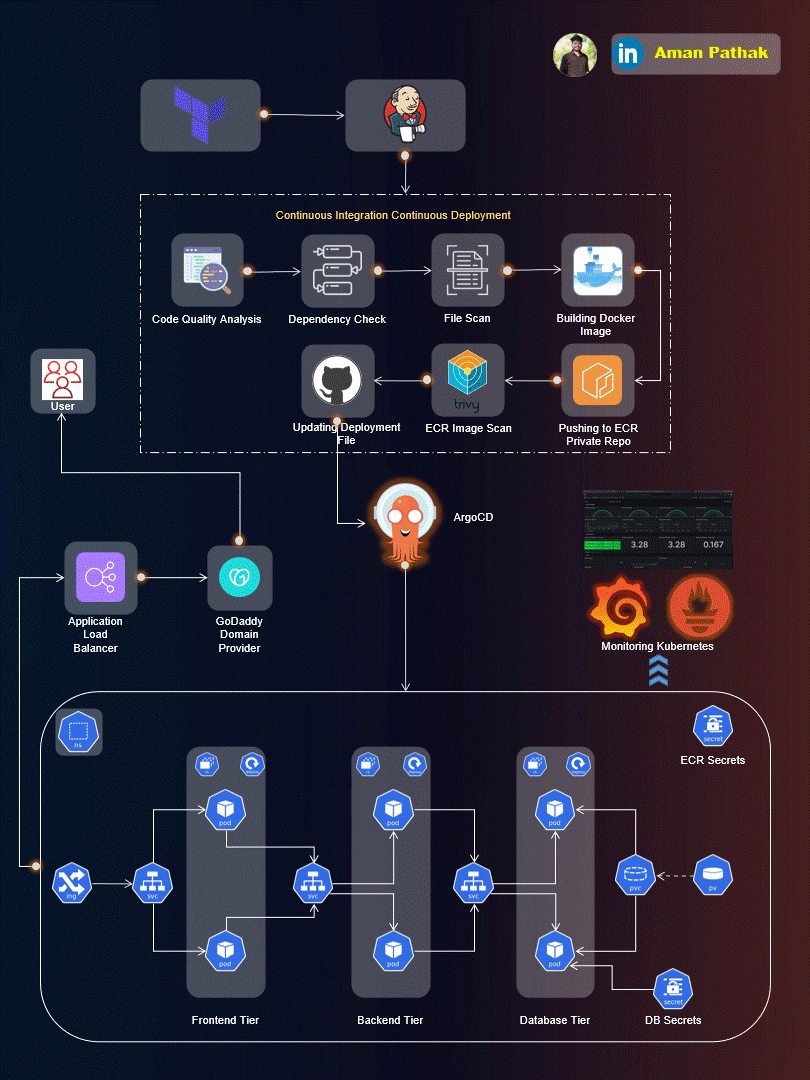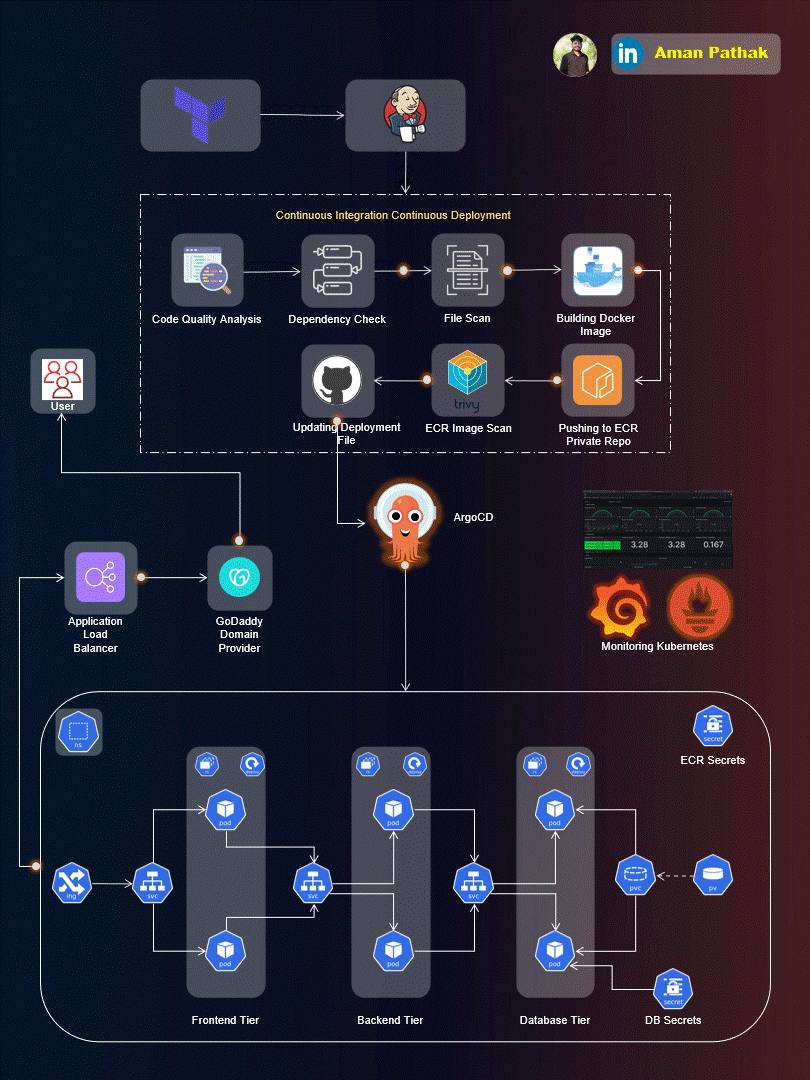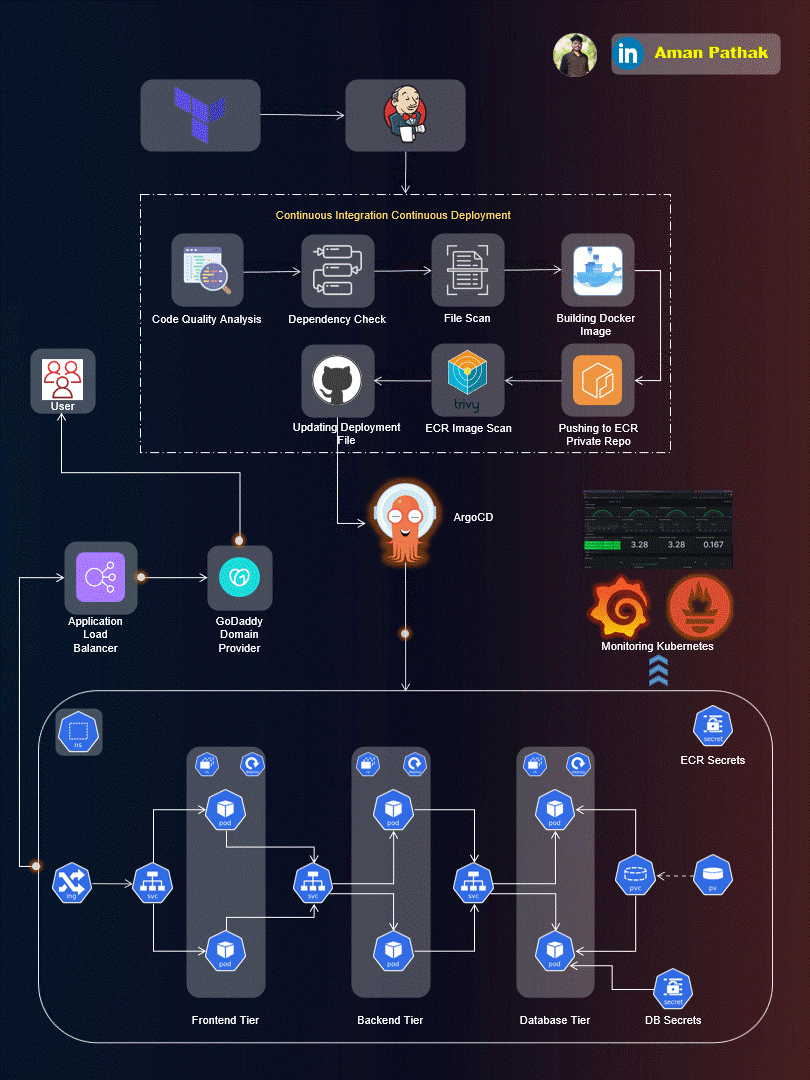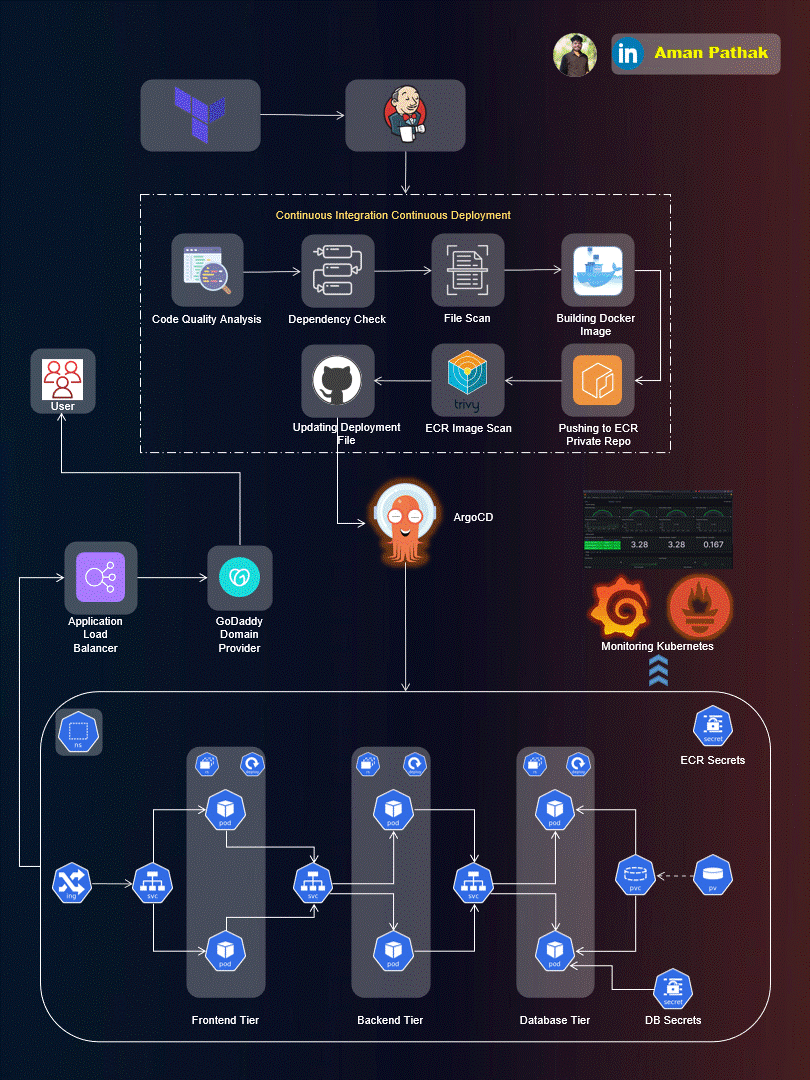
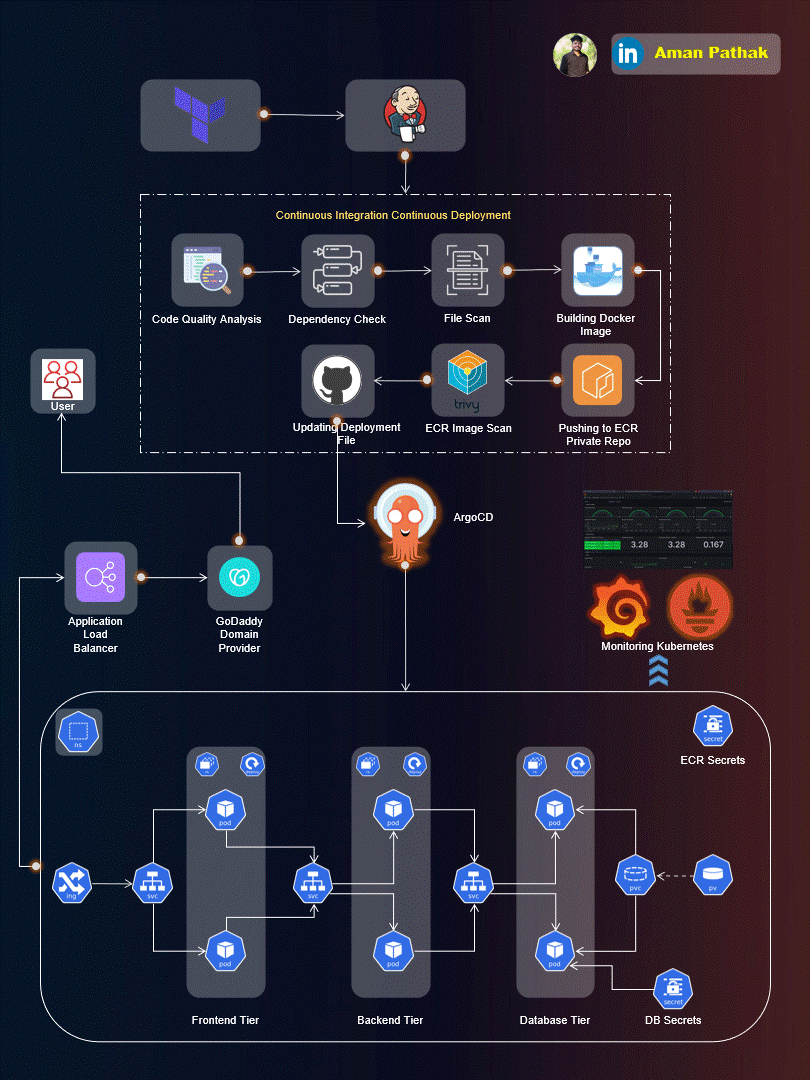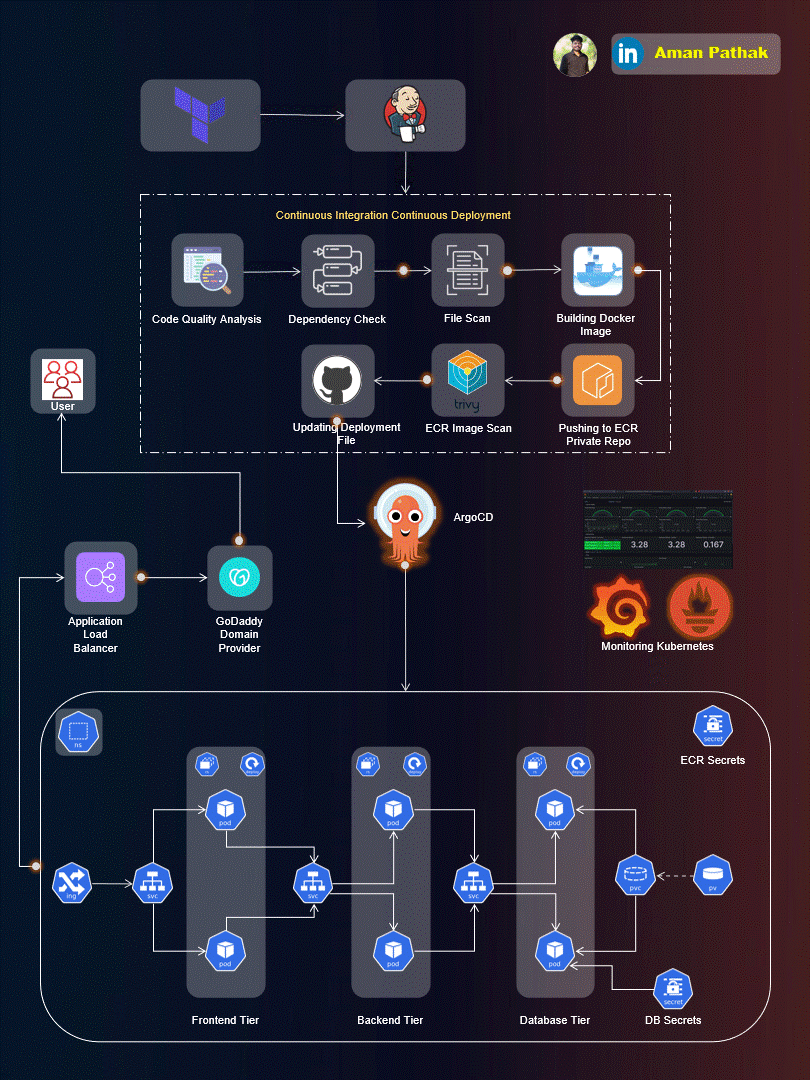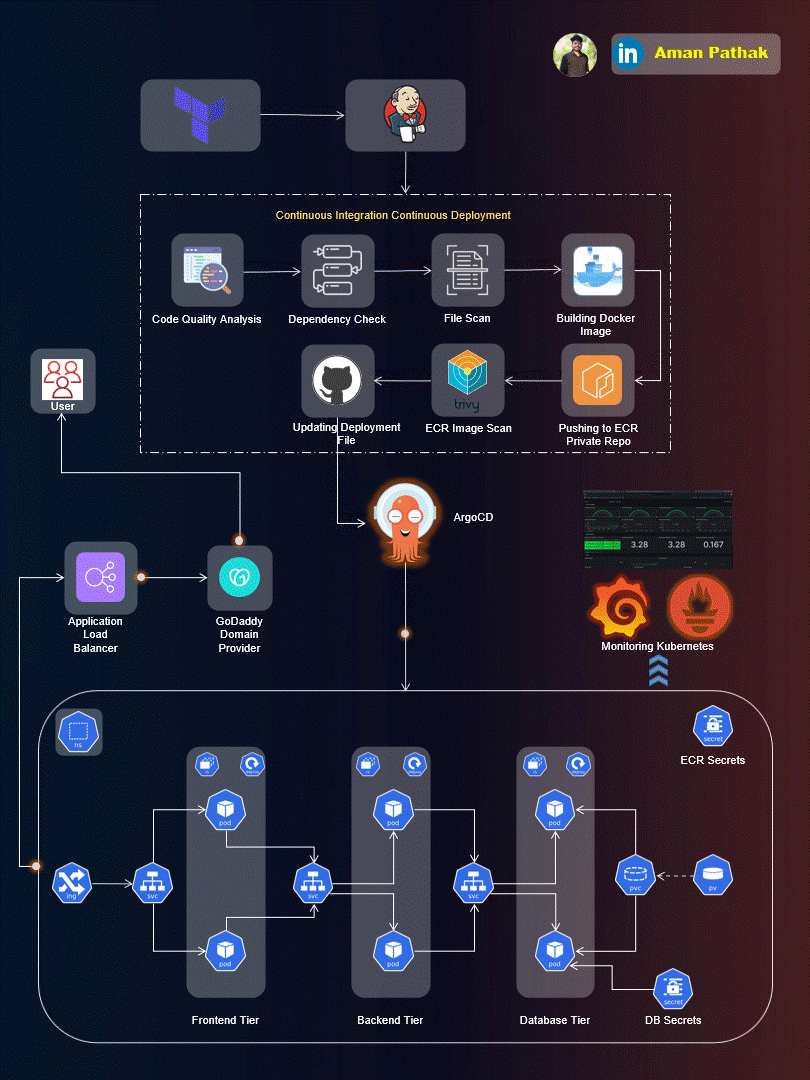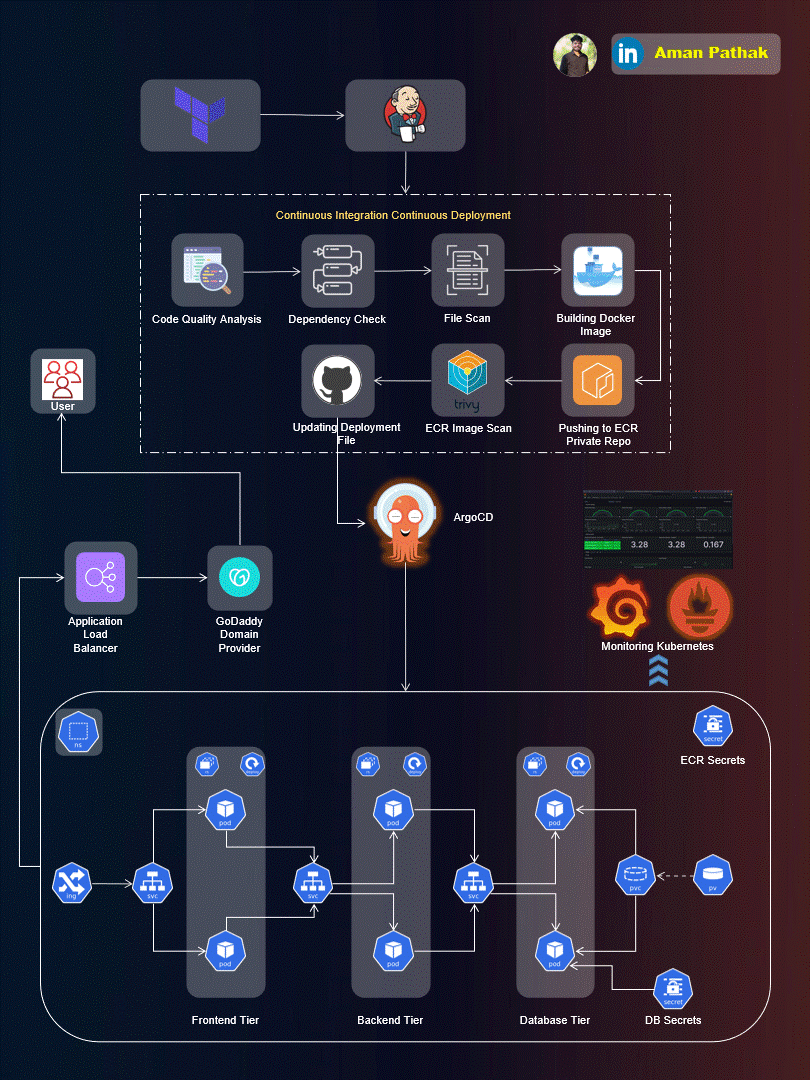
Project Introduction:
Welcome to the End-to-End DevSecOps Kubernetes Project guide! In this comprehensive project, we will walk through the process of setting up a robust Three-Tier architecture on AWS using Kubernetes, DevOps best practices, and security measures. This project aims to provide hands-on experience in deploying, securing, and monitoring a scalable application environment.
Project Overview:
In this project, we will cover the following key aspects:
IAM User Setup: Create an IAM user on AWS with the necessary permissions to facilitate deployment and management activities.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Use Terraform and AWS CLI to set up the Jenkins server (EC2 instance) on AWS.
Jenkins Server Configuration: Install and configure essential tools on the Jenkins server, including Jenkins itself, Docker, Sonarqube, Terraform, Kubectl, AWS CLI, and Trivy.
EKS Cluster Deployment: Utilize eksctl commands to create an Amazon EKS cluster, a managed Kubernetes service on AWS.
Load Balancer Configuration: Configure AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) for the EKS cluster.
Amazon ECR Repositories: Create private repositories for both frontend and backend Docker images on Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR).
ArgoCD Installation: Install and set up ArgoCD for continuous delivery and GitOps.
Sonarqube Integration: Integrate Sonarqube for code quality analysis in the DevSecOps pipeline.
Jenkins Pipelines: Create Jenkins pipelines for deploying backend and frontend code to the EKS cluster.
Monitoring Setup: Implement monitoring for the EKS cluster using Helm, Prometheus, and Grafana.
ArgoCD Application Deployment: Use ArgoCD to deploy the Three-Tier application, including database, backend, frontend, and ingress components.
DNS Configuration: Configure DNS settings to make the application accessible via custom subdomains.
Data Persistence: Implement persistent volume and persistent volume claims for database pods to ensure data persistence.
Conclusion and Monitoring: Conclude the project by summarizing key achievements and monitoring the EKS cluster's performance using Grafana.
Prerequisites:
Before starting the project, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
An AWS account with the necessary permissions to create resources.
Terraform and AWS CLI installed on your local machine.
Basic familiarity with Kubernetes, Docker, Jenkins, and DevOps principles.
Step 1: We need to create an IAM user and generate the AWS Access key
Create a new IAM User on AWS and give it to the AdministratorAccess for the testing purposes (not recommended for your Organization's Projects)
Go to the AWS IAM Service and click on Users.
Click on Create user
Provide the name to your user and click on Next.
Select the Attach policies directly option and search for AdministratorAccess then select it.
Click on the Next.
Click on Create user
Now, Select your created user then click on Security credentials and generate access key by clicking on Create access key.
Select the Command Line Interface (CLI) then select the checkmark for the confirmation and click on Next.
Provide the Description and click on the Create access key.
Here, you will see that you got the credentials and also you can download the csv file for the future.
Step 2: We will install Terraform & AWS CLI to deploy our Jenkins Server(EC2) on AWS.
Install & Configure Terraform and AWS CLI on your local machine to create Jenkins Server on AWS Cloud
Terraform Installation Script
wget -O- https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hashicorp.list
sudo apt update
sudo apt install terraform -y
AWSCLI Installation Script
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
sudo apt install unzip -y
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install
Now, Configure both the tools
Configure Terraform
Edit the file /etc/environment using the below command add the highlighted lines and add your keys at the blur space.
sudo vim /etc/environment
After doing the changes, restart your machine to reflect the changes of your environment variables.
Configure AWS CLI
Run the below command, and add your keys
aws configure
Step 3: Deploy the Jenkins Server(EC2) using Terraform
Clone the Git repository- https://github.com/AmanPathak-DevOps/End-to-End-Kubernetes-Three-Tier-DevSecOps-Project/tree/master/Jenkins-Server-TF
Navigate to the Jenkins-Server-TF
Do some modifications to the backend.tf file such as changing the bucket name and dynamodb table(make sure you have created both manually on AWS Cloud).
Now, you have to replace the Pem File name as you have some other name of your Pem file. To provide the Pem file name that is already created on AWS
Initialize the backend by running the below command
terraform init
Run the below command to check the syntax error
terraform validate
Run the below command to get the blueprint of what kind of AWS services will be created.
terraform plan -var-file=variables.tfvars
Now, run the below command to create the infrastructure on AWS Cloud which will take 3 to 4 minutes maximum
terraform apply -var-file=variables.tfvars --auto-approve
Now, connect to your Jenkins-Server by clicking on Connect.
Copy the ssh command and paste it on your local machine.
Step 4: Configure the Jenkins
Now, we logged into our Jenkins server.
We have installed some services such as Jenkins, Docker, Sonarqube, Terraform, Kubectl, AWS CLI, and Trivy.
Let’s validate whether all our installed or not.
jenkins --version
docker --version
docker ps
terraform --version
kubectl version
aws --version
trivy --version
eksctl --version
Now, we have to configure Jenkins. So, copy the public IP of your Jenkins Server and paste it on your favorite browser with an 8080 port.
Click on Install suggested plugins
The plugins will be installed
After installing the plugins, continue as admin
Click on Save and Finish
Click on Start using Jenkins
The Jenkins Dashboard will look like the below snippet
Step 5: We will deploy the EKS Cluster using eksctl commands
Now, go back to your Jenkins Server terminal and configure the AWS.
Go to Manage Jenkins
Click on Plugins
Select the Available plugins, and install the following plugins and click on Install
AWS Credentials
Pipeline: AWS Steps
Once, both the plugins are installed, restart your Jenkins service by checking the Restart Jenkins option.
Login to your Jenkins Server Again
Now, we have to set our AWS credentials on Jenkins
Go to Manage Plugins and click on Credentials
Click on global.
Select AWS Credentials as Kind and add the ID same as shown in the below snippet except your AWS Access Key & Secret Access key and click on Create.
The Credentials will look like the below snippet.
Now, We need to add GitHub credentials as well because currently, my repository is Private.
This thing, I am performing this because in Industry Projects your repository will be private.
So, add the username and personal access token of your GitHub account.
Both credentials will look like this.
Create an eks cluster using the below commands.
eksctl create cluster --name Three-Tier-K8s-EKS-Cluster --region us-east-1 --node-type t2.medium --nodes-min 2 --nodes-max 2
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region us-east-1 --name Three-Tier-K8s-EKS-Cluster
Once your cluster is created, you can validate whether your nodes are ready or not by the below command
kubectl get nodes
Step 6: Now, we will configure the Load Balancer on our EKS because our application will have an ingress controller.
Download the policy for LoadBalancer prerequisite.
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-load-balancer-controller/v2.5.4/docs/install/iam_policy.json
Create the IAM policy using the below command
aws iam create-policy --policy-name AWSLoadBalancerControllerIAMPolicy --policy-document file://iam_policy.json
Create OIDC Provider
eksctl utils associate-iam-oidc-provider --region=us-east-1 --cluster=Three-Tier-K8s-EKS-Cluster --approve
Create Service Account
eksctl create iamserviceaccount --cluster=Three-Tier-K8s-EKS-Cluster --namespace=kube-system --name=aws-load-balancer-controller --role-name AmazonEKSLoadBalancerControllerRole --attach-policy-arn=arn:aws:iam::407622020962:policy/AWSLoadBalancerControllerIAMPolicy --approve --region=us-east-1
After 2 minutes, run the command below to check whether your pods are running or not.
kubectl get deployment -n kube-system aws-load-balancer
Step 7: We need to create Amazon ECR Private Repositories for both Tiers (Frontend & Backend)
Click on Create repository
Select the Private option, provide the repository, and click on Save.
Do the same for the backend repository and click on Save
Now, we have set up with our both ECR Private Repository and
Now, we need to configure ECR locally because we have to upload our images to Amazon ECR.
Copy the 1st command for login
Now, run the copied command on your Jenkins Server.
Step 8: Install & Configure ArgoCD
We will be deploying our application on a three-tier namespace. To do that, we will create a three-tier namespace on EKS
kubectl create namespace three-tier
As you know, Our two ECR repositories are private. So, when we try to push images to the ECR Repos it will give us the error Imagepullerror.
To get rid of this error, we will create a secret for our ECR Repo by the below command and then, we will add this secret to the deployment file.
Note: The Secrets are coming from the .docker/config.json file which is created while login the ECR in the earlier steps
kubectl create secret generic ecr-registry-secret \
--from-file=.dockerconfigjson=${HOME}/.docker/config.json \
--type=kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson --namespace three-tier
kubectl get secrets -n three-tier
Now, we will install argoCD.
To do that, create a separate namespace for it and apply the argocd configuration for installation.
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/v2.4.7/manifests/install.yaml
All pods must be running, to validate run the below command
kubectl get pods -n argocd
Now, expose the argoCD server as LoadBalancer using the below command
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}'
You can validate whether the Load Balancer is created or not by going to the AWS Console
To access the argoCD, copy the LoadBalancer DNS and hit on your favorite browser.
You will get a warning like the below snippet.
Click on Advanced.
Click on the below link which appears under Hide advanced
Now, we need to get the password for our argoCD server to perform the deployment.
To do that, we have a pre-requisite which is jq. Install it by the command below.
sudo apt install jq -y
export ARGOCD_SERVER=`kubectl get svc argocd-server -n argocd -o json | jq --raw-output '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname'`
export ARGO_PWD=`kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d`
echo $ARGO_PWD
Enter the username and password in argoCD and click on SIGN IN.
Here is our ArgoCD Dashboard.
Step 9: Now, we have to configure Sonarqube for our DevSecOps Pipeline
To do that, copy your Jenkins Server public IP and paste it on your favorite browser with a 9000 port
The username and password will be admin
Click on Log In.
Update the password
Click on Administration then Security, and select Users
Click on Update tokens
Click on Generate
Copy the token keep it somewhere safe and click on Done.
Now, we have to configure webhooks for quality checks.
Click on Administration then, Configuration and select Webhooks
Click on Create
Provide the name of your project and in the URL, provide the Jenkins server public IP with port 8080, add sonarqube-webhook in suffix, and click on Create.
http://<jenkins-server-public-ip>:8080/sonarqube-webhook/
Here, you can see the webhook.
Now, we have to create a Project for frontend code.
Click on Manually.
Provide the display name to your Project and click on Setup
Click on Locally.
Select the Use existing token and click on Continue.
Select Other and Linux as OS.
After performing the above steps, you will get the command which you can see in the below snippet.
Now, use the command in the Jenkins Frontend Pipeline where Code Quality Analysis will be performed.
Now, we have to create a Project for backend code.
Click on Create Project.
Provide the name of your project name and click on Set up.
Click on Locally.
Select the Use existing token and click on Continue.
Select Other and Linux as OS.
After performing the above steps, you will get the command which you can see in the below snippet.
Now, use the command in the Jenkins Backend Pipeline where Code Quality Analysis will be performed.
Now, we have to store the sonar credentials.
Go to Dashboard -> Manage Jenkins -> Credentials
Select the kind as Secret text, paste your token in Secret and keep other things as it is.
Click on Create
Now, we have to store the GitHub Personal access token to push the deployment file which will be modified in the pipeline itself for the ECR image.
Add GitHub credentials
Select the kind as Secret text and paste your GitHub Personal access token(not password) in Secret and keep other things as it is.
Click on Create
Note: If you haven’t generated your token then, you have it generated first then paste it into the Jenkins
Now, according to our Pipeline, we need to add an Account ID in the Jenkins credentials because of the ECR repo URI.
Select the kind as Secret text, paste your AWS Account ID in Secret and keep other things as it is.
Click on Create
Now, we need to provide our ECR image name for frontend which is frontend only.
Select the kind as Secret text paste your frontend repo name in Secret and keep other things as it is.
Click on Create
Now, we need to provide our ECR image name for the backend which is the backend only.
Select the kind as Secret text, paste your backend repo name in Secret and keep other things as it is.
Click on Create
Final Snippet of all Credentials that we needed to implement this project.
Step 10: Install the required plugins and configure the plugins to deploy our Three-Tier Application
Install the following plugins by going to Dashboard -> Manage Jenkins -> Plugins -> Available Plugins
Docker
Docker Commons
Docker Pipeline
Docker API
docker-build-step
Eclipse Temurin installer
NodeJS
OWASP Dependency-Check
SonarQube Scanner
Now, we have to configure the installed plugins.
Go to Dashboard -> Manage Jenkins -> Tools
We are configuring jdk
Search for jdk and provide the configuration like the below snippet.
Now, we will configure the sonarqube-scanner
Search for the sonarqube scanner and provide the configuration like the below snippet.
Now, we will configure nodejs
Search for node and provide the configuration like the below snippet.
Now, we will configure the OWASP Dependency check
Search for Dependency-Check and provide the configuration like the below snippet.
Now, we will configure the docker
Search for docker and provide the configuration like the below snippet.
Now, we have to set the path for Sonarqube in Jenkins
Go to Dashboard -> Manage Jenkins -> System
Search for SonarQube installations
Provide the name as it is, then in the Server URL copy the sonarqube public IP (same as Jenkins) with port 9000 and select the sonar token that we have added recently, and click on Apply & Save.
Now, we are ready to create our Jenkins Pipeline to deploy our Backend Code.
Go to Jenkins Dashboard
Click on New Item
Provide the name of your Pipeline and click on OK.
This is the Jenkins file to deploy the Backend Code on EKS.
Copy and paste it into the Jenkins
Click Apply & Save.
Now, click on the build.
Our pipeline was successful after a few common mistakes.
Note: Do the changes in the Pipeline according to your project.
Now, we are ready to create our Jenkins Pipeline to deploy our Frontend Code.
Go to Jenkins Dashboard
Click on New Item
Provide the name of your Pipeline and click on OK.
This is the Jenkins file to deploy the Frontend Code on EKS.
Copy and paste it into the Jenkins
Click Apply & Save.
Now, click on the build.
Our pipeline was successful after a few common mistakes.
Note: Do the changes in the Pipeline according to your project.
Setup 11: We will set up the Monitoring for our EKS Cluster. We can monitor the Cluster Specifications and other necessary things.
We will achieve the monitoring using Helm
Add the prometheus repo by using the below command
helm repo add stable https://charts.helm.sh/stable
Install the prometheus
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
Now, check the service by the below command
kubectl get svc
Now, we need to access our Prometheus and Grafana consoles from outside of the cluster.
For that, we need to change the Service type from ClusterType to LoadBalancer
Edit the stable-kube-prometheus-sta-prometheus service
kubectl edit svc stable-kube-prometheus-sta-prometheus
Modification in the 48th line from ClusterType to LoadBalancer
Edit the stable-grafana service
kubectl edit svc stable-grafana
Modification in the 39th line from ClusterType to LoadBalancer
Now, if you list again the service then, you will see the LoadBalancers DNS names
kubectl get svc
You can also validate from your console.
Now, access your Prometheus Dashboard
Paste the <Prometheus-LB-DNS>:9090 in your favorite browser and you will see like this
Click on Status and select Target.
You will see a lot of Targets
Now, access your Grafana Dashboard
Copy the ALB DNS of Grafana and paste it into your favorite browser.
The username will be admin and the password will be prom-operator for your Grafana LogIn.
Now, click on Data Source
Select Prometheus
In the Connection, paste your <Prometheus-LB-DNS>:9090.
If the URL is correct, then you will see a green notification/
Click on Save & test.
Now, we will create a dashboard to visualize our Kubernetes Cluster Logs.
Click on Dashboard.
Once you click on Dashboard. You will see a lot of Kubernetes components monitoring.
Let’s try to import a type of Kubernetes Dashboard.
Click on New and select Import
Provide 6417 ID and click on Load
Note: 6417 is a unique ID from Grafana which is used to Monitor and visualize Kubernetes Data
Select the data source that you have created earlier and click on Import.
Here, you go.
You can view your Kubernetes Cluster Data.
Feel free to explore the other details of the Kubernetes Cluster.
Step 11: We will deploy our Three-Tier Application using ArgoCD.
As our repository is private. So, we need to configure the Private Repository in ArgoCD.
Click on Settings and select Repositories
Click on CONNECT REPO USING HTTPS
Now, provide the repository name where your Manifests files are present.
Provide the username and GitHub Personal Access token and click on CONNECT.
If your Connection Status is Successful it means repository connected successfully.
Now, we will create our first application which will be a database.
Click on CREATE APPLICATION.
Provide the details as it is provided in the below snippet and scroll down.
Select the same repository that you configured in the earlier step.
In the Path, provide the location where your Manifest files are presented and provide other things as shown in the below screenshot.
Click on CREATE.
While your database Application is starting to deploy, We will create an application for the backend.
Provide the details as it is provided in the below snippet and scroll down.
Select the same repository that you configured in the earlier step.
In the Path, provide the location where your Manifest files are presented and provide other things as shown in the below screenshot.
Click on CREATE.
While your backend Application is starting to deploy, We will create an application for the frontend.
Provide the details as it is provided in the below snippet and scroll down.
Select the same repository that you configured in the earlier step.
In the Path, provide the location where your Manifest files are presented and provide other things as shown in the below screenshot.
Click on CREATE.
While your frontend Application is starting to deploy, We will create an application for the ingress.
Provide the details as it is provided in the below snippet and scroll down.
Select the same repository that you configured in the earlier step.
In the Path, provide the location where your Manifest files are presented and provide other things as shown in the below screenshot.
Click on CREATE.
Once your Ingress application is deployed. It will create an Application Load Balancer
You can check out the load balancer named with k8s-three.
Now, Copy the ALB-DNS and go to your Domain Provider in my case porkbun is the domain provider.
Go to DNS and add a CNAME type with hostname backend then add your ALB in the Answer and click on Save
Note: I have created a subdomain backend.amanpathakdevops.study
You can see all 4 application deployments in the below snippet.
Now, hit your subdomain after 2 to 3 minutes in your browser to see the magic.
You can play with the application by adding the records.
You can play with the application by deleting the records.
Now, you can see your Grafana Dashboard to view the EKS data such as pods, namespace, deployments, etc.
If you want to monitor the three-tier namespace.
In the namespace, replace three-tier with another namespace.
You will see the deployments that are done by ArgoCD
This is the Ingress Application Deployment in ArgoCD
This is the Frontend Application Deployment in ArgoCD
This is the Backend Application Deployment in ArgoCD
This is the Database Application Deployment in ArgoCD
If you observe, we have configured the Persistent Volume & Persistent Volume Claim. So, if the pods get deleted then, the data won’t be lost. The Data will be stored on the host machine.
To validate it, delete both Database pods.
Now, the new pods will be started.
And Your Application won’t lose a single piece of data.
Conclusion:
In this comprehensive DevSecOps Kubernetes project, we successfully:
Established IAM user and Terraform for AWS setup.
Deployed Jenkins on AWS, configured tools, and integrated it with Sonarqube.
Set up an EKS cluster, configured a Load Balancer, and established private ECR repositories.
Implemented monitoring with Helm, Prometheus, and Grafana.
Installed and configured ArgoCD for GitOps practices.
Created Jenkins pipelines for CI/CD, deploying a Three-Tier application.
Ensured data persistence with persistent volumes and claims.
Stay connected on LinkedIn: LinkedIn Profile
Stay up-to-date with GitHub: GitHub Profile
Feel free to reach out to me, if you have any other queries.
Happy Learning
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aman Pathak directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aman Pathak
Aman Pathak
Hi, This is Aman Pathak a DevOps Engineer passionate about emerging technologies. I am excited to apply my knowledge and skills to help the organization deliver the best quality software products. 𝗟𝗲𝘁'𝘀 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝗻𝗲𝗰𝘁 I would love the opportunity to connect and contribute. Feel free to DM me on LinkedIn itself or reach out to me at aman.pathk23@gmail.com. I look forward to connecting and networking with people in this exciting Tech World.