[Oracle SQLcl Liquibase] Install it on Mac&Windows and use it with Oracle Database (on-premise & cloud)
 Rafal Grzegorczyk
Rafal Grzegorczyk
This blog gathers together all you need to install SQLcl (Open-Source Liquibase 4.18.0 is included, no need for a separate installation), configure it and use it with your Oracle databases - both on-premise and OCI Cloud (ATP, ADW, etc.). MacOS & Windows guide included.
For a standalone Liquibase installation guide, see my other article.
Installation steps for macOS
tested at MacbokPro with M1 Sonoma 14.2.1
SQLcl 23.3 with Open Source Liquibase 4.18.0 included
Go to the Oracle website and download the latest version of SQLcl.
Unpack the downloaded file and put it in your folder with applications.
I use /Users/rg/apps/oracle/ for that (use whatever you wish)
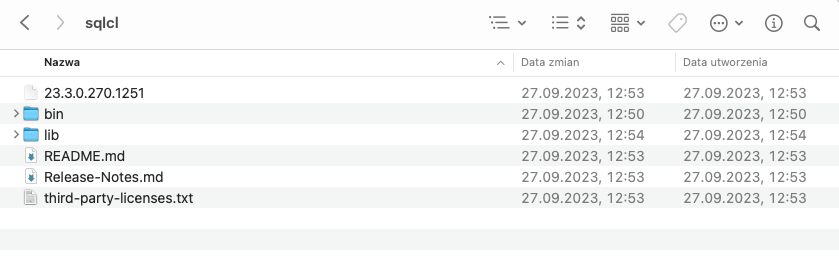
Your folder /sqlcl/ should look similar to this:
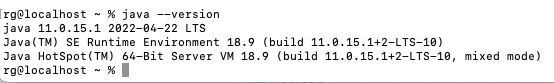
Your macOS should already have JAVA installed, but verify it by typing into the terminal:
java --version
If you don't have JAVA, install it first.
Add SQLcl to your path:
Most Macs use ZSH (Z Shell - default for MacOS and Linux)
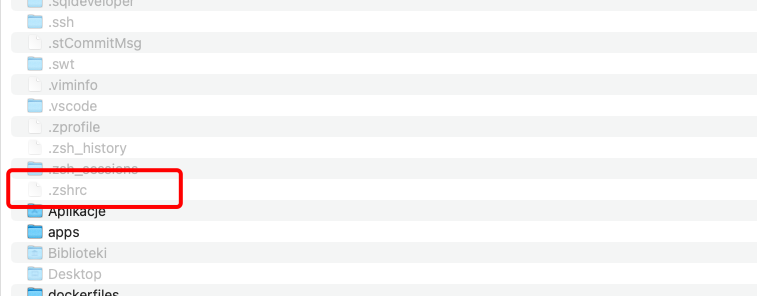
Go to /your_user/ and find .zshrc file
If you don't see it, you must make your hidden files visible by clicking "SHIFT+CMD + ."
Read this article if you can't find zshrc.
Add new line (change it for your path)
export PATH="/Users/[your_user]/apps/oracle/sqlcl/bin:$PATH"
# change the path if you use different folder

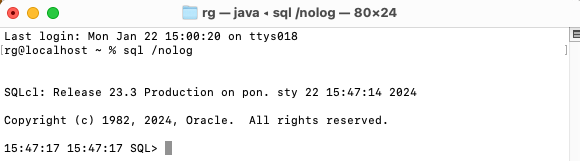
Save the file and verify if SQLcl is installed.
Open terminal and type:
sql /nolog
Enjoy your SQLcl installation!
Installation steps for Windows
tested with Windows 11
SQLcl 23.3 with Open Source Liquibase 4.18.0 included
Go to the Oracle website and download the latest version of SQLcl.

Unpack the downloaded file and put it in your folder with applications.
I use C:\Users\rgrze\tools\sqlcl-latest for that (use whatever you wish)
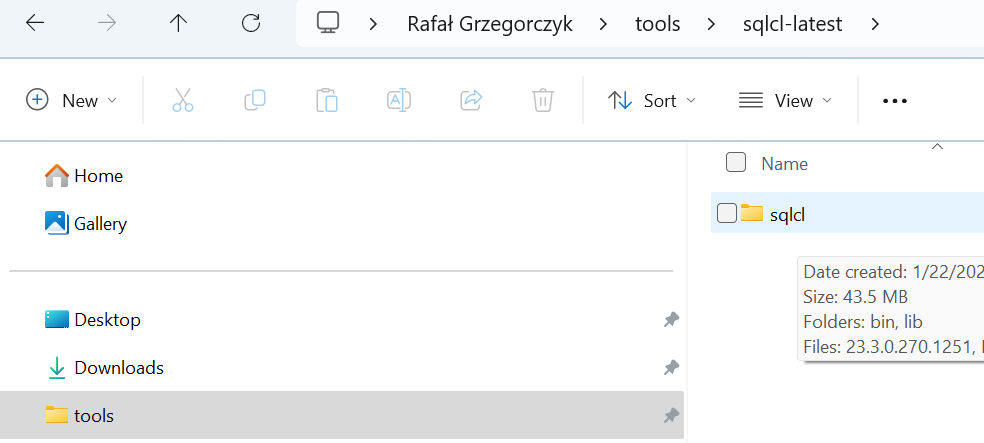
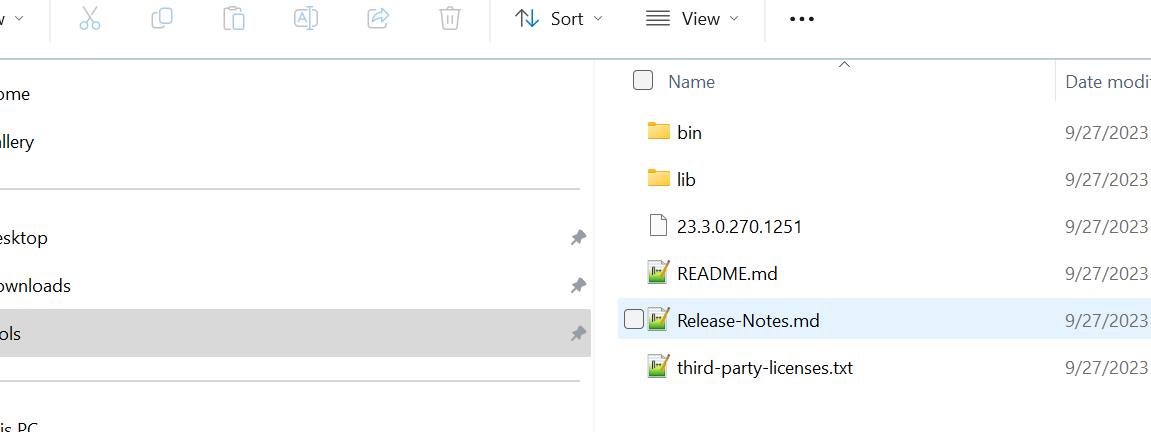
Your folder \ sqlcl \ should look similar to this:
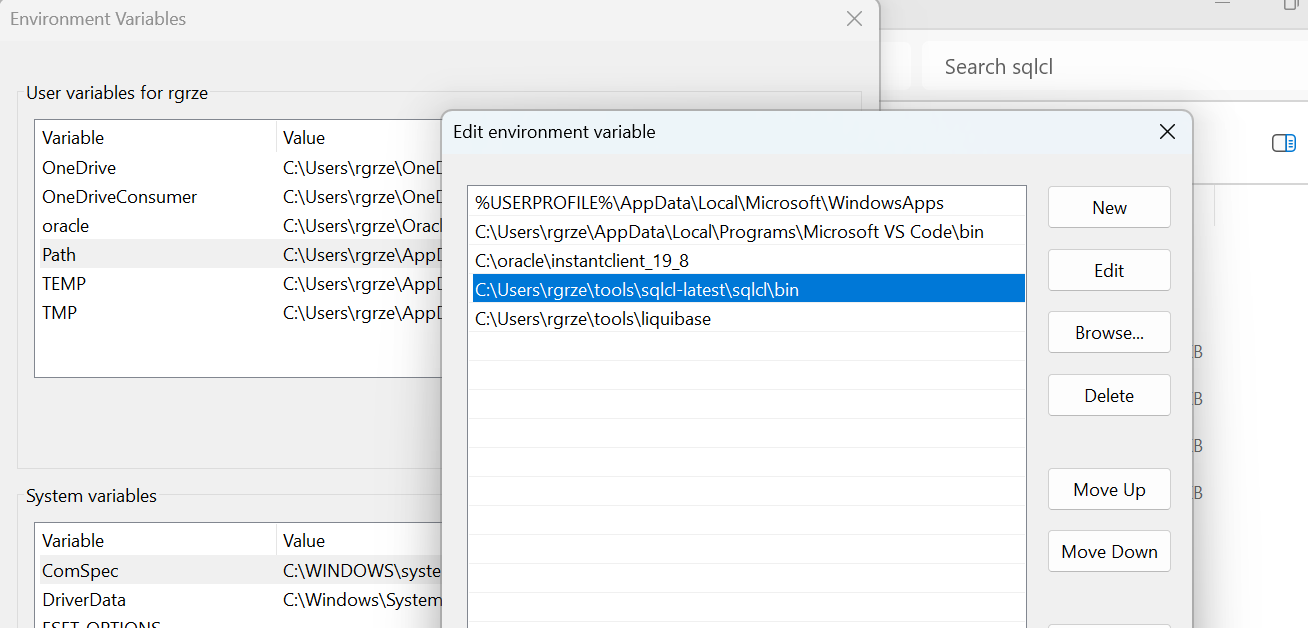
Configure your PATH. To do this, go to environment variables.
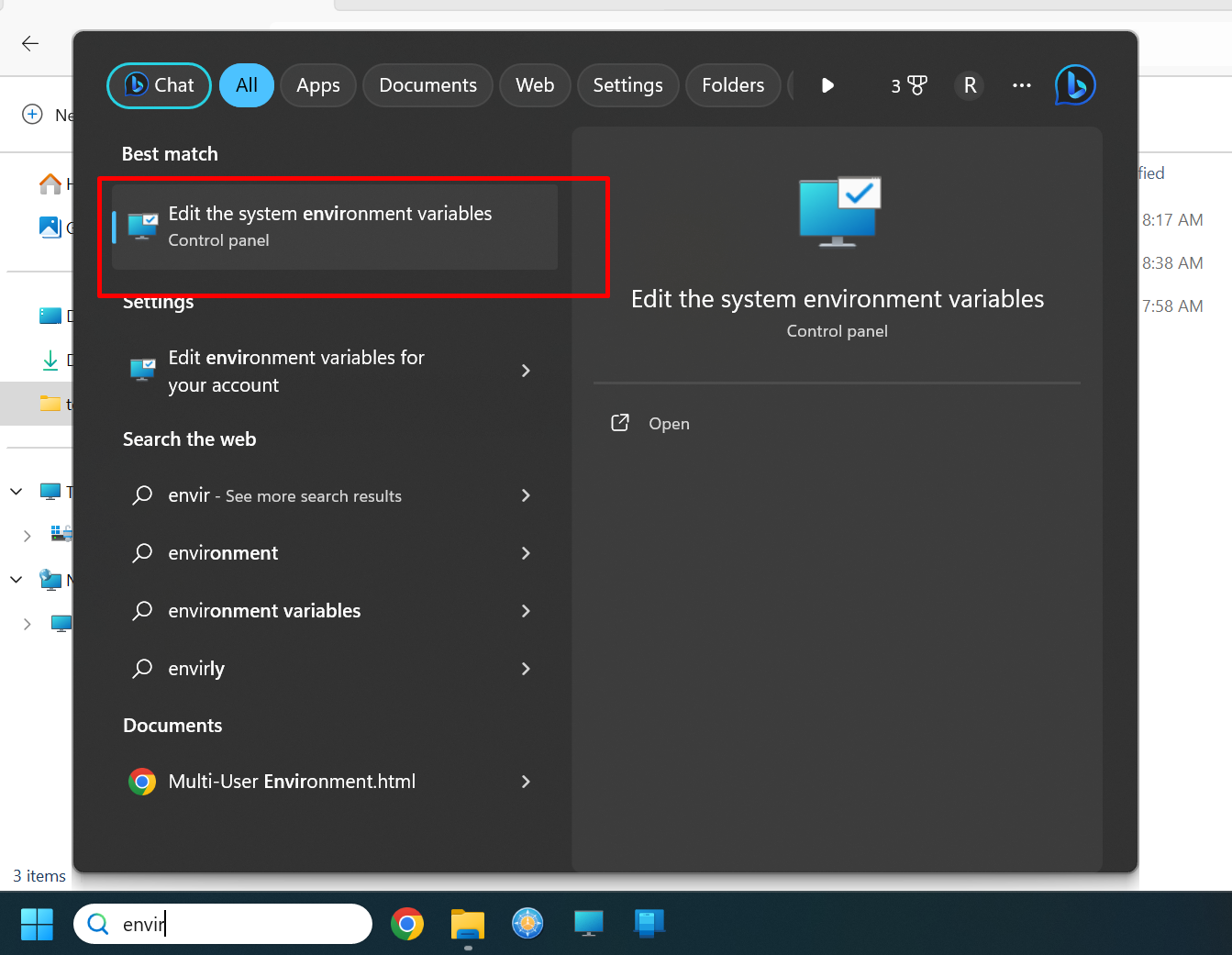
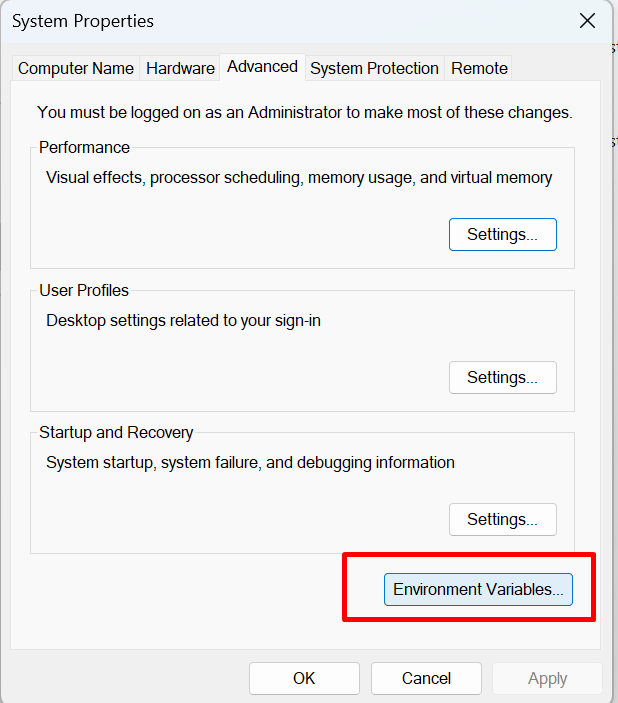
Ensure you have JAVA_HOME defined.

Go to "Path" and click on first Edit button below it.
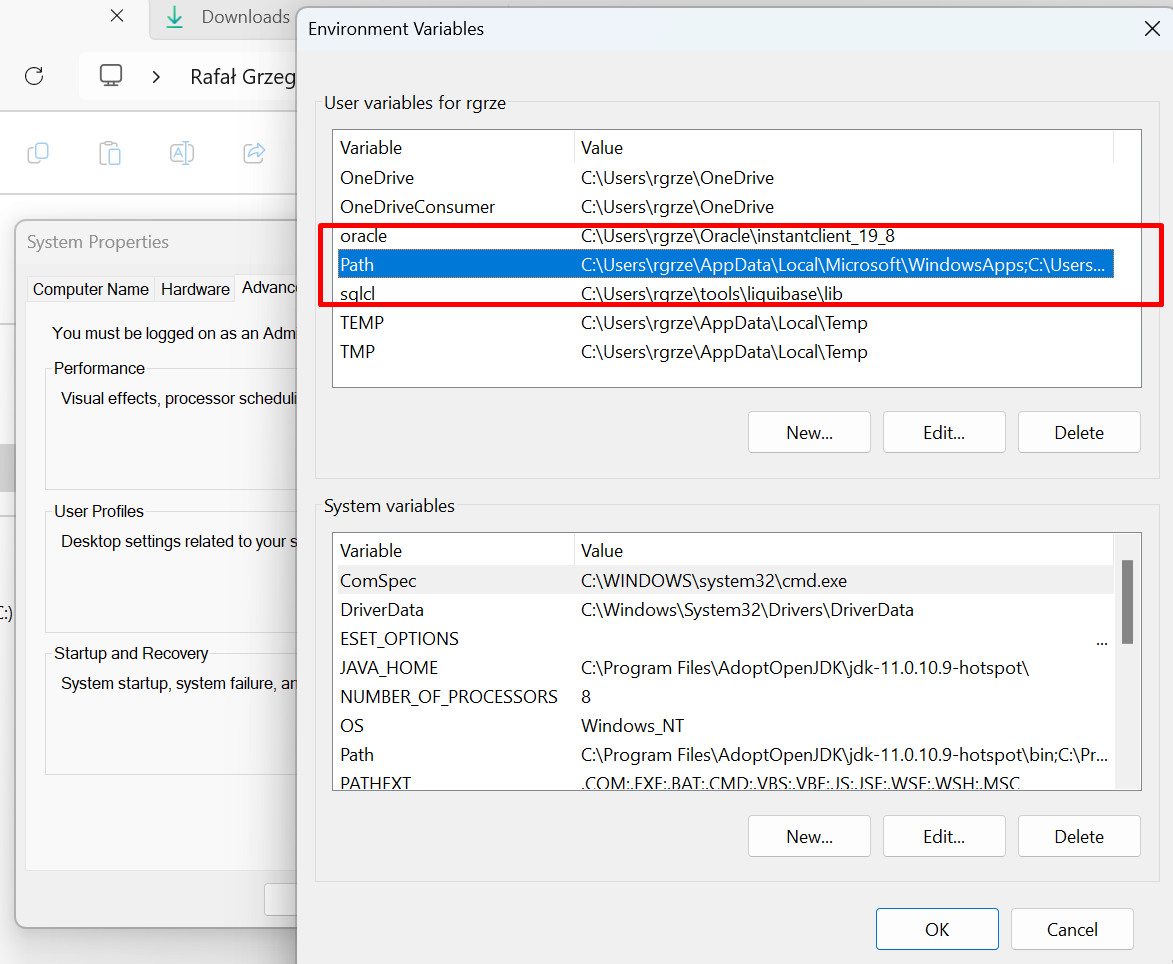
Add new PATH.
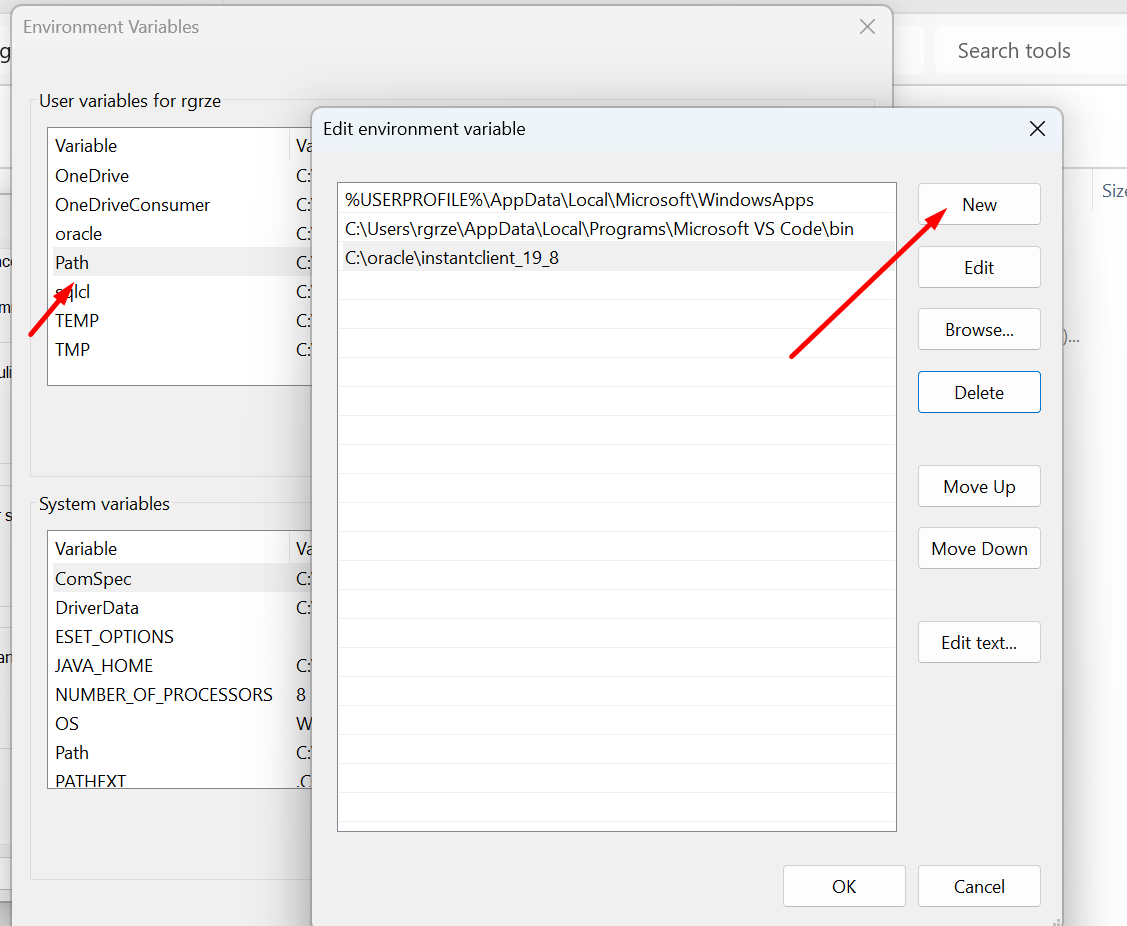
Select a location of your \sqlcl\bin folder
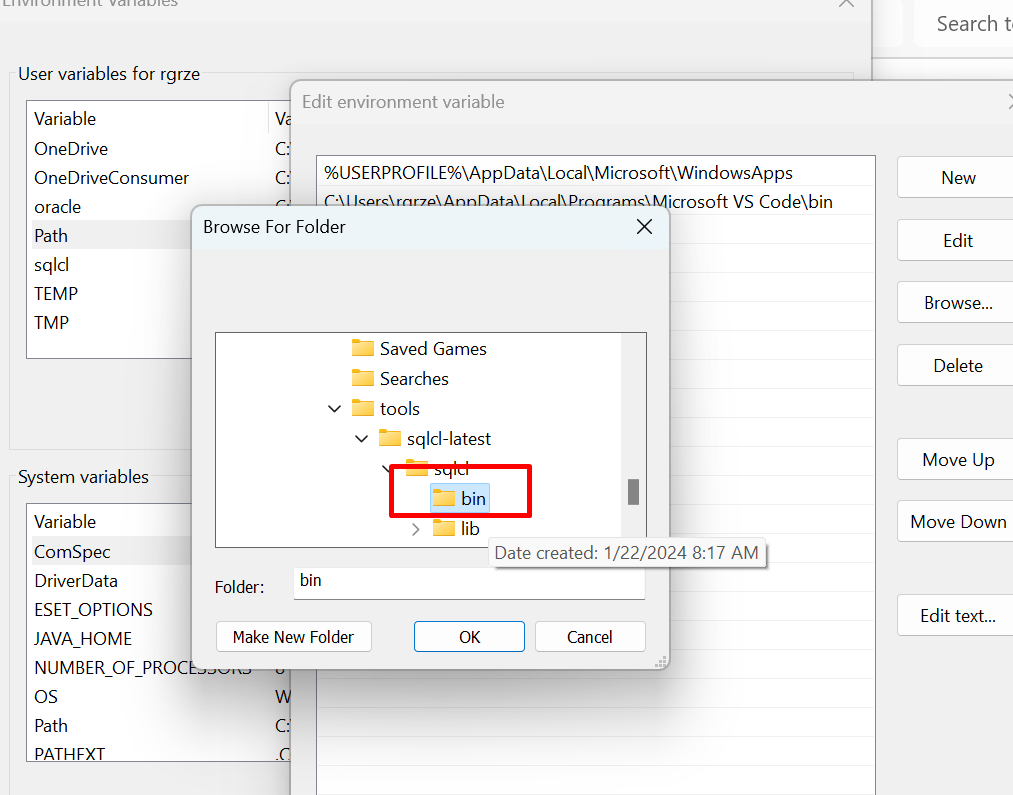
Verify installation by opening the terminal and typing:
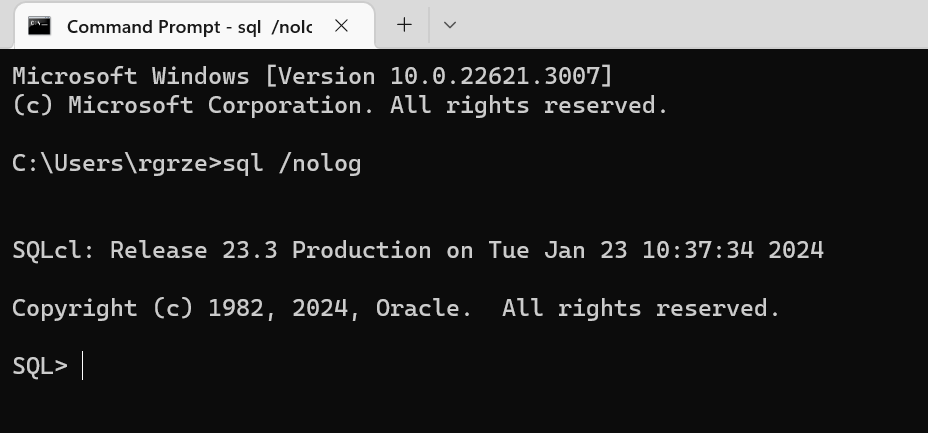
All set.
SQLcl configuration for usage with Oracle databases: on-prem & cloud
Below instructions are the same for MacOS & Windows users
Oracle Cloud Autonomous Database (ATP, ADW) using Oracle Wallet
log into your OCI account and download your instance or regional wallet
save it in your chosen location
I use /Users/rg/apps/oracle/wallets/privs for that
It looks like this:
open terminal and SQLcl ( nolog = open SQLcl without connection)
type sql /nolog
sql /nologSet the location of the wallet.
macOS:
set cloudconfig /users/rg/apps/oracle/wallets/priv/Wallet_REGIONAL.zip
Windows:
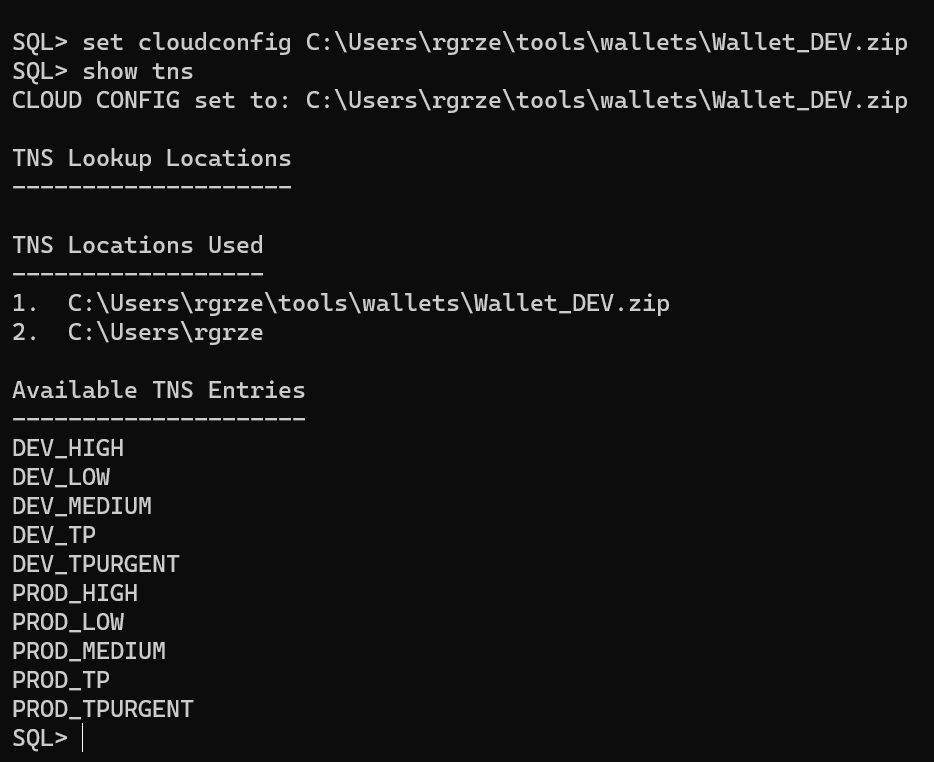
set cloudconfig C:\Users\rgrze\tools\wallets\Wallet_DEV.ziptype show tns*t*o list available entries
show tns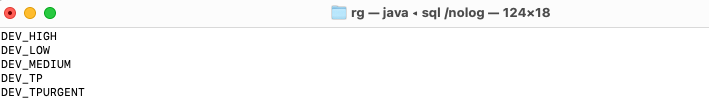
type connect username@[TNS_NAME] to connect to your database (you will be prompted for password)
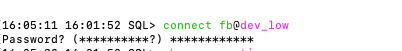
You can also type connect username/password@[TNS_NAME]
you can type**show connection - to see your current connection
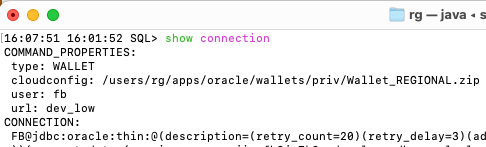
An alternative way of connecting (right after you open your terminal) is:
sql username@TNS_NAME
--or
sql username/password@TNS_NAME
Oracle Database On-Premise ( no wallet)
Just type:
--provide password
sql username/password@host:port/SID
--will be prompted for password
sql RAFAL@127.0.0.1:1521/MYSID
--or
sql /nolog
connect RAFAL@127.0.0.1:1521/MYSID
Save your connection with a friendly name and connect with ease!
This is the easiest way of connecting, e.g. to my connection called COOL
This feature is called saved connections - read more about it here.
You can use it both with on-premise and cloud connections.
Use standalone Liquibase to deploy SQLcl changesets
If you want to use standalone Liquibase, you can still deploy changesets generated by Oracle SQLcl. To do this you need to do some simple tweaks. Just follow this quick tutorial from SQLcl documentation
How to install standalone Liquibase? Just read my step-by-step tutorial.
Configure Liquibase for UTF-8 encoding (Windows users)
Read this tutorial.
How to use SQLcl + Liquibase
Read my blog series "Mastering SQLcl Liquibase"
Oracle 23.3 official documentation is here
And if you are looking for fast examples, just open SQLcl and type help to list available commands
help
For help on a topic type help <topic>
List of Help topics available:
/ @ @@ ACCEPT
ALIAS APEX APPEND AQ
ARBORI ARCHIVE_LOG ARGUMENT BLOCKCHAIN_TABLE
BREAK BRIDGE BTITLE CD
CERTIFICATE CHANGE CLEAR CLOUDSTORAGE
CODESCAN COLUMN COMPUTE CONNECT
CONNMGR COPY CS CTAS
DATAPUMP DBCCRED DDL DEFINE
DEL DESCRIBE DG DISCONNECT
EDIT EXECUTE EXIT FIND
FORMAT GET HISTORY HOST
IMMUTABLE_TABLE INFORMATION INPUT LIQUIBASE
LIST LOAD MIGRATEADVISOR MKSTORE
MODELER NET OCI OCIDBMETRICS
OERR ORAPKI PASSWORD PAUSE
PRINT PROMPT QUIT REMARK
REPEAT RESERVED_WORDS REST RUN
SAVE SCRIPT SECRET SET
SHOW SHUTDOWN SODA SPOOL
SSHTUNNEL START STARTUP STORE
TIMING TNSPING TOSUB TTITLE
UNDEFINE UNLOAD VARIABLE VAULT
WHENEVER WHICH XQUERY
- help liquibase to get more about the usage of Liquibase, etc.
help liquibase
Usage:
Liquibase|lb COMMAND {OPTIONS}
Liquibase|lb help|he [-example|-ex]
Liquibase|lb help|he COMMAND [-syntax|-sy] [-example|-ex]
The following commands are available within the Liquibase feature.
Commands:
calculate-checksum|cac
Calculates and prints a checksum for the changeset with the given id in the
format filepath::id::author
changelog-sync|chs
Marks all changes in the changelog file as executed in the database
changelog-sync-sql|chss
Output the raw SQL used by Liquibase when running changelogSync
changelog-sync-to-tag|chstt
Marks all undeployed changesets as executed starting from the top of the
changelog file and moving down up to and including the tag.
changelog-sync-to-tag-sql|chstts
Output the raw SQL used by Liquibase when running changelogSyncToTag
clear-checksums|clc
Clears all checksums and nullifies the MD5SUM column of the DATABASECHANGELOG
table so that they will be re-computed on the next database update
data|da
Generate changelogs for the data - Creates changelog for data from all objects
or as filers are specified.
db-doc|dbd
Generates JavaDoc documentation for the existing database and changelogs
diff|di
Compare two databases
diff-changelog|dic
Compare two databases to produce changesets resolving the differences and write
them to a changelog file
drop-all|dra
dropAll drops all database objects owned by the user.
future-rollback-count-sql|furcs
Generates SQL that would be used to sequentially revert the specified number of
undeployed changes
future-rollback-from-tag-sql|furfts
Generates SQL to revert future undeployed changes up to the specified tag
future-rollback-sql|furs
Generate the raw SQL needed to rollback future undeployed changes
generate-apex-object|geao
Generates the changeset for an APEX object
generate-changelog|gec
Writes Change Log XML to copy the current state of the database
generate-control-file|gecf
Generates an empty control file that can be used to start a new changelog.
generate-object|geo
Writes Change Log XML to copy the current state of the database object to a file
generate-ords-module|geom
Generates the code necessary to reproduce a module and all children using the
ORDS API's.
generate-ords-schema|geos
Generates the code necessary to reproduce all modules and children using the
ORDS API's.
generate-schema|ges
Writes Change Log XML to copy the current state of the database to files
history|hi
List all deployed changesets and their deployment ID
list-locks|lil
List the hostname, IP address, and timestamp of the Liquibase lock record
mark-next-changeset-ran|mancr
Marks the next change you apply as executed in your database
mark-next-changeset-ran-sql|mancrs
Writes the SQL used to mark the next change you apply as executed in your
database
release-locks|rel
Remove the Liquibase lock record from the DATABASECHANGELOG table
rollback|rb
Rollback changes made to the database based on the specified tag
rollback-count|rbc
Rollback the specified number of changes made to the database
rollback-count-sql|rbcs
Generate the SQL to rollback the specified number of changes
rollback-sql|rbs
Generate the SQL to rollback changes made to the database after a defined tag.
rollback-to-date|rbtd
Rollback changes made to the database back to the specified date/time
rollback-to-date-sql|rbtds
Generate SQL to rollback changes made to the database back to the specified
date/time
snapshot|sn
Capture the current state of a target database
status|st
Generate a list of pending changesets
tag|ta
Mark the current database state with the specified tag to use for roll back.
tag-exists|tae
Verify the existence of the specified tag
unexpected-changesets|unc
Generate a list of changesets that have been executed but are not in the current
changelog
update|up
Deploy any changes in the changelog file that have not been deployed.
update-count|upc
Deploy the specified number of changes from the changelog file.
update-count-sql|upcs
Generate the SQL to deploy the specified number of changes for review before
running the update command.
update-sql|ups
Generate the SQL identified in the changelog for review before running the
update command.
update-testing-rollback|uptr
Updates database, then rolls back changes before updating again. It provides
testing of rollback funtionality.
update-to-tag|uptt
Deploy changes sequentially from the newest changeset up to and including the
changeset with the specified tag.
update-to-tag-sql|uptts
Generate the SQL from the newest changeset up to and including the changeset
with the specified tag.
validate|va
Validate the changelog for errors that may cause an UPDATE to fail
version|ve
Enjoy your SQLcl with Liquibase!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rafal Grzegorczyk directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Rafal Grzegorczyk
Rafal Grzegorczyk
Oracle APEX & PL/SQL Developer with 10 years of experience in IT, including financial systems for government administration, energy, banking and logistics industry. Enthusiast of database automation. Oracle ACE Associate. Certified Liquibase database versioning tool fan. Speaker at Kscope, APEX World, SOUG, HrOUG, POUG and DOAG. Likes swimming in icy cold lakes in winter and playing basketball.