Day 1: Learn Blockchain Fundamentals
 Neeraj GS
Neeraj GS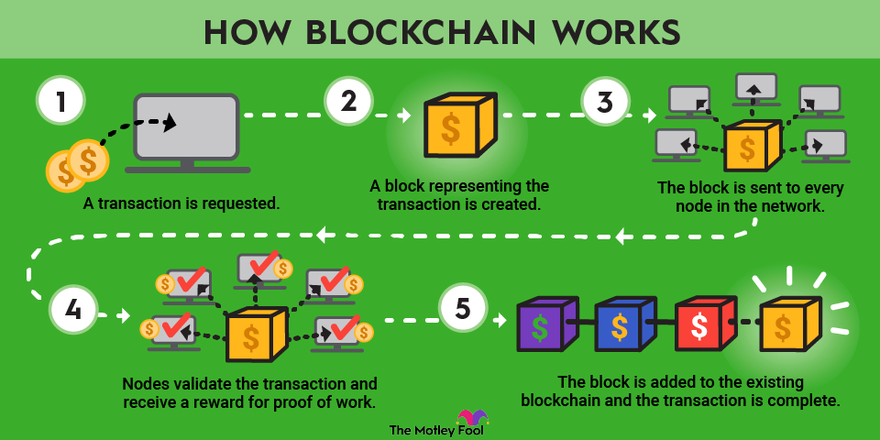
Blockchain is a distributed immutable ledger that is completely transparent. Multiple Nodes are connected to form a single Big Node. The decentralization concept is dependent on the Company's needs and decides to make it decentralized.
Distributed: Each Node has the same copy of the blockchain, If there is a change on the block it is broadcasted to All other nodes, and after acceptance, the changes are added to blocks in all nodes.
Immutable: Once a Transaction is added to the blockchain it cannot be changed.
Ledger: A Storage place where all the transactions are stored. Each Block of Blockchain contains a ledger that resembles all other blocks.
Transparent: Any Transaction performed on the Blockchain is publicly available and can be viewed by anyone, the data is encrypted and contains a public address.
Bitcoin vs Ethereum
Bitcoin
A Decentralized digital currency that can be sent on a peer-to-peer network without the need for intermediaries, basically it is a cryptocurrency that uses blockchain technology.
Can Perform only transactions as it is a Not Turing Complete Algorithm, which means it cannot run loops and run programs on its network.

Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that establishes a peer-to-peer network that securely executes and verifies application code, called smart contracts.
Can perform both transactions and deploy smart contrast on the network called Daaps[Decentralized Applications]. It is Turing Complete, as Solidity is used to write the smart contracts.

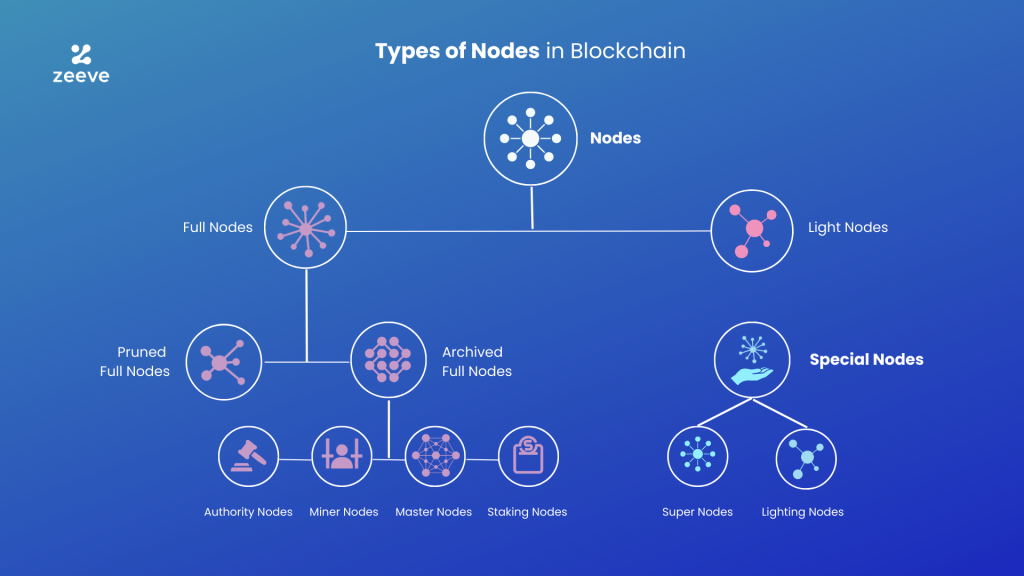
Types of Nodes in a Blockchain Network
Full Node - Can perform the mining and transactions in the blockchain. No need for third-party applications. Can install blockchain locally on the system. Validation and Verification is performed, Running 24 Hours.
Light Node - Stores only block header and depend on the full node. Stores only index and request data from the full node. No Verification and Validation is done.
Archive Node - Stores all the data from the genesis block till now. Archive of history of data and transactions.
These are the core fundamentals of blockchain and we gain more in-depth knowledge while building projects and portfolio updations. Let's Dive deep into the Solidity Programming language for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Neeraj GS directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Neeraj GS
Neeraj GS
I am a Computer Science Undergrad with Expertise in Full Stack Development with modern technologies. I am currently learning DevOps, upskilling, and building projects and learning things in public. Passionate about Web 3.0 and AI. I am looking to expand my learning in a professional setting.