Deploy Wasm functions on Kubernetes with Simplism.
 Philippe Charrière
Philippe Charrière
Deploy a Simplism Wasm Registry on Kubernetes
Disclaimer: the registry mode of Simplism is a worl in progress (at the beginning of the project, it was a facility to do some tests) and is not ready entirely for production use yet. (== it's not battle tested)
First, add these variables to the .env file:
PRIVATE_REGISTRY_TOKEN="people-are-strange"
ADMIN_REGISTRY_TOKEN="morrison-hotel"
REGISTRY_SIZE="10Mi"
PRIVATE_REGISTRY_TOKEN is to protect the downloads from the registry and the query to the registry service
ADMIN_REGISTRY_TOKEN is to protect the upload to the registry
Then, we need these three manifest files:
wget https://github.com/bots-garden/simplism/releases/download/v0.1.3/wasm-registry-volume.yaml -O ./manifets/wasm-registry-volume.yaml
wget https://github.com/bots-garden/simplism/releases/download/v0.1.3/deploy-wasm-registry.yaml -O ./manifets/deploy-wasm-registry.yaml
wget https://github.com/bots-garden/simplism/releases/download/v0.1.3/deploy-wasm-from-registry.yaml -O ./manifets/deploy-wasm-from-registry.yaml
Create a space to store the Wasm files of the Registry
We are going to store the uploaded WASM files:
set -o allexport; source .env; set +o allexport
rm -f tmp/create.wasm.registry.volume.yaml
envsubst < manifests/wasm-registry-volume.yaml > tmp/create.wasm.registry.volume.yaml
# Create namespace (if needed)
kubectl create namespace ${KUBE_NAMESPACE} --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f -
# Deploy
kubectl apply -f tmp/create.wasm.registry.volume.yaml -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
You should see:
persistentvolume/task-pv-wasm-registry-volume configured
persistentvolumeclaim/task-pv-wasm-registry-claim configured
pod/wasm-registry-store configured
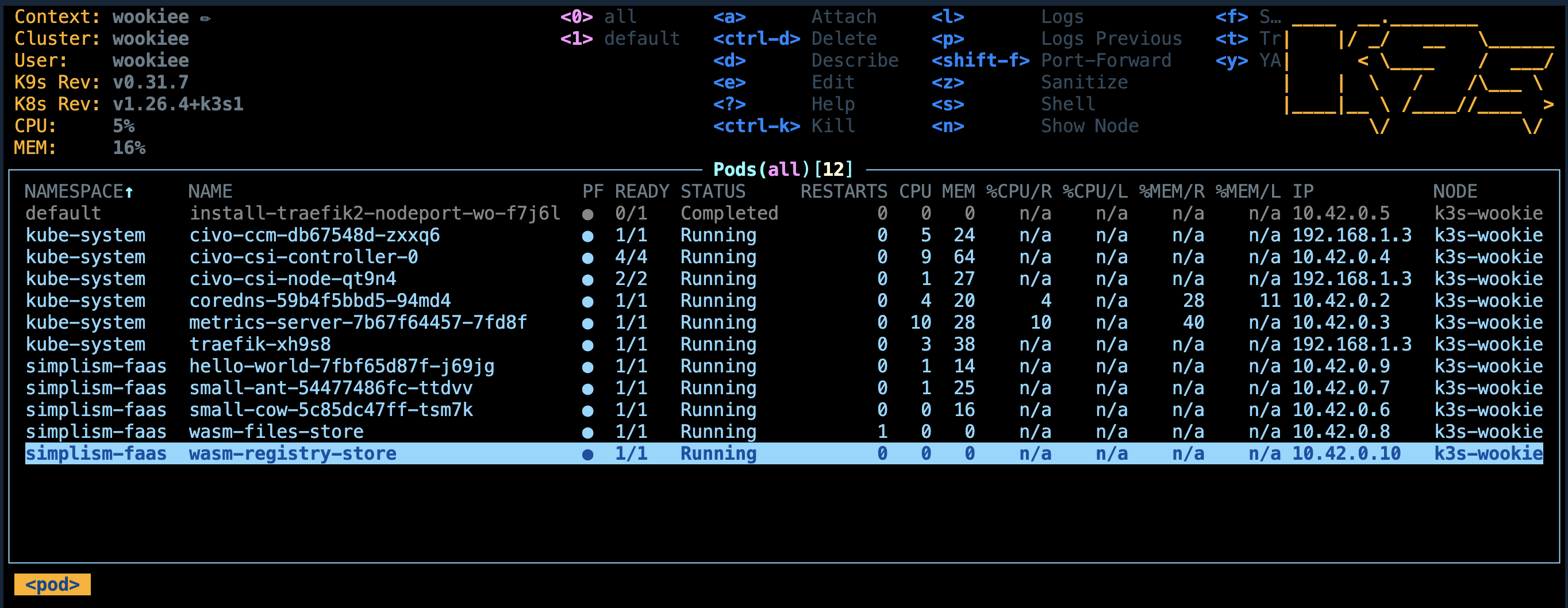
Now, we can deploy the Wasm Registry service.
Deploy the Wasm Registry
Use these commands:
set -o allexport; source .env; set +o allexport
rm -f tmp/deploy.wasm.registry.yaml
envsubst < manifests/deploy-wasm-registry.yaml > tmp/deploy.wasm.registry.yaml
# Create namespace (if needed)
kubectl create namespace ${KUBE_NAMESPACE} --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f -
# Deploy
kubectl apply -f tmp/deploy.wasm.registry.yaml -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
You should see:
service/wasm-registry created
deployment.apps/wasm-registry created
ingress.networking.k8s.io/wasm-registry created
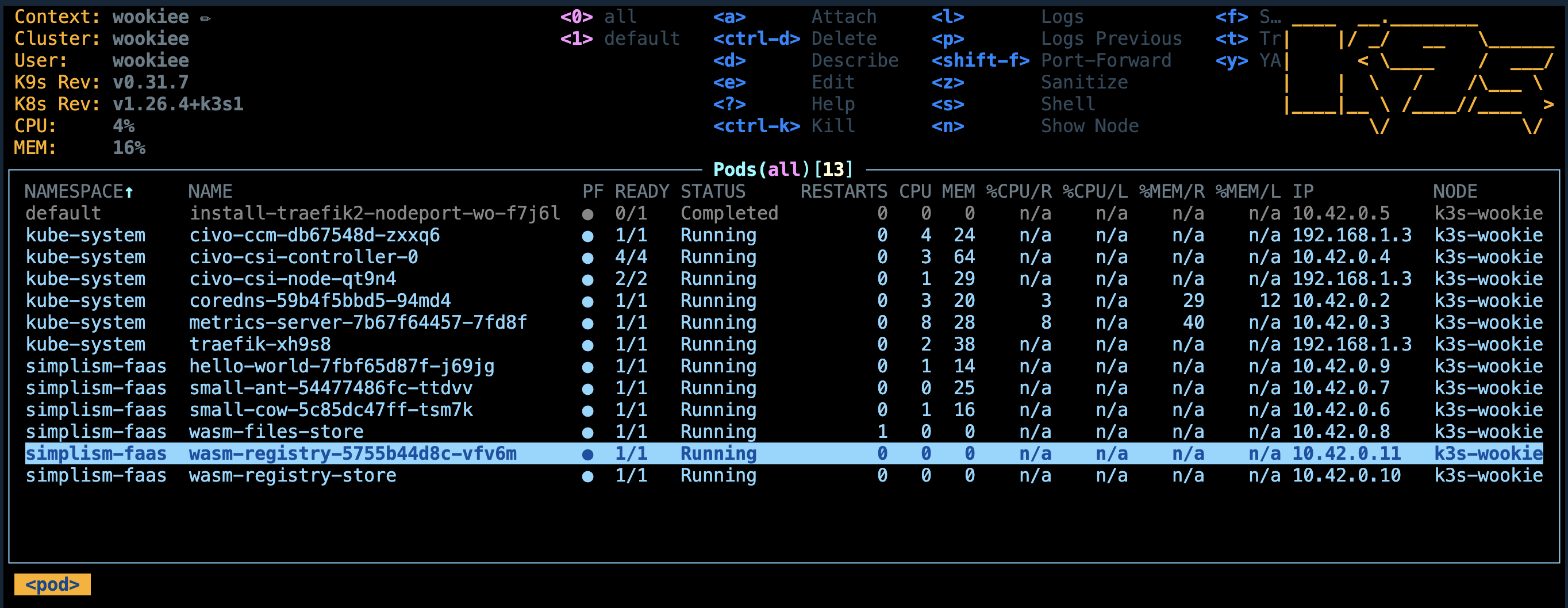
You can get the ingress of the service with this command:
kubectl describe ingress wasm-registry -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
#simplism-faas.registry.ffb140f9-7479-4308-9763-9f70628794b1.k8s.civo.com
And now you can check the Wasm Registry:
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}
# you should get:
🖖 Live long and prosper 🤗 | simplism v0.1.3
# yes I'm a Trekkie
Publish some Wasm plug-ins to the Registry
In Part 1 of this tutorial, we downloaded some WASM files, so now we are going to push them to the Wasm registry:
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}/registry/push \
-H 'admin-registry-token: morrison-hotel' \
-F 'file=@./wasm-files/small-cow.wasm'
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}/registry/push \
-H 'admin-registry-token: morrison-hotel' \
-F 'file=@./wasm-files/small_ant.wasm'
Now you can get the list of the wasm files:
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}/registry/discover \
-H 'private-registry-token: people-are-strange' \
-H 'content-type:text/plain; charset=UTF-8'
# you should get this output:
+------------------+--------------------------------------+---------+---------------------+
| NAME | PATH | SIZE | CREATED |
+------------------+--------------------------------------+---------+---------------------+
| small-cow.wasm | wasm-registry-files/small-cow.wasm | 194165 | 2024-01-26 07:27:00 |
| small_ant.wasm | wasm-registry-files/small_ant.wasm | 2246665 | 2024-01-26 07:27:07 |
+------------------+--------------------------------------+---------+---------------------+
If you prefer a JSON output:
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}/registry/discover \
-H 'private-registry-token: people-are-strange' \
-H 'content-type:application/json; charset=UTF-8'
And, you can download "manually" the Wasm files:
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}/registry/pull/small-cow.wasm -o small-cow.wasm \
-H 'private-registry-token: people-are-strange'
So, let's deploy the Wasm functions using the registry.
Deploy a Wasm function from the registry
Then, we can deploy the functions from the registry:
set -o allexport; source .env; set +o allexport
export SERVICE_NAME="small-cow"
export WASM_FILE="small-cow.wasm"
export WASM_URL="http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}/registry/pull/${WASM_FILE}"
export FUNCTION_NAME="handle"
# as we already deploy this service, remove it before
kubectl delete -f tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
rm -f tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml
envsubst < manifests/deploy-wasm-from-registry.yaml > tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml
# Create namespace (if needed)
kubectl create namespace ${KUBE_NAMESPACE} --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f -
# Deploy
kubectl apply -f tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
(Note that I removed the previous deployment with this command:
kubectl delete -f tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE})
You should see:
service/small-cow created
deployment.apps/small-cow created
ingress.networking.k8s.io/small-cow created
You can get the ingress of the service with this command:
kubectl describe ingress ${SERVICE_NAME} -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
#simplism-faas.small-cow.ffb140f9-7479-4308-9763-9f70628794b1.k8s.civo.com
Now you can call the function:
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.${SERVICE_NAME}.${DNS} -d '👋 Hello World 🌍'
# you should get:
^__^
(oo)\_______
(__)\ )\/\
||----w |
|| ||
👋 Hello World 🌍
🎉 Let's do it for the other Wasm function:
set -o allexport; source .env; set +o allexport
export SERVICE_NAME="small-ant"
export WASM_FILE="small_ant.wasm"
export WASM_URL="http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.registry.${DNS}/registry/pull/${WASM_FILE}"
export FUNCTION_NAME="handle"
# as we already deploy this service, remove it before
kubectl delete -f tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
rm -f tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml
envsubst < manifests/deploy-wasm-from-registry.yaml > tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml
# Create namespace (if needed)
kubectl create namespace ${KUBE_NAMESPACE} --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f -
# Deploy
kubectl apply -f tmp/deploy.${SERVICE_NAME}.yaml -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
You should see:
service/small-ant created
deployment.apps/small-ant created
ingress.networking.k8s.io/small-ant created
You can get the ingress of the service with this command:
kubectl describe ingress ${SERVICE_NAME} -n ${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
#simplism-faas.small-ant.ffb140f9-7479-4308-9763-9f70628794b1.k8s.civo.com
Now you can call the function:
curl http://${KUBE_NAMESPACE}.${SERVICE_NAME}.${DNS} -d '✋ Hey people 🤗'
# you should get:
/\/\
\_\ _..._
(" )(_..._)
^^ // \\
✋ Hey people 🤗
Get the list of the deployed Wasm functions:
kubectl get ingress -l component=simplism-function --namespace simplism-faas
You should get:
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
small-ant <none> simplism-faas.small-ant.d730feb5-db34-4e86-8e93-fb848e7c5808.k8s.civo.com d730feb5-db34-4e86-8e93-fb848e7c5808.k8s.civo.com 80 90m
hello-world <none> simplism-faas.hello-world.d730feb5-db34-4e86-8e93-fb848e7c5808.k8s.civo.com d730feb5-db34-4e86-8e93-fb848e7c5808.k8s.civo.com 80 83m
small-cow <none> simplism-faas.small-cow.d730feb5-db34-4e86-8e93-fb848e7c5808.k8s.civo.com d730feb5-db34-4e86-8e93-fb848e7c5808.k8s.civo.com 80 49s
And that's it 🎉!
Don't forget that I created a project with all the files of this tutorial, and I "gitpodified" the project, so you don't need to install anything: https://github.com/bots-garden/simplism-on-k8s
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Philippe Charrière directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
