Win32 API programming with C - Closing the window
 Ciprian Fusa
Ciprian FusaWhen the user closes a window, that action triggers a sequence of window messages.
The user can close an application window by clicking the Close button, or by using a keyboard shortcut such as ALT+F4. Any of these actions causes the window to receive a WM_CLOSE message. The WM_CLOSE message gives you an opportunity to prompt the user before closing the window.
Here is an example of how a program might handle WM_CLOSE.
case WM_CLOSE:
if (MessageBox(hwnd, L"Really quit?", L"My application", MB_OKCANCEL) == IDOK)
{
DestroyWindow(hwnd);
}
// Else: User canceled. Do nothing.
return 0;
In this example, the MessageBox function shows a modal dialog that contains OK and Cancel buttons. If the user clicks OK, the program calls DestroyWindow. Otherwise, if the user clicks Cancel, the call to DestroyWindow is skipped, and the window remains open. In either case, return zero to indicate that you handled the message.
When a window is about to be destroyed, it receives a WM_DESTROY message. This message is sent after the window is removed from the screen, but before the destruction occurs (in particular, before any child windows are destroyed).
In your main application window, you will typically respond to WM_DESTROY by calling PostQuitMessage.
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
PostQuitMessage puts a WM_QUIT message on the message queue, causing the message loop to end.
Here is a flow chart showing the typical way to process WM_CLOSE and WM_DESTROY messages:
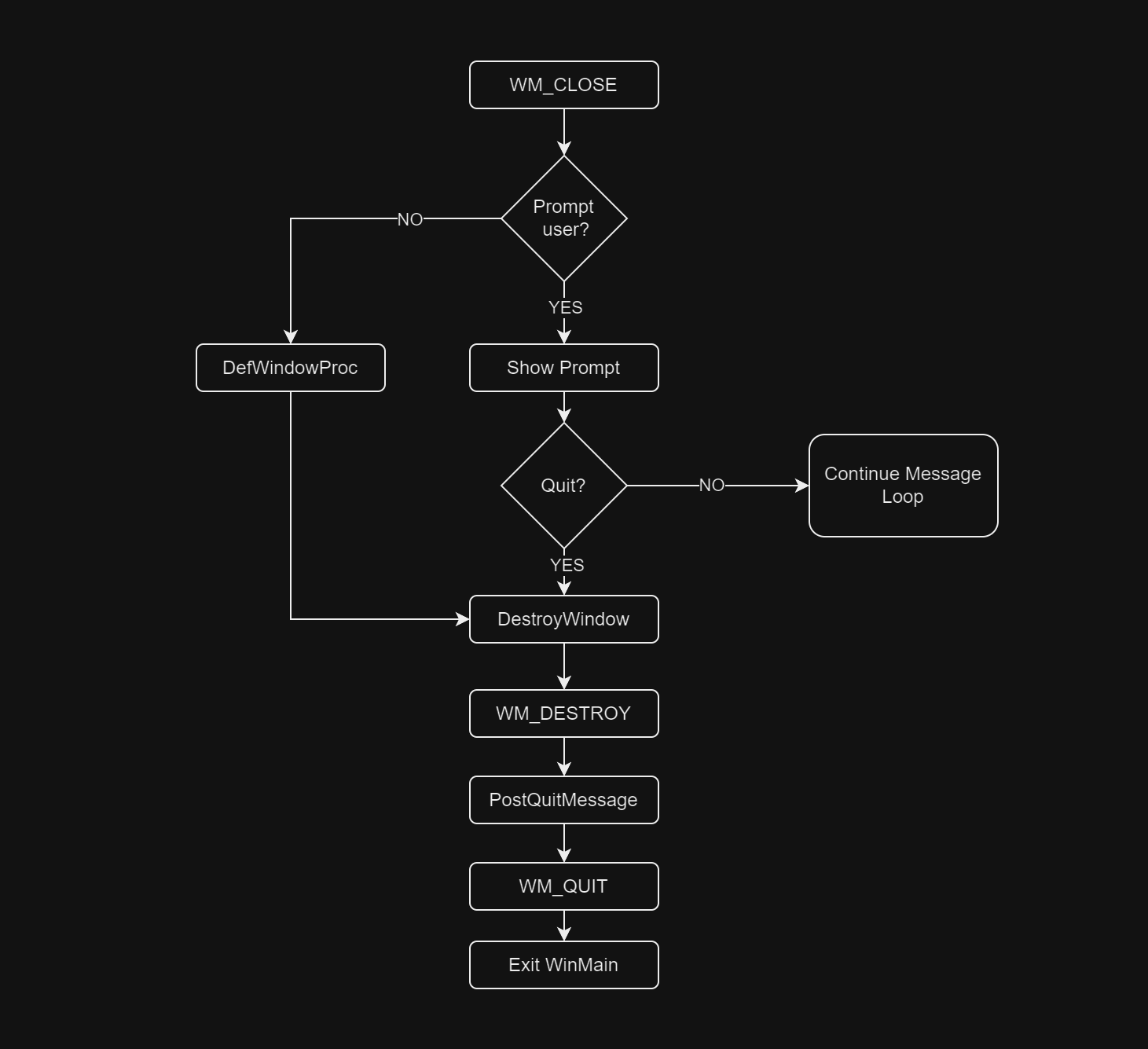
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/learnwin32/your-first-windows-program
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ciprian Fusa directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ciprian Fusa
Ciprian Fusa
I am a .NET Developer and Consultant with over 15 years of experience, I specialize in crafting scalable, high-performance applications that drive business growth and innovation.