🌟Day 6 -File Permissions and Access Control Lists
 Sandeep Kale
Sandeep Kale
🔈File Permissions with Examples
Linux file permissions are used to control who can read, write, and execute a file. This is important because Linux systems are multi-user, and file permissions are a security mechanism that protects system files from users and viruses.
Mainly Linux has three types of file permissions:
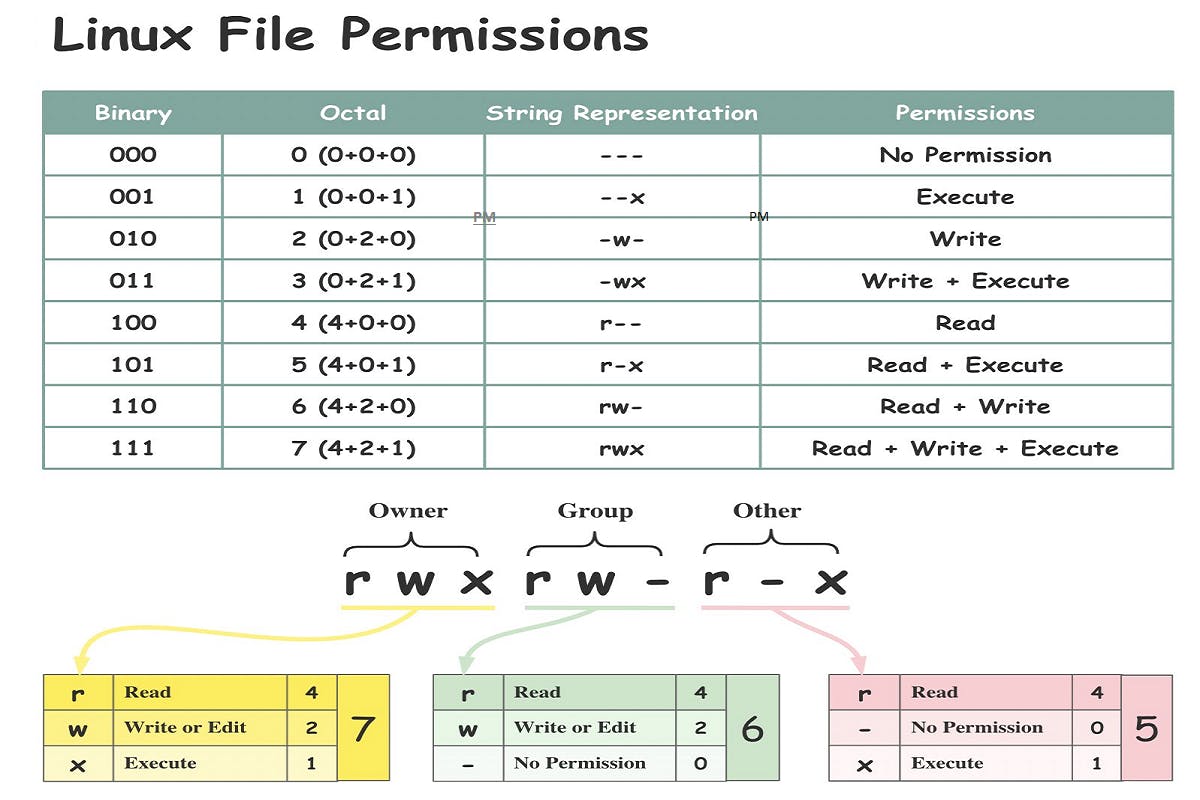
Read (r): Allows a user or group to view a file.
Write (w): Allows a user to write or modify a file or directory.
Execute (x): Allows a user or group to execute a file or view a directory.
◼️How do you view Linux file permissions?
- ls -l: The
lscommand along with its-l(for long listing) option will show you metadata about your Linux files, including the permissions set on the file.
Here is Some examples:
✔️Create a simple file and do ls -ltr to see the details of the files:
ls -ltr
✔️owner — The owner of the file or application and If you want to change the ownership of a file and directory use "chown".
chown newowner file.txt
✔️group — The group that owns the file or application and To change the group permission of file and directory use "chgrp".
chgrp newgroup file.txt
✔️To change the other users permissions of a file or directory used "chmod"
chmod o+r file.txt - set permission read only
chmod o+w file.txt - set permission write only
chmod o+x file.txt - set permission execute only
🔈Access Control List (ACL)
It is a mechanism for controlling access to file and directories on a Linux System. ACLs allows you to specify permissions for individual users and groups.
✔️To view the Access Control List for a file or directory, use getfacl command.
e.g. To view the ACLs for the file /etc/passwd
getfacl /etc/passwd
✔️To set or modify the Access Control List for a file or directory, use setfacl command.
e.g. To add the user newuser to the ACL for the file /etc/passwd with read and write permissions use setfacl -m command.
setfacl u:newuser:rw /etc/passwd
✔️To set the Access Control List for a file or directory, For group use setfacl -m command.
e.g. To set all permission to group Devops with read and write and execute permissions for directory repo.
setfacl -m g:Devops:rwx /repo
✔️To remove modify the Access Control List for a file or directory, For group Devops use setfacl -x command.
e.g. To set all permission to group Devops with read and write and execute permissions for directory repo.
setfacl -m g:Devops:rwx /repo
✔️To remove modify the Access Control List for a file or directory, For newuser use setfacl -x command.
e.g. To remove all permission to newuser for directory repo.
setfacl -x u:newuser: /repo
♻️Conclusion
Understanding file permissions and Access Control Lists (ACLs) is vital for securing computing environments. File permissions in Linux regulate access, while ACLs provide granular control.
📚 Happy Learning :)
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sandeep Kale directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
