💡AWS 07-Days Challenge, Day-04
 Neha Adwankar
Neha AdwankarAWS RDS
A cloud service for relational databases is Amazon RDS. Relational database management is reduced by Amazon RDS through automation. Multiple instances are created by Amazon RDS for high availability and failovers. PostgreSQL, MySQL, Maria DB, Oracle, SQL Server, and Amazon Aurora are supported by Amazon RDS.
Features of AWS RDS
Automated Backups: Amazon RDS automatically backs up your database and allows you to restore to any point in time within the retention period.
High Availability: RDS provides options for high availability, such as multi-AZ deployments, which automatically replicate your database to a standby instance in a different availability zone for failover support.
Scalability: You can easily scale your database resources up or down based on your application's needs. This includes adjusting compute and storage resources without impacting your database's availability.
Security: Amazon RDS provides security features such as network isolation using Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), encryption at rest and in transit, and the ability to manage database access through security groups and IAM (Identity and Access Management) roles.
Monitoring and Metrics: RDS provides various monitoring tools and metrics through Amazon CloudWatch, allowing you to monitor database performance and set up alerts.
DynamoDB
A fully managed NoSQL database service, Amazon DynamoDB, is offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It is intended to offer smooth scaling along with quick and reliable performance. With single-digit millisecond performance at any size, DynamoDB is a key-value and document database that can be used for small projects as well as large-scale business solutions.
Key features of Amazon DynamoDB include:
Fully Managed: DynamoDB is a fully managed service, meaning AWS handles administrative tasks such as hardware provisioning, setup, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance. This allows developers to focus on building applications rather than managing infrastructure.
NoSQL Model: DynamoDB is a NoSQL database, which means it does not rely on the traditional relational database model. It supports both key-value and document data models, providing flexibility in how data is organized and accessed.
Scalability: DynamoDB is designed for seamless scalability. It can automatically and elastically scale both read and write capacity to handle varying workloads. This allows applications to scale horizontally without any manual intervention.
Global Tables: DynamoDB supports the creation of global tables that can replicate data across multiple AWS regions. This feature helps achieve low-latency access to data for users located in different geographic regions.
Security: DynamoDB provides robust security features, including encryption at rest and in transit, fine-grained access control through AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), and integration with AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for encryption key management.
AWS Lambda
Amazon Serverless Computing is offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) under the Lambda service. It frees you from server provisioning and management, so you can execute your code. Code can be run in reaction to events with Lambda, such as modifications to data in an Amazon S3 bucket, updates to DynamoDB tables, or HTTP requests made through Amazon API Gateway. You don't need to worry about server provisioning, scaling, or maintenance because Lambda automatically scales and manages the computing resources required to run your code.
Set up and configure a MySQL database on AWS RDS
Open Amazon RDS and click on Create Database
Select MySQL as database type
In the Templates section, choose the Free Tier.
DB instance identifier — default
Master username: admin
Master password: choose a password.
Confirm password: Confirm the password
**Availability Zone: Us-**east-1
Initial Database Name: database-2
Go to your instance and type this command to connect.
docker exec -it [container ID] bash
bash-4.4# mysql -u root -p
enter password
mysql>use testdb;
show tables;
Or
mysql -h endpoint url -u admin -p



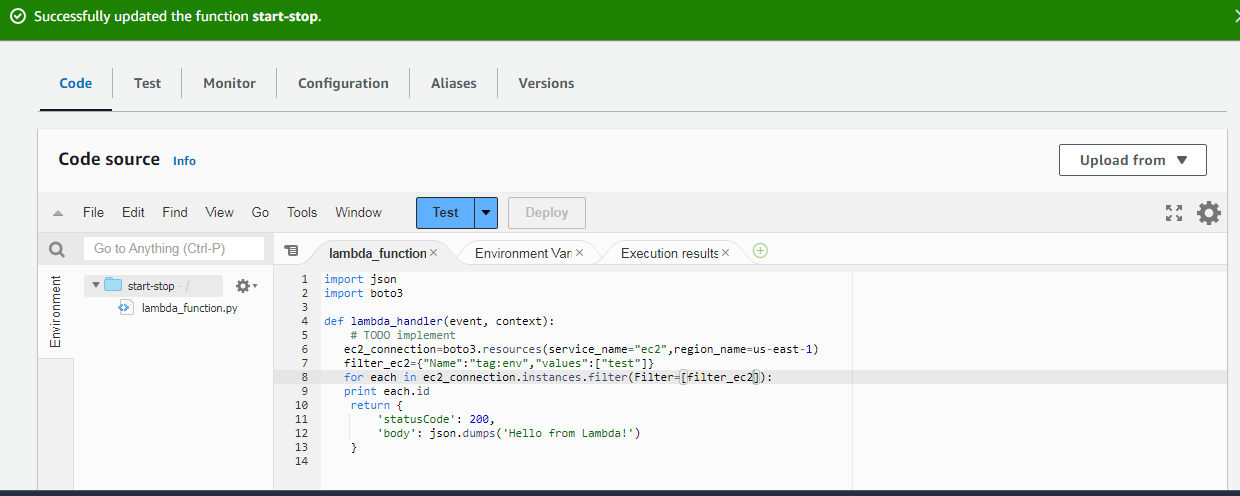
Create an AWS Lambda function that will start or stop instances based on their instance tag.
1. First, create an EC2 instance.
2. Create Tags
3. Create IAM role for Lambda Function
4. Create a lambda function.
5. Write lambda function code.
6. Deploy and Test
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Neha Adwankar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Neha Adwankar
Neha Adwankar
🚀I aspire to secure a dynamic role as a DevOps engineer, leveraging my strong determination as a software testing expert. I am eager to tackle a challenging position where I can effectively utilize my expertise in deploying DevOps strategies, optimizing operational efficacy, and nurturing cohesive software delivery procedures. Adept in DevOps practices, cloud technologies, and the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), encompassing analysis, scripting, testing, automation, documentation, and robust support capabilities.




