Lecture # 27 - Disk Partitioning and Disk Management
 Abdullah Bin Altaf
Abdullah Bin Altaf
Disk Partition:
Disk partition refers to creation of one or more regions on secondary storage. This is created to manage regions separately. Disk partition is the first step of preparing a new installed disk and and is done before creating the file system.
Data Partition:
Data partition refers to normal Linux system data including the root partition containing all data to start up and run the system.
Swap Partition:
Swap partitions refers to expansion of computer's physical memory, an extra memory on the hard disk.
Adding Additional Disk Drive in VM:
Open VMwarwe.
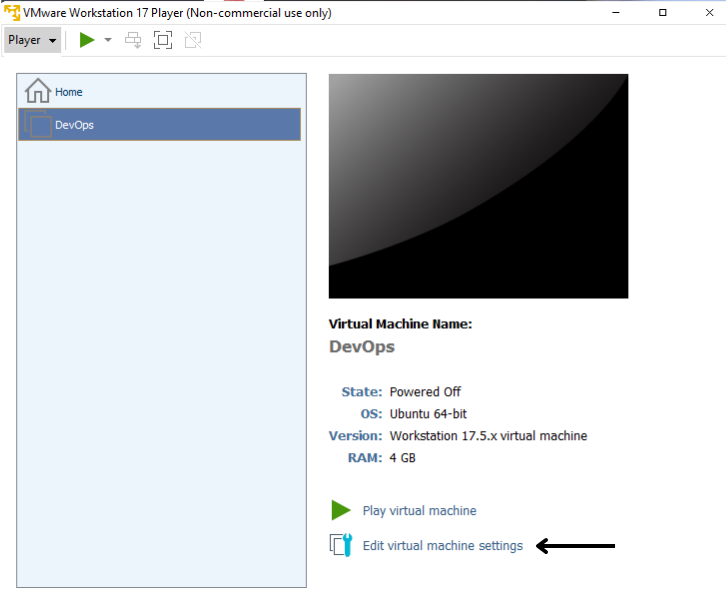
Click on 'Edit virtual machine settings'.
Click on 'Add...' button.

Select 'Hard Disk' and click on' Next >' button.
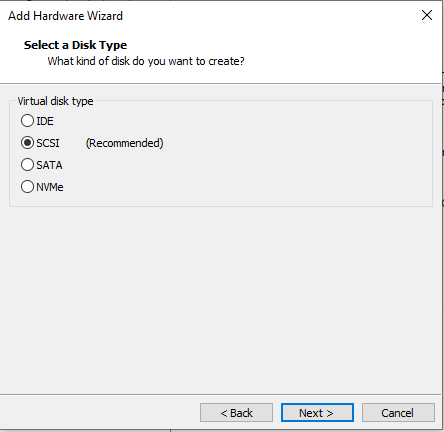
Select the type of your choice and click on 'Next >' button. I am using SCSI.
Select 'Create a new virtual disk' and click on 'Next >' button.
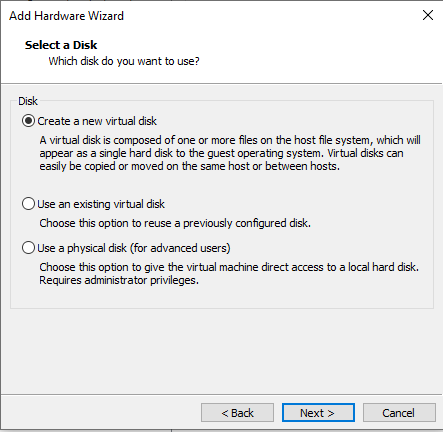
Choose the disk size and click on 'Next >' button.
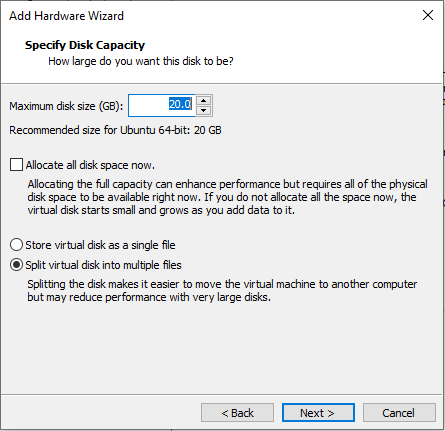
Choose the location to store the disk file and click the 'Finish' button.
Now start your virtual machine.
Commands:
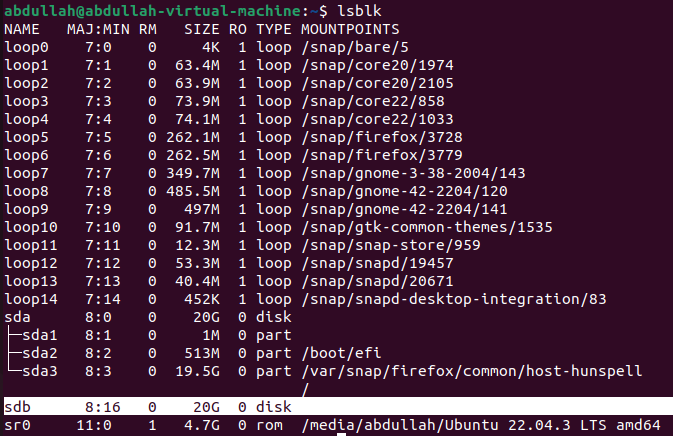
To see the disk is attached or not:
To see that the new disk is attached or not
lsblkis used. The selected line shows that the new disk is attached.
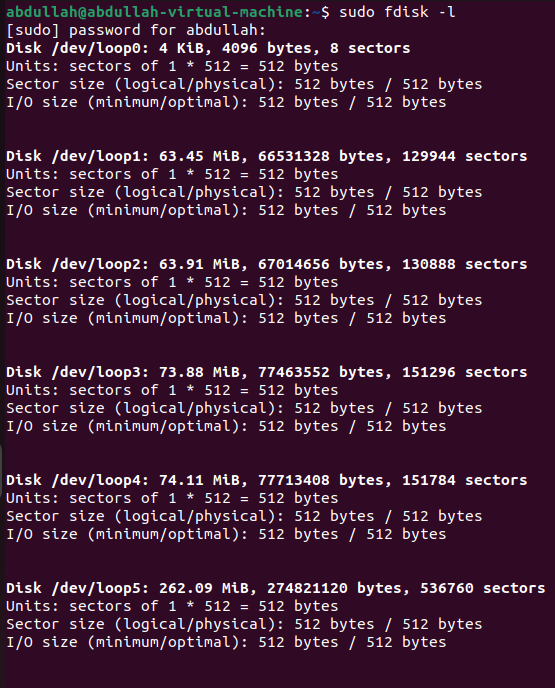
List the partition table:
To list the partition table
sudo fdisk -lis used.
List the partition table of specified disk:
To list the partition table of a specified disk
sudo fdisk -l [disk-name]is used.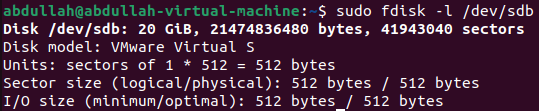
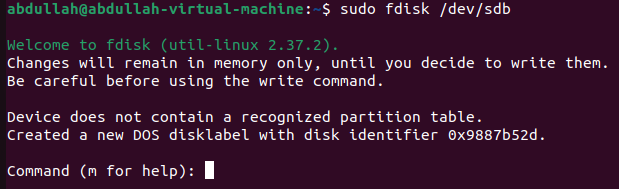
fdisk:
Enter fdisk command prompt:
To enter fdisk command prompt
sudo fdisk [disk-name]is used.
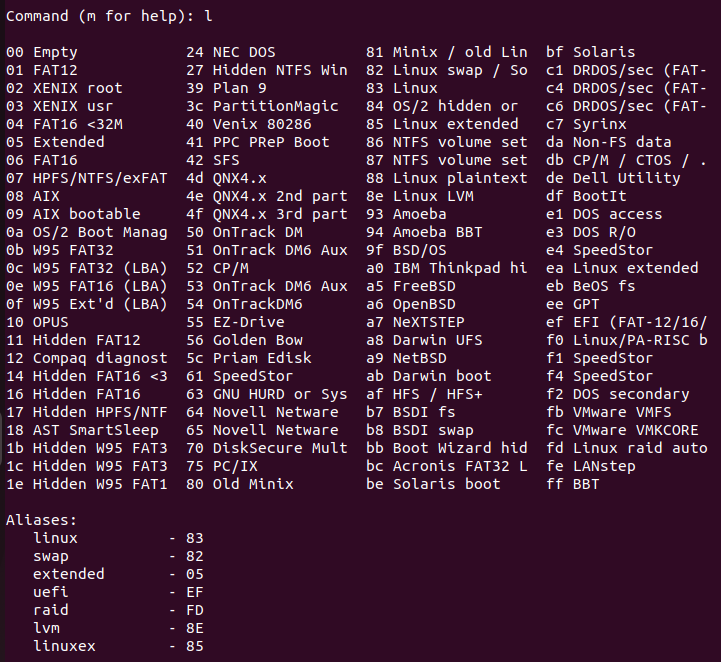
List known partition types:
To list kown partition types
lis used in the fdisk command prompt.
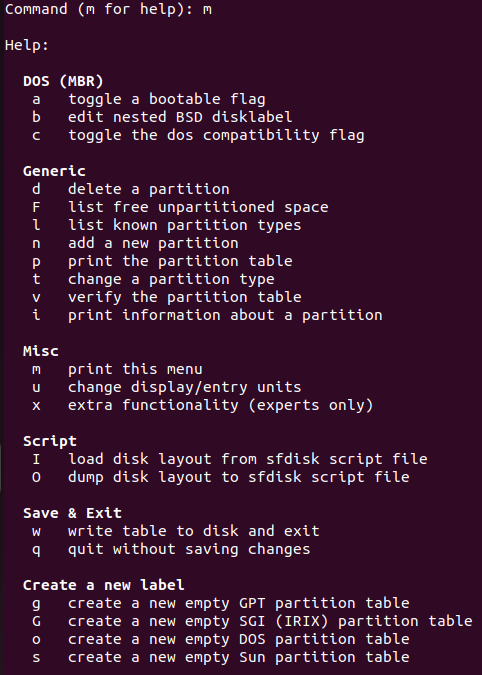
Help:
For help
mis used in the fdisk command prompt.
Print Partition Table:
To print partition table
pis used in the fdisk command prompt.
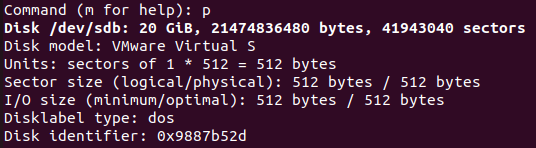
Create a Partition:
To create a partition or add a new partition
nis used in the fdisk commnd prompt.
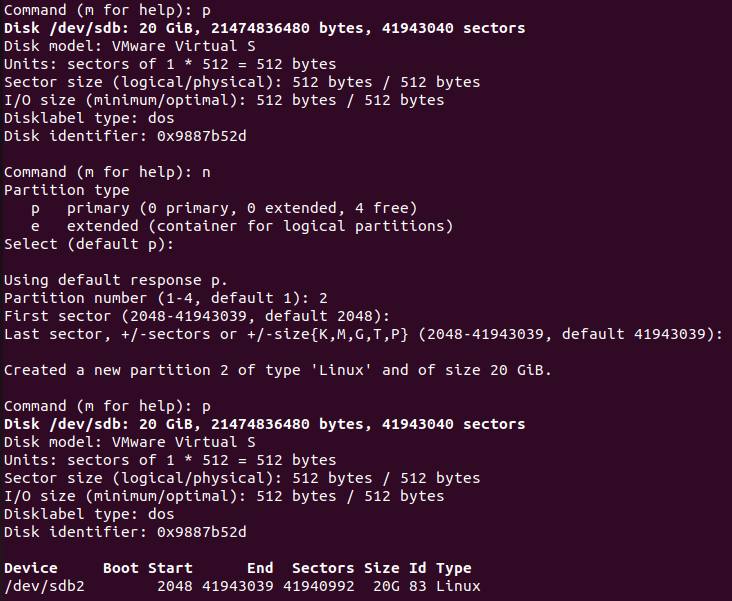
Save table and quit:
To save the table and quit
wis used in the fdisk command prompt.
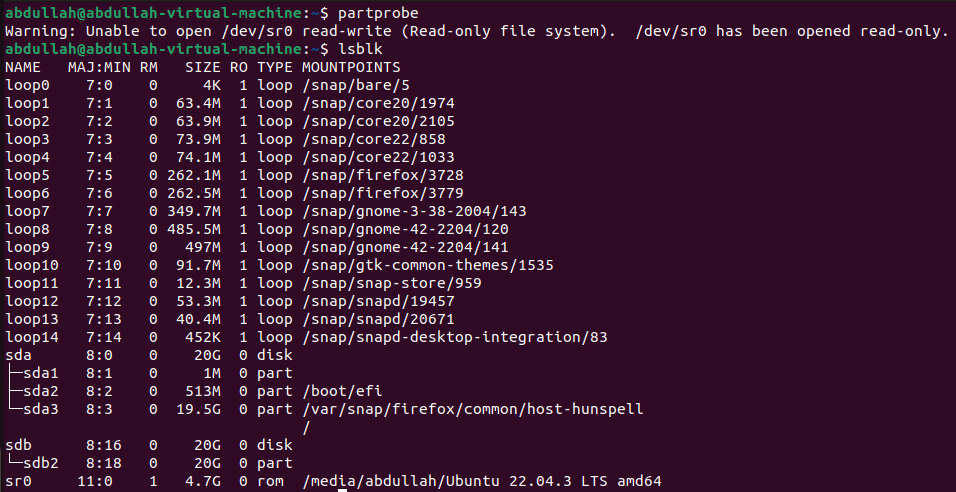
Command After fdisk:
See the updated table without rebooting:
To see the altered partition table without rebooting the system
partprobeis used.
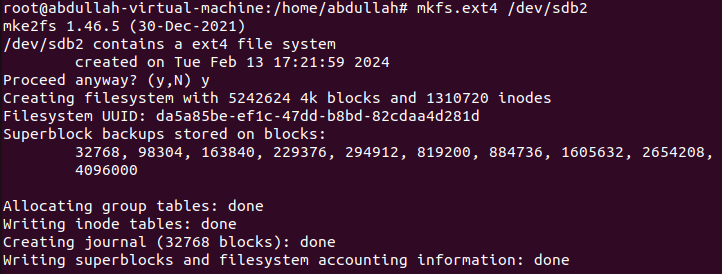
Attach a file system:
To attach a file system with a partition
mkfs.ext4 [partition-name]is used. To attach a file system to the partition you'll have to first move to the root user usingsudo bash.
Mount with mount-point:
To mount the partition
mount [partition-name] [directory-name]is used.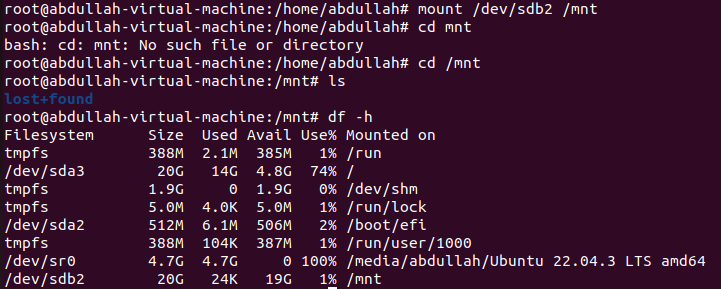
File Systems:
ext4:
The fourth extended filesystem, commonly used in Linux distributions due to its reliability, performance, and support for large file sizes and volumes.
NTFS:
The New Technology File System, developed by Microsoft and commonly used in Windows operating systems. It supports features like file compression, encryption, and access control lists (ACLs).
FAT32:
The File Allocation Table 32-bit file system, commonly used in removable storage devices due to its compatibility with various operating systems and devices.
exFAT:
The Extended File Allocation Table file system, developed by Microsoft and designed for flash drives and external storage devices with large capacities.
XFS:
A high-performance journaling file system commonly used in Linux environments for handling large volumes of data and supporting advanced features like metadata checksums and online resizing.
Btrfs:
The B-tree filesystem, developed for Linux and designed for scalability, reliability, and support for advanced features like snapshots, checksums, and RAID-like functionality.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Abdullah Bin Altaf directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
