Why you should Learn Python in 2024
 Kennedy Ekanem
Kennedy Ekanem
Introduction: Understanding Python's Core Features
Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics.
Now let's break it down:
Open Source: Python's source code is freely available for anyone to inspect, modify, and distribute.
Interpreted: Python code is executed line by line by an interpreter, rather than being compiled into machine code before execution. This allows for easier debugging and more flexibility.
Object-oriented: Python supports object-oriented programming (OOP), a programming paradigm that uses objects – data structures consisting of data fields and methods – to design and organize code.
High-level: Python is considered a high-level programming language, meaning it abstracts away low-level details like memory management and CPU instructions, making it easier for programmers to write and understand code.
Dynamic Semantics: Python has dynamic semantics, meaning that variables do not need to be declared with their data types before they are used, and the type of a variable can change during execution.
As of February 2024, Python remains the most popular programming language according to the TIOBE index.
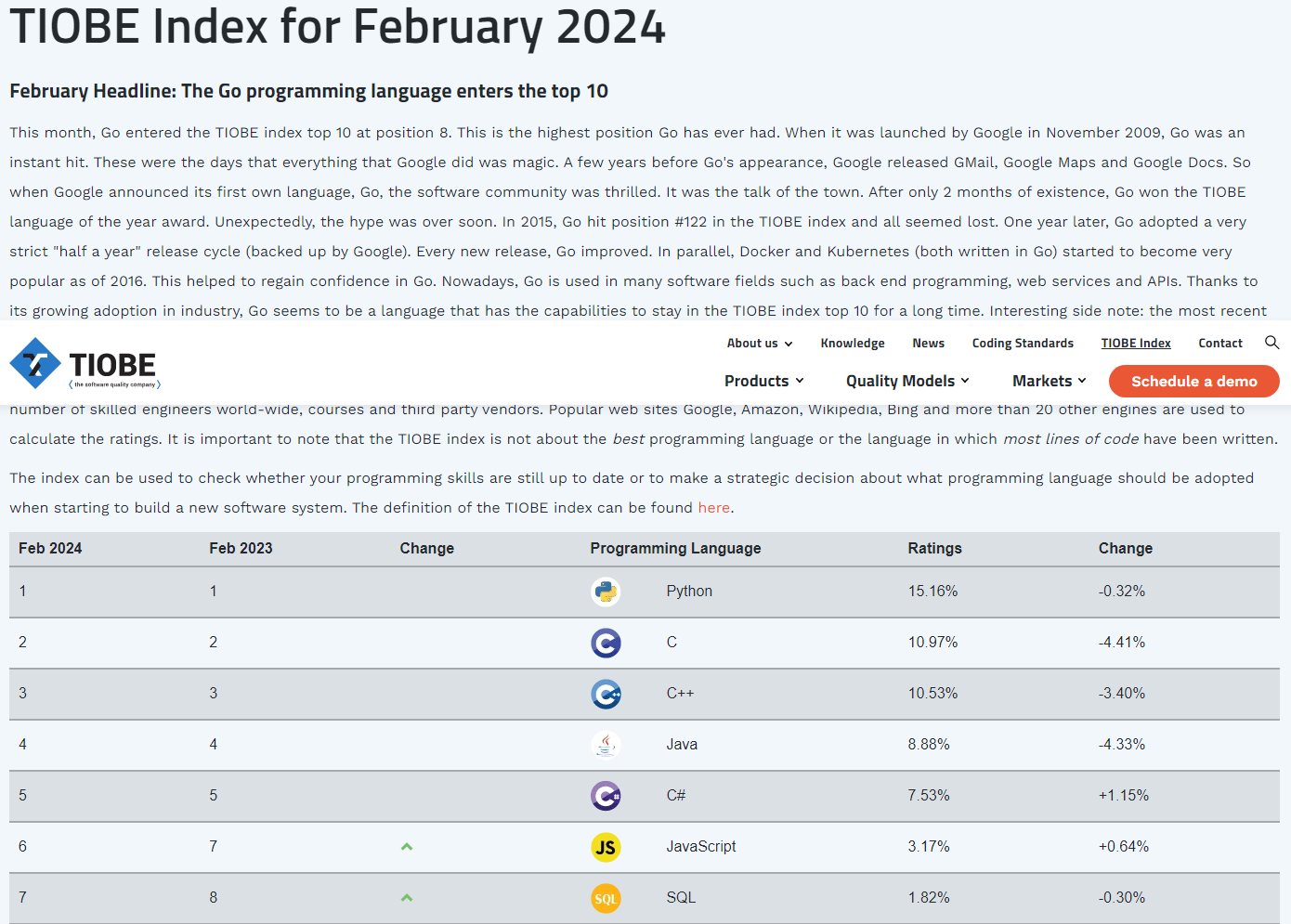
Tiobe Index for February 2024
Why Python Matters: Exploring its Key Benefits
Python's popularity is not only attributed to its core features but also the following advantages:
Intuitive syntax: Python has a syntax that closely resembles natural language, making it easier for beginners to understand and learn. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals who are new to programming.
Ease of writing, reading, and debugging: Due to its human-friendly syntax, Python code is easy to write, read, and debug. This aspect simplifies the process of writing programs and understanding existing codebases, which can enhance productivity and collaboration among developers.
Extensive standard library: Python comes with a comprehensive standard library that includes a wide range of modules and functions for various tasks such as file I/O, networking, database access, and more. This extensive collection of built-in tools eliminates the need for developers to reinvent the wheel and allows them to accomplish tasks efficiently.
Additional libraries and modules: In addition to its standard library, Python also offers a vast ecosystem of third-party libraries and modules that extend its functionality further. These additional libraries cover diverse domains such as data science, web development, machine learning, and more. They are typically well-documented and maintained, providing developers with a wealth of resources to leverage in their projects.

Photo credits: openletter
Python's Role in Software Development: A Comprehensive Approach
Python's versatility makes it indispensable throughout the software development lifecycle, from initial prototyping to ongoing maintenance. Its applications span various stages, including:
Build Control: Python facilitates build control processes, ensuring smooth project management and version control.
Automated Compilation: Python enables automated continuous compilation, enhancing efficiency and ensuring code consistency.
Prototyping: Python's rapid development capabilities make it ideal for prototyping, allowing developers to quickly iterate and test ideas.
Bug Tracking: Python aids in bug tracking by providing tools and frameworks for effective debugging and issue resolution.
Testing: Python's testing frameworks support comprehensive testing methodologies, ensuring software reliability and quality assurance.
Software Maintenance: Python's readability and maintainability simplify software maintenance tasks, enabling developers to efficiently manage and update codebases.
Python's Practical Applications
Here's a detailed overview of what Python can be used for, feel free to study, research, and explore:
Web Development:
Python offers frameworks and tools that facilitate web development by providing libraries and utilities for handling various aspects of web applications, including routing, templating, database interaction, authentication, and more.
Django: A high-level Python web framework that enables rapid development of web applications with a focus on security and maintainability.
Flask: A lightweight Python web framework that is easy to learn and provides a simple yet flexible way to build web applications.
FastAPI: A modern, fast (high-performance) web framework for building APIs with Python, based on Python type annotations and asynchronous programming.

Python web frameworks
Checkout this LinkedIn post Viswathika Kathaperumal to learn more about these Python web frameworks.
CLI Development
Short for Command Line Interface development, it refers to the process of creating software applications or tools that interact with users through text-based commands entered into a command-line interface (CLI)
argparse: A standard library module that helps create command-line interfaces and parse command-line arguments.
Click: A third-party package that simplifies the process of creating command-line interfaces with features like automatic help generation and handling of arguments.
Typer: A library built on top of Click that provides an easy way to create CLI
applications with automatic help documentation, shell completion...
Learn more about Python CLI developmenthere.
GUI Development:
Graphical User Interface development, refers to the process of creating user interfaces for software applications that enable users to interact with the application visually, typically using graphical elements such as windows, buttons, menus, and dialog boxes.
Kivy: A cross-platform Python library for developing multi-touch applications with natural user interfaces.
PyQt: A set of Python bindings for the Qt application framework, allowing the creation of GUI applications with Python.
tkinter: A standard library module that provides a simple GUI toolkit for Python, enabling the creation of basic desktop applications.
Learn Python GUI Development for Desktop – PySide6 and Qt Tutorial
Python Desktop GUI App with SQLite DB (PyQt/PySide/Qt Designer) | Modern GUI
Game Development:
Arcade: A Python library specifically designed for creating 2D video games, suitable for beginners learning to program.
PyGame: A set of Python modules for developing games and multimedia applications, providing access to graphics, sound, and input handling.
Data Science and Machine Learning:
Data science is a multidisciplinary field that combines expertise in statistics, mathematics, computer science, and domain knowledge to extract insights and knowledge from structured and unstructured data.
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on developing algorithms and techniques that enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed.
Keras: A high-level neural networks API written in Python that runs on top of TensorFlow, designed for ease of use and rapid prototyping.
TensorFlow: A powerful open-source library for machine learning and deep learning, with support for deploying models on various platforms.
scikit-learn: A machine learning library that provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis.
Data Analysis, Data Visualization, Scientific Computing, and web scraping:
Data analysis and visualization in Python involve using various libraries and tools to process, analyze, and visually represent data in a meaningful way.
Data Analysis:
Data analysis involves collecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to extract insights, make predictions, and support decision-making. Python provides several powerful libraries for data analysis, such as:
pandas: A versatile library for data manipulation and analysis. It provides efficient data structures (like DataFrame and Series) and data analysis tools for working with structured (tabular) data.
NumPy: A fundamental library for scientific computing in Python. It supports large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a collection of mathematical functions.
SciPy: A library that builds on NumPy and provides many user-friendly and efficient numerical routines, such as routines for numerical integration, interpolation, optimization, linear algebra, and statistics.
scikit-learn: A machine learning library that provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis. It includes various algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, dimensionality reduction, and more.
Data Visualization:
Data visualization involves creating visual representations of data to communicate information clearly and effectively. Python offers several libraries for creating static, interactive, and web-based visualizations:
Matplotlib: A comprehensive library for creating static, animated, and interactive visualizations in Python. It provides a wide range of plotting functions and supports various output formats, including PNG, JPG, PDF, SVG, and more.
Seaborn: A data visualization library based on Matplotlib. It provides a high-level interface for creating attractive statistical graphics that allow you to explore and understand data more easily.
Bokeh: A library for creating interactive and web-based visualizations. It allows you to create interactive plots, dashboards, and data applications that can be embedded in web browsers.
Plotly: A library for creating interactive, web-based visualizations. It supports a wide range of chart types and provides tools for creating customized dashboards and reports.
Dash: A framework for building analytical web applications. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating interactive data visualizations and dashboards that can be deployed on the web.
Scientific computing:
Scientific computing in Python involves leveraging the language and its libraries to solve engineering problems via numerical computation. These tools provide essential functionalities for numerical computation, data manipulation, visualization, machine learning, and symbolic mathematics, making Python a powerful language for scientific computing. NumPy, SciPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, Jupyter Notebook/JupyterLab, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow and PyTorch, Statsmodels, and SymPy.
Web Scraping:
Python's libraries empower developers to scrape websites and create bots for various purposes, from data collection to automated interactions.
Beautiful Soup: A library for parsing HTML and XML documents, providing a simple way to extract data from websites.
Scrapy: A high-level web scraping framework that allows you to crawl websites and extract structured data.
DevOps and Automation:
Python is a valuable language for DevOps and writing scripts and programs due to its simplicity, versatility, and ability to automate various tasks. This process is also called scripting.
Monitoring: Python scripts can be used to automate monitoring tasks and send notifications in case of system issues. Libraries like psutils can be used for process and system monitoring.
Deployment: Python modules like Cuisine and Fabric can be used to automate the deployment, configuration, and management of applications across different environments (development, testing, production).
CI/CD and Configuration Management: Python simplifies the automation of continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, making the process more efficient and error-free.
Cloud Automation: Python SDKs and libraries like Boto (AWS), google-cloud-storage (Google Cloud Platform), and Apache Libcloud can be used to automate the creation, configuration, and management of applications and infrastructure in the cloud.
Platform Independence: Python's platform independence allows it to run seamlessly across multiple environments, making it suitable for DevOps workflows.
Extending DevOps Tools: Python can be used to customize and extend popular DevOps tools like Ansible, Docker, Jenkins, and Kubernetes. Many of these tools are built using Python or have Python interfaces.
Ansible: A tool for provisioning, configuring, and deploying software, often used in DevOps workflows.
Docker Compose: A tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications, enabling you to manage and run complex applications with multiple components.
Python's simplicity, extensive libraries, and cross-platform compatibility make it a valuable asset for automating various DevOps tasks and integrating with existing tools and workflows.
Checkout O’Reilly's Python for DevOps
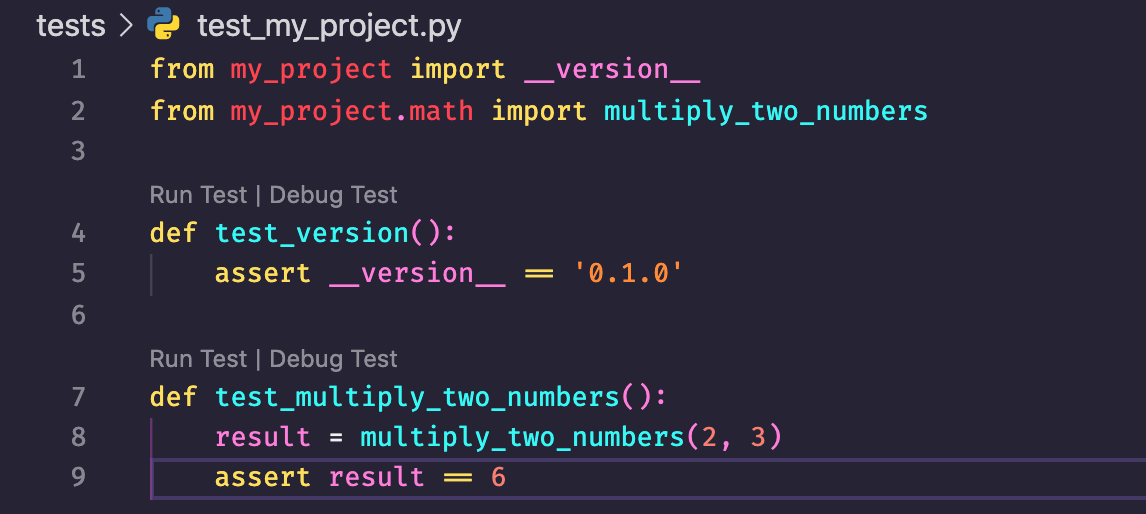
Testing:
Testing is critical for ensuring software quality. Testing should be integrated into the development lifecycle to catch bugs early, ensure code quality, and facilitate future enhancements. Python's testing ecosystem provides a wide range of tools and frameworks to support various testing needs, such as:
Unit Testing: Using
unittestto test individual code units in isolation.Doctest: Writing tests as examples in docstrings to verify code correctness.
pytest: A popular third-party framework that simplifies test writing, providing features like fixture management and test discovery.
Mocking and Patching: Isolating components from dependencies using mocks and patches from
unittest.mock.Test Runners and Automation: Tools like
toxandpytest-xdistto run tests across multiple environments and parallelize execution.Web Application Testing: Frameworks like
SeleniumandSplinterfor browser-based testing and automation.
Embedded Systems and Robotics:
MicroPython: A lean and efficient implementation of Python designed to run on microcontrollers and in constrained environments.
CircuitPython: A programming language based on Python that simplifies coding for microcontrollers, allowing you to write code for physical computing projects.
Microservices:
Python is also well-suited for building microservices, which are small, independent services that work together to form a larger application. Microservices architecture allows for scalability, flexibility, and easier maintenance of complex systems. Python has several frameworks and libraries that support the development of microservices:
FastAPI: As mentioned earlier, FastAPI is a high-performance web framework that can be used to build microservices and APIs. It supports asynchronous programming, making it a great choice for building efficient and scalable microservices.
Flask: a lightweight web framework, is also a popular choice for building microservices. Its simplicity and flexibility make it easy to create small, focused services.
Nameko: a Python framework specifically designed for building microservices. It provides features like service discovery, message queues, and event-driven architecture to simplify the development of distributed systems.
Falcon: is a high-performance Python web framework for building APIs and microservices. It emphasizes simplicity, speed, and reliability, making it a good choice for building efficient and scalable microservices.
Connexion: Connexion is a Python library that simplifies the process of building microservices and APIs using the OpenAPI Specification (formerly known as Swagger). It allows you to define your API using OpenAPI and automatically generates the necessary code.
These frameworks and libraries provide a wide range of functionality and enable Python developers to create diverse applications across various domains.
Find Python projects you can buildhere.
Understand why you’re learning Python.
Firstly, it’s important to figure out your motivations for wanting to learn Python. It’s a versatile language with all kinds of applications. So, understanding why you want to learn Python will help you develop a tailored learning plan. Whether you're interested in automating tasks, analyzing data, or developing software, having a clear goal in mind will keep you motivated and focused on your learning journey. Some questions to ask yourself might include:
What are my career goals? Are you aiming for a career in data science, web development, software engineering, or another field where Python is commonly used?
What problems am I trying to solve? Are you looking to automate tasks, analyze data, build a website, or create a machine learning model, build microservices? Python can be used for all these tasks and more.
What interests me? Are you interested in working with data or building applications? Or perhaps you're intrigued by artificial intelligence? Your interests can guide your learning journey. You can enjoy Python for pure fun: Converting text to ASCII art,
What is my current skill level? If you're a beginner, Python's simplicity and readability make it a great first language. If you're an experienced programmer, you might be interested in Python because of its powerful libraries and frameworks.
To contribute to Community Projects: Contribute to Open Source projects on GitHub or collaborate with other Python enthusiasts on fun coding projects. Join coding communities and participate in hackathons or coding challenges. Land internships such as Google Summer of Code (GSOC), OUTREACHY, RGSOCMLH Fellowship
Finally,
While learning Python can be a valuable skill, it doesn't directly address the issue of low income. The real solution lies in securing a job after gaining proficiency in Python. In my next article, I will explain Python developer jobs and the essential skills you should learn based on real-world job requirements. See the article "What Jobs need python?"
The good news is that utilizing Andrew Hibberman's techniques on 'How to learn anything fast,' even if you're a total beginner, it takes just 20 hours to learn the fundamentals of Python for any purpose.
Recommendations
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Kennedy Ekanem directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Kennedy Ekanem
Kennedy Ekanem
I talk about Linux and Open source