Osi Model
 Dipesh Pal
Dipesh Pal
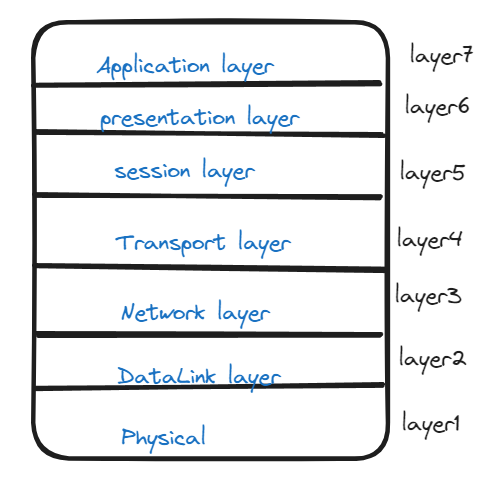
The Open System Interconnection model is a conceptual framework that divides network communication function into seven layers
Every Layer is a package of protocols and provides certain capabilities
Why Its Important?
- It encapsulates every type of network communication across both the software and hardware components
It helps to understand how any request or response architecture works
1.Application Layer(layer 7)
The application layer is concerned with the specific type of application itself and its standardized communication methods. For example, browsers can communicate using Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS), and HTTP and email clients can communicate using POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) and SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
Some more Protocol used in Application layer are - HTTP,FTP,NFS,FMTP,SNMP,TELNET,IRC,NNTP
2.Presentation Layer(layer 6)
Presentation Layer is involved in 3 tasks
-Translation
-Compression
-Encryption/Decryption
Presentation Layer receives the raw data from Application Layer
Translation :-
In this stage the raw data is converted into Binary data.
Compression:-
The large Binary data would be compressed into smaller Binary code
there can be two type of compression -
1)Lossy
2)Lossless
Encryption/Decryption:-
The Binary would be Encrypted by **SSL(Secure Socket Protocol) ,**and in receiving time data will be decrypted
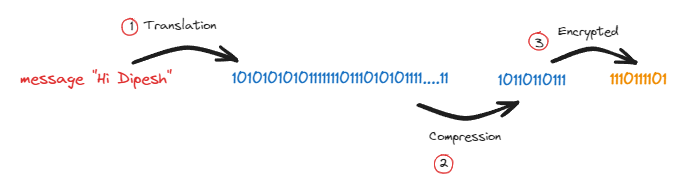
3.Session Layer(layer 5)
Suppose , You have a plan for a party , U have hired some helpers that each activity runs smoothly ,they will help to - setting up , assisting ,Cleaning, Closing
Session Layer is like that helpers , It helps to -
setting up
managing connection
enabling sending & receiving connection
termination of connection
It does three things-
Authentication
Authorization
Session Management(which packet belongs to which file(img/txt/etc) )
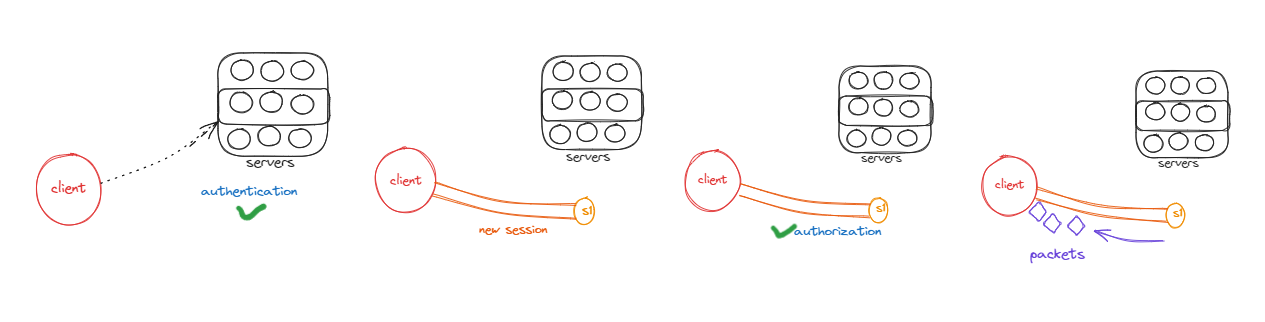
After authentication It creates a new session with the server , Then if authorization is done , It start sending file through packets and after finishing the work it terminates the session.
4.Transport Layer(layer 4)
Transport Layer ensures the relaibility of Communication by
Segmentation
Flow Control
Error Control
Segmentation :-
The data received from Session layer , is divided into small data unit which is called as Segments . Each segment has Sequence No.(To reasamble to correct order) and Port No.(helps each segment to correct application)
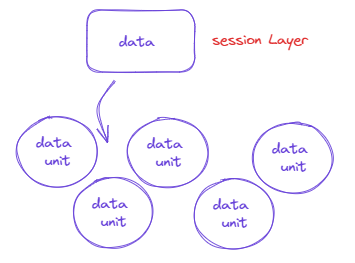
Flow Control :-
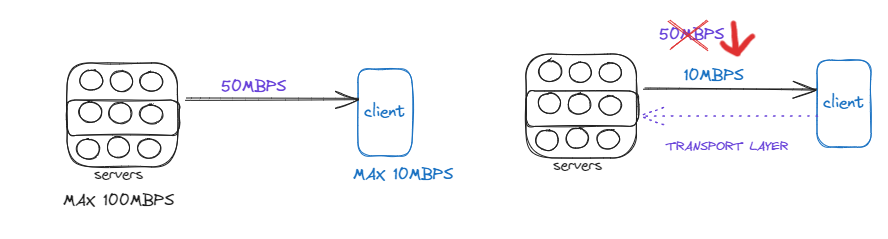
In Flow Control, It used to manage the amount of data sent from one endpoint to another to ensure that the receiving endpoint can handle the data without being overwhelmed. It prevents the sender from sending data faster than the receiver can process it, thereby preventing congestion and packet loss also prevents from sending data slower , so that the transmission will happen smoothly
Suppose ,
A server can transmitted MAX 100MBPS and Client can process data MAX 10MBPS and server starts transmitting at 50MBPS speed
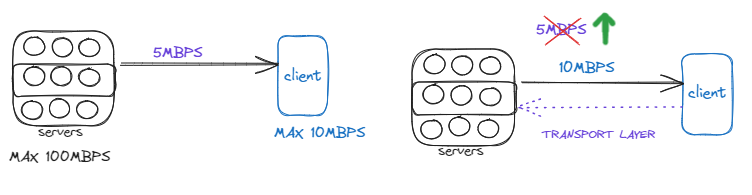
Also If server starts transmitting at lower speed
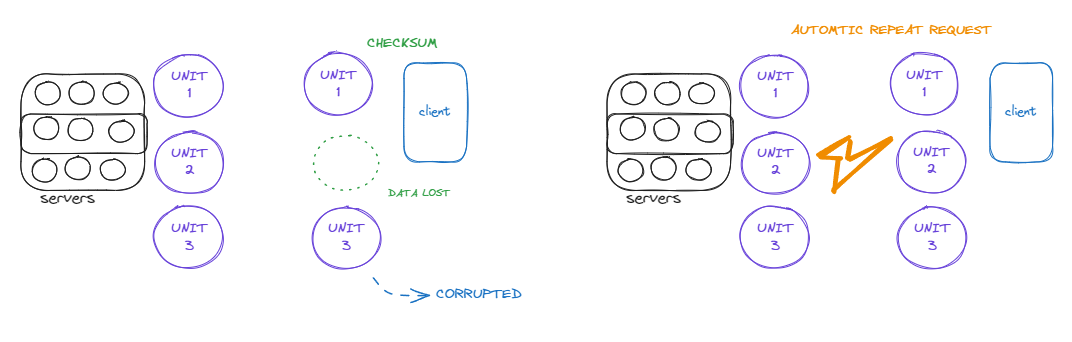
Error Control:-
It involves detecting and correcting errors that may occur during data transmission, thereby ensuring that the data arrives at the destination intact and in the correct order.
If any packet is lost during the transmission and lost data unit is required then it runs Automatic Repeat Request to retrieve the data unit in client side
Protocol which are used in this layer are TCP and UDP
TCP is used when Connection-Oriented Transmission is required , It means It involves feedback of receiving every packet with correct order.
and for that feedback Its slower.
UDP is used when Connectionless Transmission is required .It means there will be no feedback , no matter if any packet is lost or not.
5.Network Layer (layer 3)
After receiving the Segments from Transport Layer Network layer does three things
logical addressing
routing
path determination
Logical addressing:-
In this step It adds two IP Addresses (receiver and sender). It can be IPv4 or IPv6 . The whole thing is called an IP Packet.
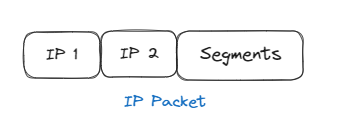
IP Addresses ensures that each data packet reaches its correct destination.
Routing:-
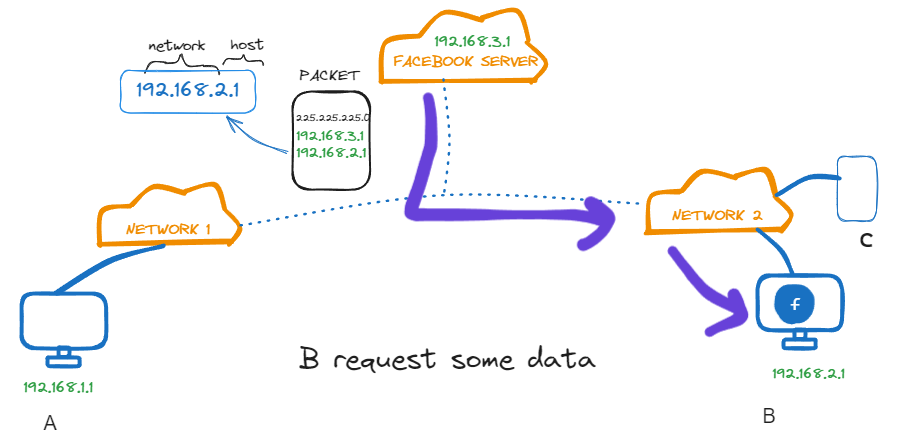
Suppose A is Connected to the Network 1 and B & C both are connected with Network 2.
and B requests Facebook.com for some data ,
Network Layer will add a mask with the Packet . ex :- assume it adds 225.225.225.0 as mask which tells that the first three combination in IP2 represents Network and last combination represents hosts
So packet will reach to Network 2 and then Computer B
Path Determination:-
A computer can connected to a Server through various ways , choosing the best path data delivery is called path determination
Layer 3 uses protocols like :-
OSPF(Open Shortest Path First)
BGP(Border Gateway Protocol)
IS-IS(Intermediate System - Intermediate System)
6.DataLink Layer(layer 2)
There are Two Types of Addressing is happened in OSI model
Logical Addressing - Done at Network Layer
Physical Addressing - Will be done at Datalink Layer
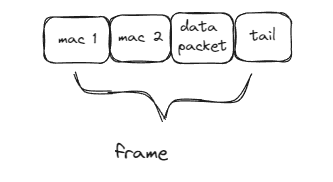
Datalink Layer will add MAC Addresses of the Receiver and sender within the Packet.
What is MAC Address ?It is a 12-digit Alphanumerical Number embedded in Network Interface Card(NIC) of Computer by Manufacturer.
Now Its called Frame.
7.Physical Layer(layer 1)
This is the outer layer of this model.
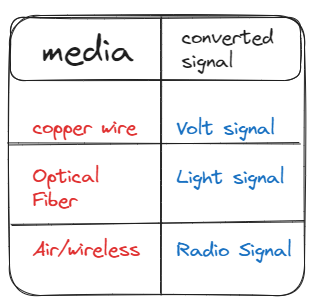
Till Now we recieived Binary Data , Physical Layer will convert it into Signal
And From the receiver side it will convert the signal to binary data and proceed further steps.
According to the media it will convert into different signals
Here media means the connection media not the img/video
Not all internet-based systems and applications follow the TCP/IP model or the OSI model.
Both the OSI and TCP/IP models are open standards. They’re designed so that anyone can use them, or further build them out to meet specific requirements.
Organizations also design their own internal, proprietary standards, including protocols and models, that are closed-source and only for use within their systems.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Dipesh Pal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
