#90daysofdevops { Day -5}
 Nikhil Kathale
Nikhil Kathale
So welcome today is day 5 of the challenge! We will perform some tasks today which will give us some hands-on experience on shell scripting, and as usual, BOOOOOOM! Our confidence 💻💥🚀 is about to skyrocket! Get ready for an exciting day of scripting that will leave you feeling pumped and ready to conquer new challenges! Let's dive in and make today's session unforgettable! 🔥✨
TASK -1
You have to do the same using Shell Script i.e using either Loops or command with start day and end day variables using arguments -
##okay so this is the result , i have return the steps in # please just don't copy the commands as it is cause the directories location may differ from user to user.##
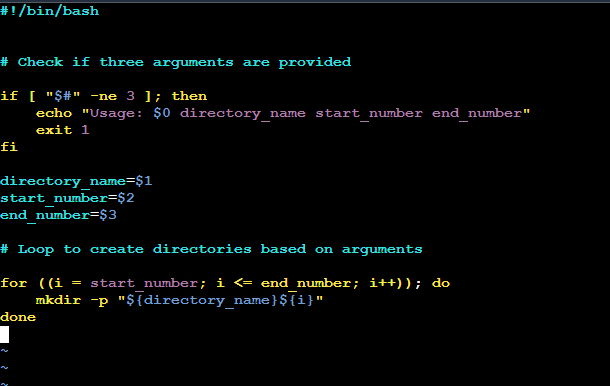
This is the output -
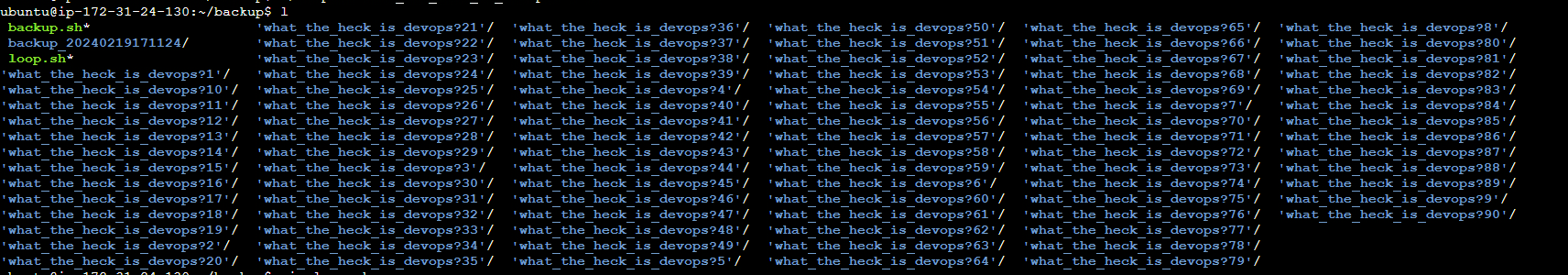
TASK -2
Create a Script to backup all your work done till now.
Here's a breakdown of what the script does:
Set the source and destination directories.
Create a timestamp to use in the backup file name.
Check if the source directory exists.
Create a compressed tarball (.tar.gz) of the source directory and its contents.
Check if the backup was successful.
##okay so this is the result , i have return the steps in # please just don't copy the commands as it is cause the directories location may differ from user to user.##
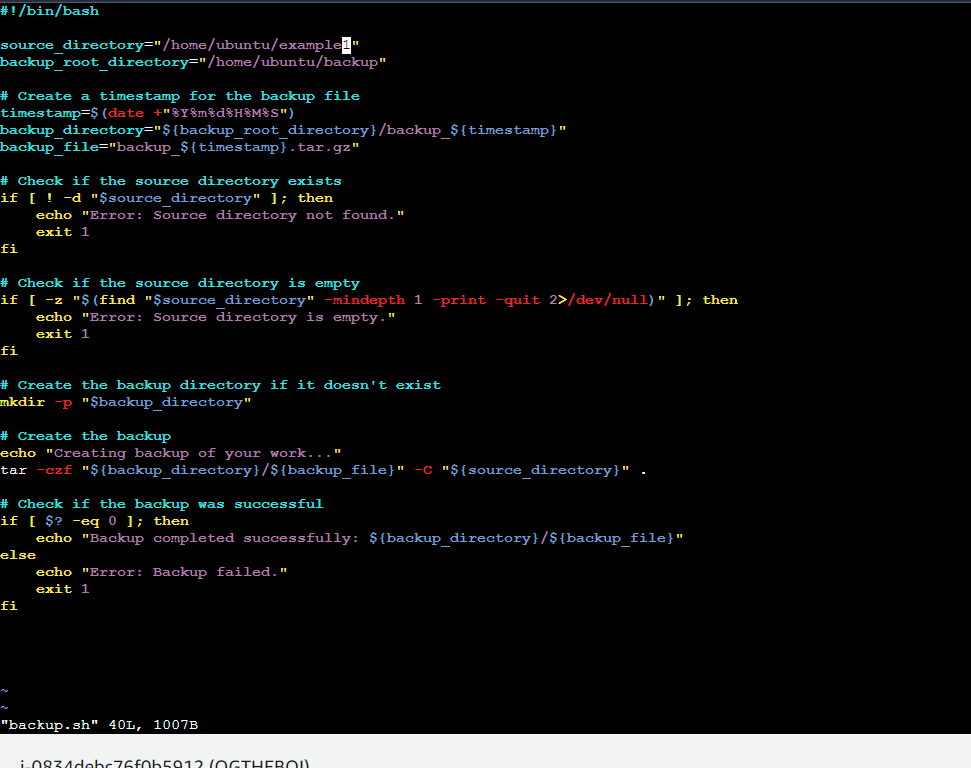
This is the output -

TASK -3
What is Cron and Crontab?
Cron is like the punctual wizard of the Linux world! ⏰✨ It's a time-based job scheduler, always on time, never fashionably late. Imagine if your computer had a personal assistant dedicated to running tasks at specific times – that's Cron for you! 🧙♂️💻
Now, let's talk about its sidekick, Crontab! 📅🤖 Crontab is like the stylish planner where you jot down when you want Cron to sprinkle its magic. It stands for "Cron Table," and it's where you schedule tasks with a dash of elegance! ✨📝
Together, they make the ultimate dynamic duo of automation in the Linux universe! 🚀🌌 So, when you want your tasks to be executed with the precision of a Swiss watch, call in Cron and Crontab – the superheroes of scheduling! 🦸♂️🦸♀️💥
A crontab file consists of lines representing individual jobs. Each line has six fields that define the schedule for a particular task:
Minute (0-59)
Hour (0-23)
Day of Month (1-31)
Month (1-12)
Day of Week (0-7, where both 0 and 7 represent Sunday)
Command to be executed
TASK -4
What is User management ?
In Linux, user management refers to the processes and tools used to create, modify, and manage user accounts on a system. User accounts are essential for controlling access to the system's resources and ensuring proper security measures. Let's explore some key aspects of user management in Linux! 🐧👩💻🔐
Creating Users:
To create a new user, the useradd command is commonly used. For example:
bashCopy codesudo useradd -m username
The -m flag ensures the home directory for the user is created. 🏡
Setting Passwords:
Use the passwd command to set or change a user's password:
bashCopy codesudo passwd username
After running this command, you'll be prompted to enter the new password securely. 🔒
Modifying User Properties:
The usermod command allows you to modify various user properties. For instance, to add a user to a specific group:
bashCopy codesudo usermod -aG groupname username
The -aG flags append the user to the specified group. 🤝
Deleting Users:
To remove a user, the userdel command can be employed:
bashCopy codesudo userdel -r username
The -r flag removes the user's home directory as well, ensuring a complete removal. 🚮
Managing User Groups:
Group management is integral too. The groupadd, groupmod, and groupdel commands help create, modify, and delete groups. 👥
Understanding /etc/passwd and /etc/shadow:
User information is stored in the /etc/passwd file, while encrypted passwords are stored in /etc/shadow. These files play a crucial role in user management. 📁🔐
Superuser and Sudo:
The superuser, often referred to as "root," has elevated privileges. The sudo command allows regular users to execute commands with superuser privileges, enhancing security. 👑🚀
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Tools:
For those who prefer a graphical interface, Linux provides tools like users-admin or gnome-system-tools that offer a user-friendly way to manage users and groups. 🖥️🔧
Linux user management is a fundamental aspect of system administration, ensuring secure and organized access to resources. Whether working from the command line or utilizing graphical tools, effective user management is key to maintaining a well-configured and secure Linux environment! 🌐✨
Connect with me on LinkedIn👔🌐:https://www.linkedin.com/in/nikhil-kathale-27544a1b5/
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nikhil Kathale directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
