Deploy Your Own AI Chat Buddy - The Qwen Chat Model Deployment with HuggingFace Guide
 Farruh
FarruhTable of contents

Alright, you tech-savvy human, brace yourself for a thrilling adventure into the land of artificial intelligence! We're not just dipping our toes here; we're diving headfirst into the deep end with the Qwen Chat Model. What's on the agenda? Setting up a cleverer chatbot than a fox and respecting privacy like a top-notch secret agent. Intrigued? You should be! Let's start our journey by understanding Generative AI and LLM (Large Language Model).
Generative AI
Generative AI refers to the branch of artificial intelligence focused on creating new content, whether text, images, music, or other forms of media. This type of AI leverages machine learning models, particularly generative models, to understand patterns, features, and relationships in large datasets and generate outputs that are new and often indistinguishable from human-created content.
Types of Generative Models
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): A type of neural network architecture where two models (the generator and discriminator) are trained simultaneously. The generator creates new data instances while the discriminator evaluates them. The process results in increasingly more convincing outputs.
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): These models generate new instances similar to the input data. They're often used in image generation.
Transformers: Originally designed for NLP tasks, transformer models like GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) can generate coherent and contextually relevant text. They are also being adapted for generative tasks for other types of data.
Applications
Content Creation: Generative AI can produce original artwork, write stories or articles, compose music, and create virtual environments for games and simulations.
Data Augmentation: It can generate additional training data for machine learning models, helping to improve their accuracy and robustness.
Personalization: Algorithms can tailor content to individual preferences, improving user engagement.
Drug Discovery: Generative models can propose new molecular structures for drugs that could be effective against specific diseases.
Challenges
Quality Control: Ensuring that the generated content meets quality standards and is free of biases present in the training data.
Computational Requirements: Training generative models often requires significant computational power and large datasets.
Interpretability: Understanding how these models make decisions and generate outputs can be challenging, which impacts trust and reliability.
Generative AI continues to evolve rapidly, and its capabilities are expanding the boundaries of what machines can create, offering both exciting opportunities and challenges that need to be managed responsibly.
LLM

What are Large Language Models (LLMs)? They are a type of artificial intelligence based on deep learning techniques that are designed to understand, generate, and work with human language. They are called "large" because they consist of many millions, or even billions, of parameters, which allow them to capture a wide array of language nuances and contexts.
LLMs are trained on vast amounts of text data and use architectures such as Transformer neural networks, which have the ability to process sequences of data (like sentences) and pay attention to different parts of the sequence when making predictions. This makes them particularly effective for a range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as:
Text generation: LLMs can write essays, create poetry, or generate code based on prompts given to them.
Translation: They are capable of translating text between various languages with a high degree of accuracy.
Question answering: LLMs can provide answers to questions by understanding context and extracting information.
Summarization: They can condense long documents into concise summaries.
Sentiment analysis: LLMs can determine the sentiment behind the text, such as identifying if a review is positive or negative.
Why Qwen? A Quick Rundown
Are you on the lookout for an AI that can chat, create content, summarize, code, and much more, all while respecting your right to privacy? Look no further, the Qwen Chat Model is here to transform your data center into a bastion of secure AI-powered interactions.
Qwen isn't your average chatbot. It's built on a massive language model and has been trained on a staggering 3 trillion tokens of multilingual data. This AI marvel understands both English and Chinese intricately and has been fine-tuned for human-like interaction.
Why Go Local with Qwen?

Deploying Qwen locally on your server is about taking control. It's about ensuring that the conversations you have, the data processed, and the privacy promised remain under your purview. Whether you're a business looking to integrate an intelligent chat system, a developer keen on AI research, or simply an enthusiast eager to explore the bounds of conversational AI, Qwen is your go-to choice.
Now, why would you want to host this LLM locally? Three words: Control, speed, and privacy. You keep your data close to your chest, responses come at lightning speed, and you can rest easy knowing that your chatbot isn't blabbing your secrets all over the public services.
Open-Source and Community-Driven
The spirit of innovation in AI is amplified by the open-source community. In keeping with this tradition, the full source code for the Qwen Chat Model is readily available on GitHub for anyone interested in diving into the mechanics of the model, contributing to its development, or simply using it as a learning resource. Whether you're a researcher, developer, or AI hobbyist, you can access the source code at Qwen.
Before You Begin: The Essentials
Before we set sail on this tech odyssey, let's make sure you've got all your ducks in a row:
A Linux server with a GPU card – 'cause let's face it, speed is of the essence.
Python 3.6 or higher – the magic wand of programming.
pip or Anaconda – your handy dandy package managers.
Git (optional) – for those who like their code served fresh from the repository.
NVIDIA drivers, CUDA Toolkit, and cuDNN – the holy trinity for GPU acceleration.
Got all that? Fabulous! Let's get our hands dirty (figuratively, of course).
Crafting the Conversation: Where to Run Your Python Code

Whether you're a die-hard fan of Visual Studio Code, a PyCharm enthusiast, or someone who enjoys the interactive flair of Jupyter Notebooks, the Python code for chatting with Qwen is flexible and IDE-agnostic. All you need is an environment that supports Python, and you're all set to bring your AI chat buddy to life.
Here's a pro tip: If you're using VSCode, take advantage of the built-in terminal to run your Python scripts seamlessly. Just open the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), type Python: Run Python File in Terminal, and let VSCode do the heavy lifting. You'll see Qwen's responses right in your integrated terminal.
For those of you who prefer PyCharm, running your code is just as smooth. Right-click on your script and select Run 'script_name.py', and watch as the IDE executes your conversation with Qwen. PyCharm's powerful tools and debugging features make it a great choice for developing more complex interactions.
And it doesn't end there – there's a whole plethora of IDEs and code editors that welcome Python with open arms. Pick the one that suits your workflow best, and start chatting away!
Setting Up Shop: The Environment
First thing's first, let's prep your Linux server. Ensure your package list is as fresh as the morning breeze and that Python and pip are ready to work their magic:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip
Now for the secret ingredient: a virtual environment. It's like having a personal workspace where you can make a mess without someone yelling at you to clean up:
pip install --user virtualenv
virtualenv qwen_env
source qwen_env/bin/activate
The Toolbox: Installing Dependencies
Before we bring Qwen to life, you'll need some tools. Think of this as gathering ingredients for a Michelin-star meal:
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
pip install transformers
Remember to match PyTorch with your CUDA version – it's like pairing a fine wine with the right cheese.
Awakening Qwen: Model Initialization
Speaking the Same Language: The Tokenizer
Words are just words until Qwen gives them meaning. That's where the tokenizer comes in, turning your musings into something Qwen can chew on:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen-7B-Chat", trust_remote_code=True)
The Brains of the Operation: The Model
Qwen's mind is vast and ready to be filled with your conversations. Here's how to wake up the sleeping giant:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen-7B-Chat", device_map="auto", trust_remote_code=True).eval()
Depending on your hardware, you might opt for different precision modes like BF16 or FP16. It's like tuning your guitar for that perfect pitch.
Engaging in a Continuous Dialogue with Qwen
Now comes the heart-thumping part – it's time to chat with Qwen! But before you get carried away with the back-and-forth, let's talk about something crucial: the art of conversation continuity.
Here's a sneak peek at the kind of repartee you can expect:
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, "Greetings, Qwen! How's life in the digital realm?", history=None)
print("Qwen:", response)
In our opening gambit, we're greeting Qwen with no strings attached – that is, no conversational history. By setting history=None, we're telling Qwen, "This is the start of our chat." Qwen, with nothing but the current prompt to go on, will respond with the freshness of a new interaction.
Now, watch the magic of context unfold:
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, "Any thoughts on the meaning of life, the universe, and everything?", history=history)
print("Qwen:", response)
In this round, we pass along the history we received from our previous exchange. This is like handing Qwen a diary of everything we've talked about so far. With this historical context, Qwen can craft a response that's not just witty or profound but also connected to our ongoing conversation. It's the difference between chatting with a wise friend who knows you and asking questions of a stranger.
Why 'history' Matters: Think of history as the thread that strings our conversation's pearls together. Without it, each response from Qwen would be an isolated pearl, beautiful but solitary. With history, every pearl is knotted securely to the last, creating a beautiful and cohesive string of dialogue. Context is king in conversation, and history is the bearer of context.
Keeping the Conversation Flowing: Just like in human interactions, referring to past comments, jokes, or stories makes for engaging banter. Qwen, armed with the history of the conversation, can recall and reference past exchanges, making for a chat that's as continuous as it's captivating.
Ready, Set, Converse!
Now that you're a pro on the importance of context with the history parameter, fire up that demo script and get ready for an engaging chat with Qwen. Whether you're discussing the cosmos or the best recipe for digital cookies, Qwen's ready to follow your conversational lead with all the grace of a seasoned conversationalist.
Also, you can fire up that script and start the conversation. It's like opening Pandora's box, but instead of chaos, you get delightful banter:
python qwen_chat.py
And there you have it, my friend – you've got your very own AI chat buddy, ready to conquer the world of conversation.
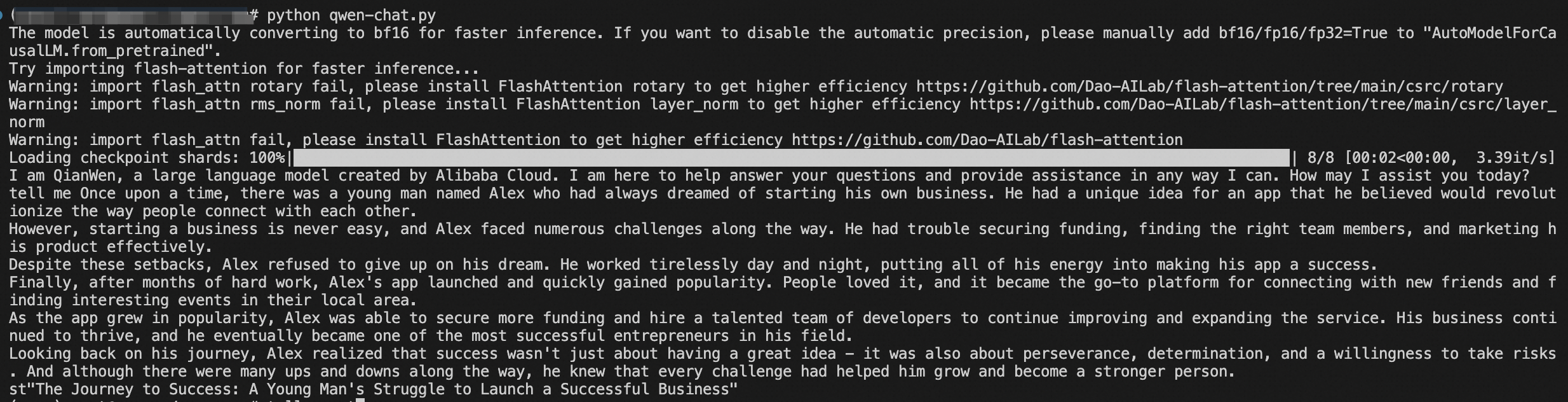
Engage with Qwen: Demo Code on GitHub
For those eager to dive in and start chatting with Qwen, a demo showcasing how to interact with the model is conveniently available. The demonstration code can be found on GitHub, which provides a hands-on example of how to utilize the Qwen Chat Model for conversation. The code is designed to be clear and user-friendly, allowing you to experience the capabilities of Qwen firsthand.
To try out the demo, visit the GitHub repository at Awesome-Qwen and explore the examples directory. Here's how you can clone the repository and run the demo:
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/k-farruh/Awesome-Qwen.git
# Navigate to the repository
cd Awesome-Qwen
# Install the necessary dependencies (if you haven't already)
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run the demo script
python qwen_chat.py
Wrapping Up: The Grand Finale
Congratulations! You've navigated the treacherous waters of AI deployment like a seasoned captain. Qwen is now snugly settled on your server, and your data is as safe as houses.
Explore the capabilities of Qwen, contribute to its development, and join a community of like-minded individuals passionate about advancing the state of AI conversations. Check out the Awesome-Qwen GitHub Repository for more information and to get started.
So, go forth and engage in epic dialogues with your shiny new AI sidekick. And who knows? Maybe Qwen will surprise you with its digital wisdom or a joke that'll have you ROFL.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Farruh directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
