A Beginner's Guide to Cloud Computing
 Divya Mahajan
Divya Mahajan
Link to exam: https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-cloud-practitioner/
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services—such as storage, processing power, databases, networking, and software—over the internet.
- Instead of owning and maintaining physical hardware and infrastructure, users can access and utilize these services remotely through third-party cloud providers on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The Five Characteristics of cloud computing
| Aspect | Description | Example |
| On-demand self-service | Provision computing resources without human interaction from the service provider. | Provisioning virtual machines (VMs) for application testing. |
| Broad network access | Access cloud resources over the internet from any device. | Accessing CRM software from laptops, tablets, or smartphones. |
| Resource pooling and multi-tenancy | Share and allocate resources among multiple users securely without monopolizing entire resources | Hosting multiple virtual servers from different organizations on the same physical hardware. |
| Rapid elasticity and scalability | Scale resources up or down quickly to adapt to workload changes, optimizing cost. | Automatically increasing server capacity during peak shopping seasons for an e-commerce site. |
| Measured service | Pay for actual resource usage, ensuring cost-effectiveness. | Paying for the data transferred by a video streaming service. |
Deployment Models
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Ownership | Third-party providers | Organization-owned | Combination |
| AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform | Company XYZ's private data center | Company ABC using AWS for some services and private servers for others | |
| Accessibility | Over the internet | Within company's network | Both |
| Infrastructure Control | Limited | Full | Varied |
| Security | Provider-managed | Organization-managed | Combination |
| Customization | Limited | Full | Varied |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Depends on infrastructure | Varies based on deployment model |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go | Initial investment + operational costs | Varies based on deployment model |
| Compliance | Provider certifications | Organization control | Varied |
Service Models
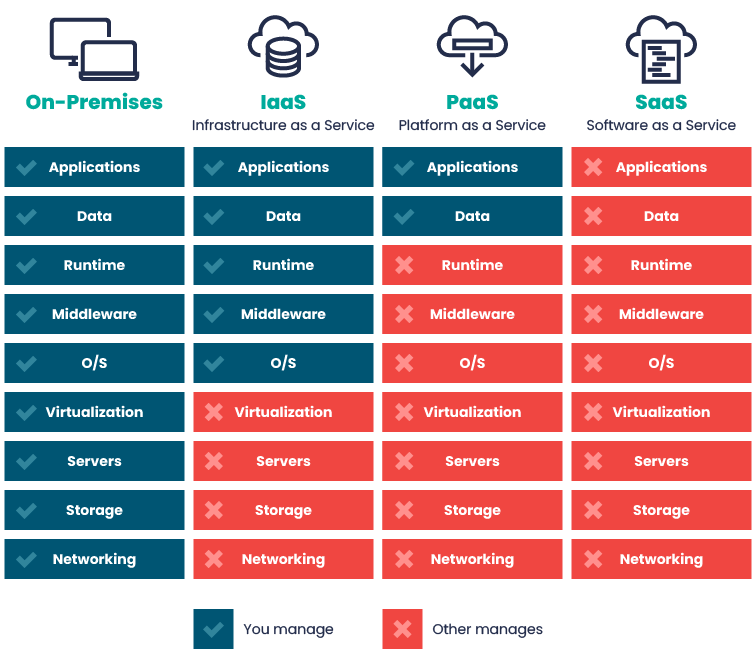
Reference: https://www.nearshore-it.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/nearshore_2023.07.17_graphic_1.png
| Aspect | On-Premise | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Scalability | Limited | High | Platform-dependent | High |
| Flexibility | Limited | Flexible | Moderate | Limited |
| Control | Full | Less | Limited | Minimal |
| Maintenance | User | Provider | Provider | Provider |
| Examples | In-house data centers, self-hosted software. | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform. | Heroku, Google App Engine, Azure App Service. | Salesforce, Google Workspace, Dropbox. |
The Six Advantages of Cloud Computing
| Advantage | Description | Example |
| Trade fixed expense CAPEX for variable expense OPEX | Pay only for the computing resources you use, avoiding upfront investments in data centers and servers. | Paying for storage and processing power used. |
| Lower costs | Access lower costs by leveraging cloud provider's aggregated usage, resulting in reduced pay-as-you-go prices. | Achieving lower infrastructure costs. |
| Stop guessing capacity | Scale resources up or down as required, eliminating the need for forecasting infrastructure needs and dealing with over-provisioning or under-provisioning. | Scaling up server capacity during peak traffic. |
| Increase speed and agility | Provision new IT resources rapidly, accelerating experimentation, development, and deployment processes. | Launching new application features quickly. |
| Reduced TCO and OPEX by avoiding running and maintaining data centers | Shift focus from managing infrastructure to delivering value to customers, freeing resources for innovation and business growth. | Investing in customer-centric applications. |
| Go global in minutes | Deploy applications globally with minimal effort, providing low-latency access and a superior user experience worldwide. | Launching web applications internationally. |
Reference:https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-overview/six-advantages-of-cloud-computing.html
Problems Solved by cloud computing
| Problem | Solution |
| Flexibility | Scale resources as needed for changing demands. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Pay only for resources used, reducing upfront costs. |
| Scalability | Scale resources up or down to handle varying workloads. |
| Elasticity | Dynamically on demand, allocate resources in real-time. |
| High availability | Redundant infrastructure and data replication across multiple locations ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime. |
| Fault tolerance | Maintain reliability against hardware failures + disruptions |
| Agility | Rapidly develop and deploy applications. |
| Data security and compliance | Protect data with robust security measures + certifications |
| Collaboration and remote work | Facilitate teamwork and remote work. |
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Divya Mahajan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Divya Mahajan
Divya Mahajan
Experienced Technical developer with 6+ years' global collaboration. Proficient in Python, Go, React, Next.js, Django, various databases, Cloud & DevOps (AWS EC2, Docker, Kubernetes), and Big Data tools. Skilled in data structures and algorithm, API development, and end-to-end software engineering. Excels in back-end development, front-end design, Root Cause Analysis, and product management to deliver superior user experiences. Holds a master’s degree in computer engineering.