Project: User Management with Bash Scripting
 Tejal
Tejal 
Managing the user accounts on a Linux system is a crucial task for system administrators.
It involves creating, deleting, resetting passwords and listing user accounts efficiently.
Let's start:
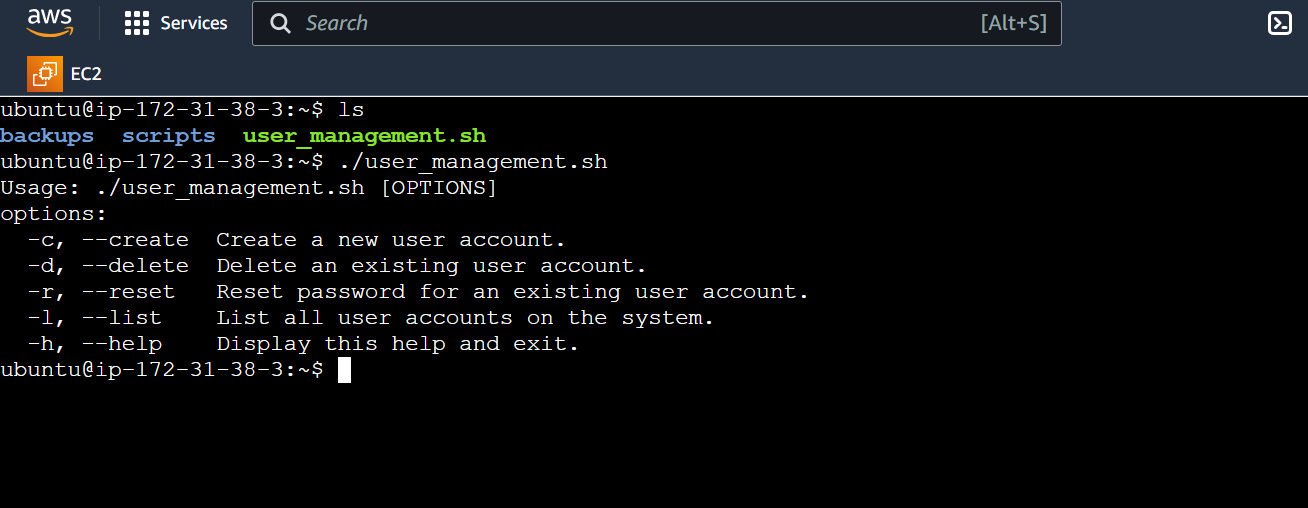
Script Overview: The purpose of user_management.sh script is it provides command-line interface for performing various user management tasks:
#!/bin/bash
# Function to display usage information and available options
function display_usage {
echo "Usage: $0 [OPTIONS]"
echo "options:"
echo " -c, --create Create a new user account."
echo " -d, --delete Delete an existing user account."
echo " -r, --reset Reset password for an existing user account."
echo " -l, --list List all user accounts on the system."
echo " -h, --help Display this help and exit."
}
display_usage
Creating a New User Account: The
create_userfunction guides the administrator through the process of creating a new user account. It prompts the administrator to enter a new username and password.# Function to create a new user account function create_user { read -p "Enter the new username: " username # Check if the user name already exists if id "$username" &>/dev/null; then echo "Error: The username '$username' already exists. Please choose a different username." return 1 fi # Prompt for password (Note: you might want to use 'read -s' to hide the password input) read -p "Enter the password for $username: " password # Create the user account using sudo if sudo useradd -m -p "$password" "$username"; then echo "User account '$username' created successfully." else echo "Error: Failed to create user account '$username'." return 1 fi }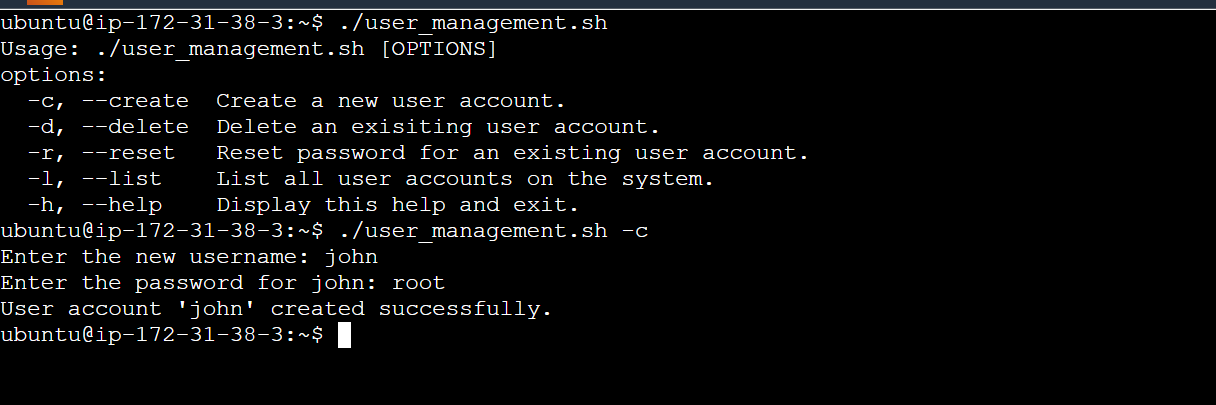
Deleting an Existing User Account: The
delete_userfunction facilitates the deletion of an existing user account. It asks the administrator to enter the username of the account to be deleted. If the username exists, it utilizessudo userdel -rto delete the user account along with their home directory and mailbox. Otherwise, it displays an error message indicating that the username doesn't exist.# Function to delete an existing user account function delete_user { read -p "Enter the username to delete: " username # Check if the username exists if id "$username" &>/dev/null; then if sudo userdel -r "$username" 2>/dev/null; then # Redirect stderr to /dev/null echo "User account '$username' deleted Successfully." else echo "Error: Failed to delete user account '$username'." return 1 fi else echo "Error: The username '$username' does not exist. Please enter a valid username." return 1 fi }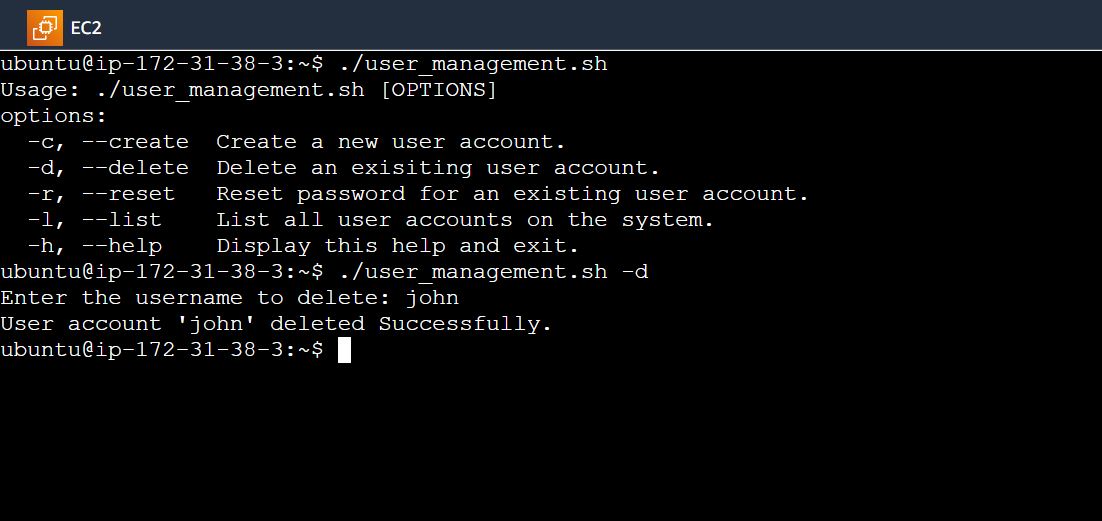
Resetting Password for an Existing User Account: The
reset_passwordfunction enables the admin to reset the password for an existing user account. It prompts the administrator to enter the username for which the password needs to be reset. After verifying the username's existence, it set the new password using echousername:password | chpasswd# Function to reset the password for an existing user account function reset_password { read -p "Enter the username to reset password: " username # Check if the username exists if id "$username" &>/dev/null; then # Prompt for password (Note: you might want to use 'read -s' to hide the password input) read -p "Enter the new password for $username: " password # Set the new password echo "$username:$password" | sudo chpasswd echo "Password for user '$username' reset successfully." else echo "Error: The username '$username' does not exist. Please enter a valid username." fi }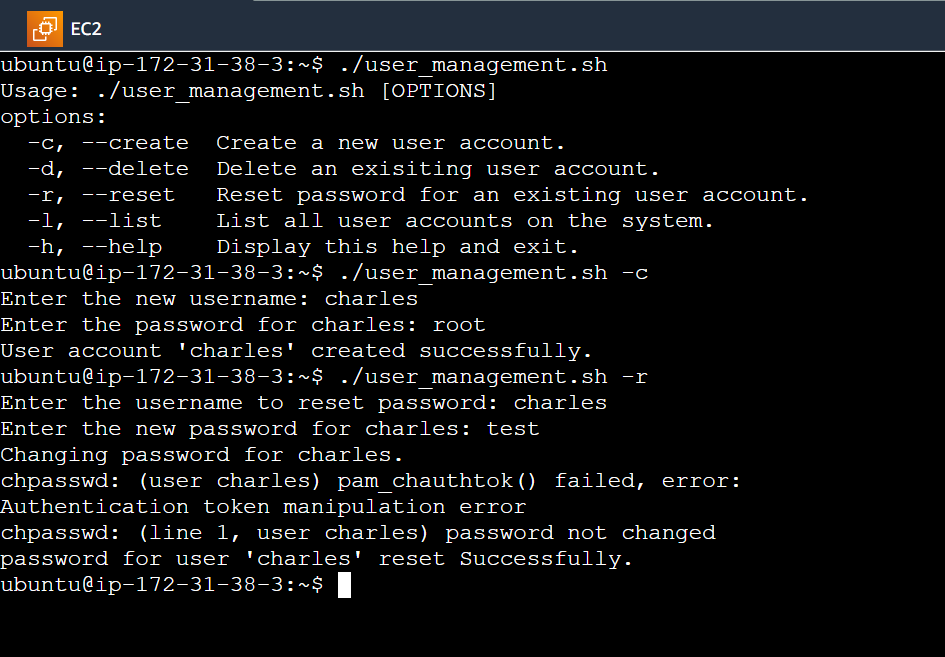
Listing All User Accounts: The
list_usersfunction provides a simple way to view all user accounts present on the system. It reads the etc/passwd file and formats the output to display a list of usernames along with their corresponding user IDs.# Function to list all user accounts on the system function list_users { echo "User accounts on the system:" cat /etc/passwd | awk -F: '{print "- " $1 " (UID: " $3 ")"}' }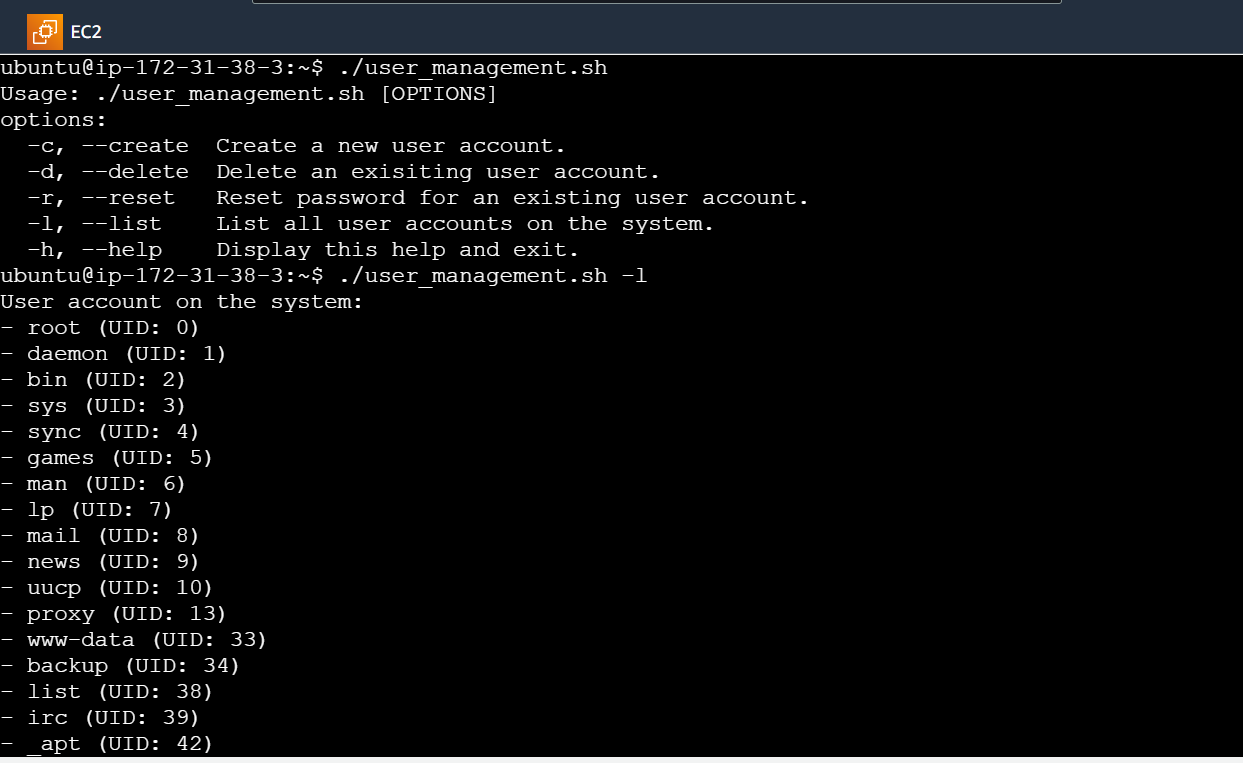
Conclusion: By using Bash scripting, system admin can automate and simplify user management tasks on Linux systems.
GitHub Repository Link:
Happy Learning!!
Thanks For Reading 🙂
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tejal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Tejal
Tejal
Hi, I am Tejal a Java Developer with over 3 years of experience. I’m interested in Cloud ☁ Currently I am upskilling in multi-cloud technologies and DevOps.