JavaScript Local Storage
 Subham Dash
Subham DashTable of contents

In the dynamic landscape of web development, delivering exceptional user experiences is non-negotiable. One key component enabling developers to achieve this goal is local storage. Let's delve into the realm of local storage, its capabilities, and how it empowers developers to create immersive web experiences.
What is Local Storage?
Local storage is a web storage mechanism that allows web applications to store data locally within a user's browser. Unlike session-based storage mechanisms like cookies, local storage persists beyond browser sessions, providing a means to retain data even after the user closes the browser or navigates away from the page.
How Local Storage Works?
It works through Web Apis.
| Methods | Description |
| setItem() | To add data in LocalStorage. |
| getItem() | To retrieve the data from LocalStorage |
| removeItem() | To delete data from LocalStorage using a key |
| clear() | To remove all the LocalStorage items |
| key() | To retrieve data means(key name) from LocalStorage at a specified index |
| length() | To get the number of key/value pairs. |
Data Structure - key: value (value is always string in local storage)
- Local Storage can't store data other than strings. If in case you want to store an object or array then you have to stringify it first then you can store
setItem( )
This method is used to store data in localStorage. It accepts a key as its first argument and then a value as the second argument.
localStorage.setItem("name", "Subham Dash");
As I told localStorage stores data as strings, so if you want to save data such as objects and arrays, you need to convert them to strings using the JSON.stringify() method.
//Storing objects in LocalStorage
const userDetails = {
name: "Subahm Dash",
location: "Bangalore",
age: 26,
hobby: "Writing blogs on web development"
};
localStorage.setItem("userDetails", JSON.stringify(userDetails));
//Storing arrays in LocalStorage
const closeFriends = ["Subham", "Rahul", "Chandan"];
localStorage.setItem("names", JSON.stringify(closeFriends));
getItem()
Use the getItem() method to retrieve data from localStorage. This method accepts a single parameter, which is key used when saving data.
For data that are objects or arrays, we can parse them after getting the values.
localStorage.getItem("name");
// output : 'Subham Dash'
localStorage.getItem("userDetails");
// output : '{"name":"Subahm Dash","location":"Bangalore","age":26,"hobby":"Writing blogs on web development"}'
JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("closeFriends"))
// output: ["Subham", "Rahul", "Chandan"]
removeItem()
Use the removeItem() method to remove data from localStorage. This method accepts an key as a parameter
localStorage.removeItem("name");
localStorage.removeItem("userDetails");
here, from the local storage name and userDetails key-value pairs get deleted.
clear()
Use the clear() method to remove all the data from LocalStorage.
localStorage.clear();
key()
Use key(index) method to retrieve data(key name) from localStorage, where index represents the nth data you want to retrieve.
localStorage.key(3);
length()
Use the length() method to get the number of keys present in the localStorage at the current moment.
localStorage.length()
Size Limit
The limit for most browsers is around 5 to 10 megabytes per origin (i.e., per domain and protocol).
It's essential to note that this limit is for each origin (combination of protocol, hostname, and port), meaning that different subdomains or paths within the same domain may have separate storage limits.
Synchronous or Asynchronous
It is synchronous, which means it will block your main thread and do your computation until and unless it is done, it won't move ahead
Data Persistence
It won't delete until and unless you delete the data from Local Storage either manually, through browser API, or directly via browser settings
Local Storage has no expiration time.
How to Access LocalStorage in Browser
Go to any website or web application and open the browser console by pressing F12 on the keyboard.
Next, click on the Application tab, and in the menu on the left, you will see
LocalStoragein the Storage tab as shown below.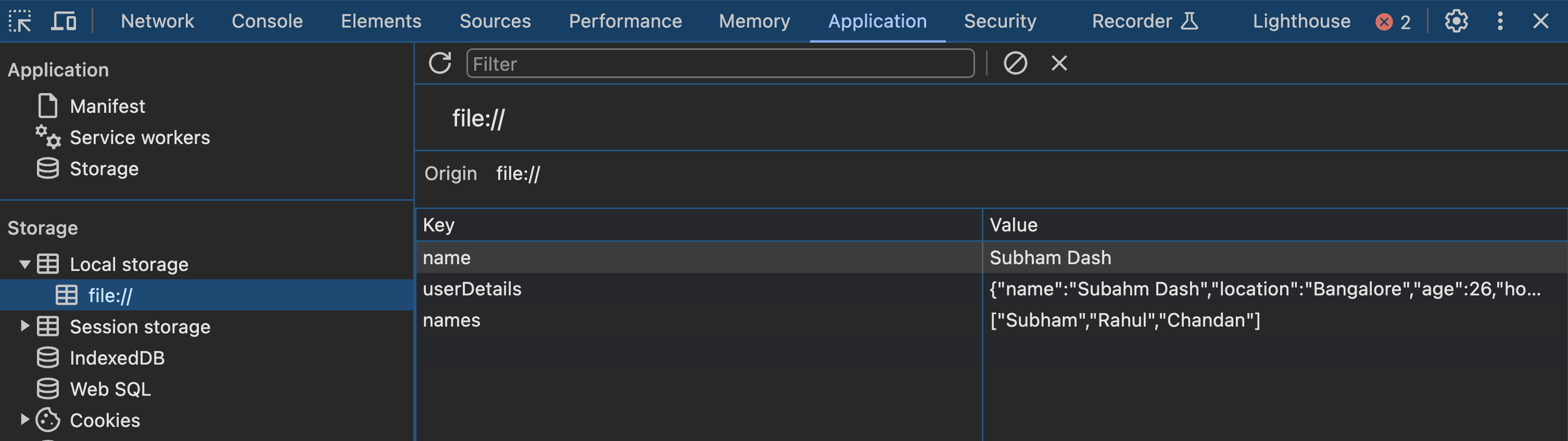
Practical Applications of Local Storage
Personalization
Local storage enables developers to personalize user experiences by storing user preferences, settings, and customization options. This allows for tailored interactions that resonate with individual users, fostering engagement and loyalty.
Offline Functionality
With local storage, web applications can provide offline functionality by caching essential resources, data, and content. Users can continue to access and interact with the application even in the absence of an internet connection, ensuring uninterrupted productivity and convenience.
Performance Optimization
By caching frequently accessed data locally, developers can optimize performance and reduce server load. This not only improves response times but also conserves bandwidth, making web applications more efficient and scalable.
Conclusion
In an era where user expectations are constantly evolving, local storage emerges as a powerful tool for web developers seeking to deliver seamless, personalized experiences. By leveraging the capabilities of local storage, developers can enhance performance, improve security, and unlock new possibilities in web application development. Let's embrace the potential of local storage and embark on a journey to redefine the future of web experiences.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Subham Dash directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Subham Dash
Subham Dash
👋 Hey there! I'm Subham Dash, a front-end developer passionate about crafting intuitive user experiences with React. With a solid foundation in JavaScript and TypeScript, I have expertise in building dynamic and responsive web applications. 🛠️ In my toolkit, you'll find a diverse set of skills and technologies. I possess hands-on experience ranging from backend development using Express and Node.js, to containerization utilizing Docker. Additionally, I have worked on CircleCI and AWS. ⚡️ When it comes to testing, I'm all about ensuring quality and reliability. I dive into automation testing with Selenium and Cypress, ensuring seamless user experiences across all platforms. 💻 Outside of coding, I enjoy exploring the world of databases with SQL, and MongoDB and mastering version control with Git. Continuously learning and growing is my mantra, and I'm always excited to dive into new challenges and technologies. 🌟 Let's connect and share our experiences in frontend development, React, and beyond. Feel free to reach out for discussions, collaborations, or just to geek out about tech. Happy coding! 🚀😊🚀