Test Driven Development in Ruby Using Linux System
 Janak Singh Dhami
Janak Singh DhamiTable of contents
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a powerful methodology that emphasizes writing tests before implementing code, ensuring a more robust and error-resistant software development process. In this blog post, we’ll explore how to implement TDD in Ruby on a Kali Linux system, providing step-by-step guidance for setting up your environment and writing effective tests.
Prerequisites:
Install Ruby*:* Ensure that Ruby is installed on your Kali Linux system. You can use the following command to install Ruby:
sudo apt-get install ruby-fullCreate a new Ruby project: Set up a new directory for your Ruby project. Navigate to the project directory in the terminal.
mkdir gamecd gameFor Simple Test:
Create a ruby file named “game.rb”.
touch game.rbOpen file using Vim.
vim game.rbPaste this code then,
class RockPaperScissors def play(player1, player2) if (player1 == "rock" && player2 == "scissors" || player1 == "scissors" && player2 == "paper" || player1 == "paper" && player2 == "rock") 'Player 1 Wins' elsif(player1 == player2) 'Tie' else 'Player 2 Wins' end end endCtrl+C:wq!Create test file named “game_test.rb”
touch game_test.rbOpen test file
vim game_test.rbPaste this code
require_relative 'game.rb' require 'minitest/autorun' describe "RockPaperScissors" do it "returns 'Player 1 Wins' when rock vs scissors" do # Assemble # Action result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("rock", "scissors") # Assert assert_equal('Player 1 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 1 Wins' when scissors vs paper" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("scissors", "paper") assert_equal('Player 1 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 1 Wins' when paper vs rock" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("paper", "rock") assert_equal('Player 1 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 2 Wins' when scissors vs rock" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("scissors", "rock") assert_equal('Player 2 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 2 Wins' when paper vs scissors" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("paper", "scissors") assert_equal('Player 2 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 2 Wins' when rock vs paper" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("rock", "paper") assert_equal('Player 2 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Tie' when scissors vs scissors" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("scissors", "scissors") assert_equal('Tie', result) end it "returns 'Tie' when paper vs paper" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("paper", "paper") assert_equal('Tie', result) end it "returns 'Tie' when rock vs rock" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("rock", "rock") assert_equal('Tie', result) end endCtrl+C:wq!Run the game_test.rb file
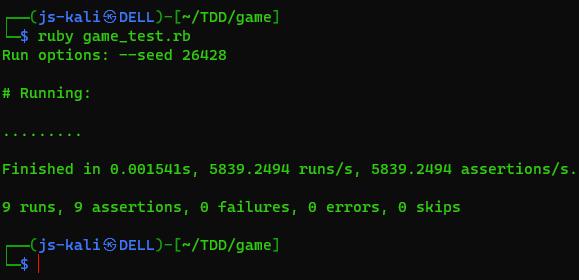
ruby game_test.rb
Conclusion: Test-Driven Development with Minitest in Ruby on a Kali Linux system provides a lightweight yet effective approach to writing reliable code. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can establish a TDD workflow for your Ruby projects using Minitest. Happy testing and coding!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Janak Singh Dhami directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Janak Singh Dhami
Janak Singh Dhami
I'm Full Stack Developer and UX/UI Designer from Nepal