What is Amazon Elastic Block Storage?
 Jay Tillu
Jay Tillu
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a cloud-based storage service offered by AWS. It provides high-performance block storage that can be attached to EC2 instances. Think of EC2 instances as virtual servers in the cloud and EBS volumes as virtual hard drive in the cloud. Whether you're running databases, file systems, or any other application requiring storage, EBS offers the necessary infrastructure.
If you stop or terminate an Amazon EC2 instance, all the data on the attached EBS volume remains available. To create an EBS volume, you define the configuration (such as volume size and type) and provision it. After you create an EBS volume, it can attach to an Amazon EC2 instance. Because EBS volumes are for data that needs to persist, it’s important to back up the data. You can take incremental backups of EBS volumes by creating Amazon EBS snapshots.
Key Features of Amazon EBS
Block storage: EBS stores data in blocks, similar to a hard drive. This allows for faster access to individual pieces of data compared to object storage services.
Persistence: Unlike EC2 instance storage, which is temporary, EBS volumes are persistent. This means your data remains even if you stop or terminate your EC2 instance.
Scalability: EBS allows you to adjust your storage capacity on the fly. Whether you need to scale up to accommodate growing data or scale down to optimize costs, EBS makes it effortless. You can create, attach, and resize volumes as needed without any downtime.
Snapshots: EBS snapshots provide a powerful mechanism for backup and disaster recovery. By taking point-in-time snapshots of your volumes, you can create backups that are stored in Amazon S3. These snapshots serve as a safety net, allowing you to restore volumes or create new ones with ease.
Performance Options: Amazon EBS offers a variety of volume types to cater to diverse workload requirements. Whether you need low-latency SSD storage (General Purpose SSD or Provisioned IOPS SSD) or cost-effective HDD storage (Throughput Optimized HDD or Cold HDD), there's a suitable option for your needs.
High Availability: EBS volumes are designed for high availability within an AWS region. Data is replicated within an Availability Zone (AZ) to protect against hardware failures. Additionally, snapshots are redundantly stored across multiple AZs, enhancing durability and reliability.
Best Practices for Amazon EBS
To make the most of Amazon EBS, consider the following best practices:
Regularly backup your data using EBS snapshots to ensure data integrity and disaster recovery readiness.
Choose the appropriate volume type based on your application's performance requirements and budget constraints.
Utilize EBS encryption to secure your data at rest, protecting it from unauthorized access.
Monitor EBS volume metrics and performance to proactively address any issues and optimize resource utilization.
What is Amazon EBS Snapshots?
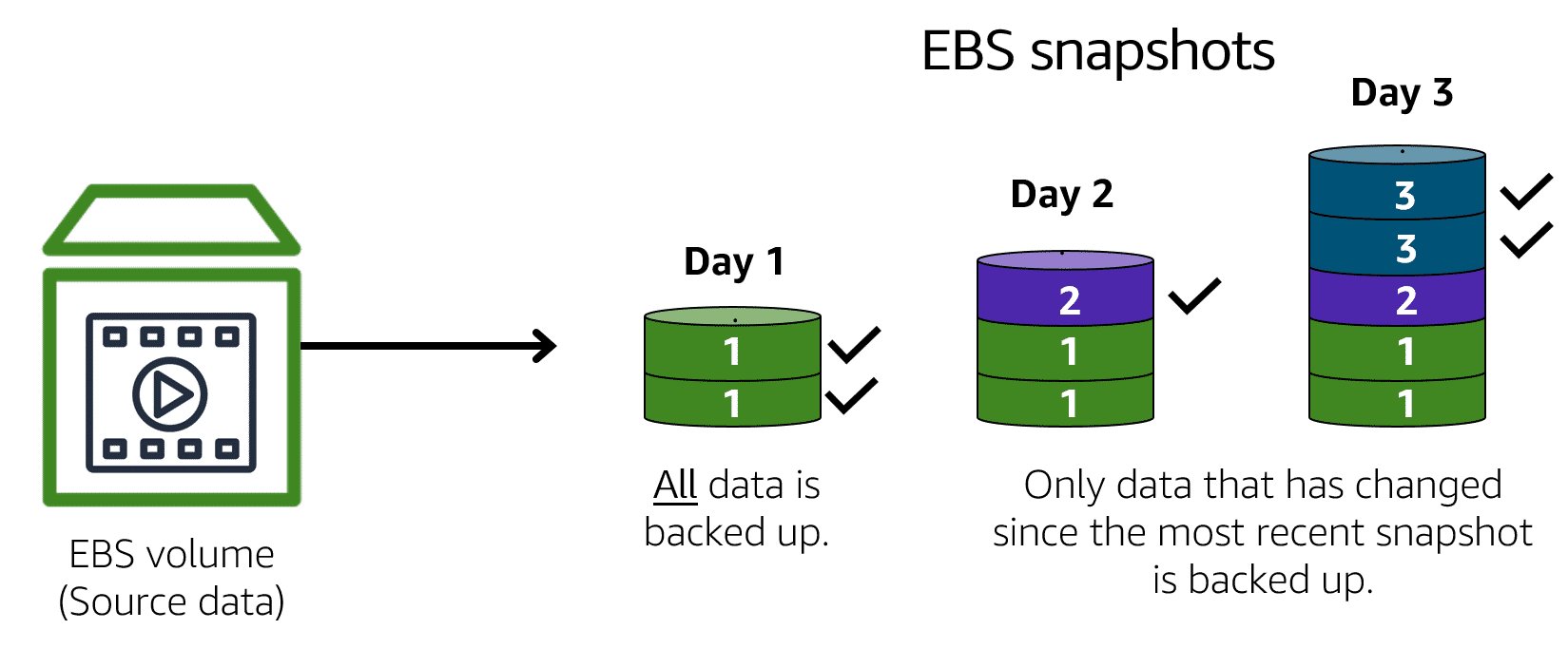
Amazon EBS snapshots are essentially point-in-time backups for your EBS volumes. They capture a complete copy of all the data on your EBS volume at a specific moment. These snapshots are saved in Amazon S3, providing a separate and secure location for your backups, independent of the original EBS volume.
Key points about EBS Snapshots
Purpose: EBS snapshots are primarily used for data protection. They allow you to recover your data in case of accidental deletion, corruption, or for disaster recovery scenarios.
Storage: Snapshots are stored in S3, a highly durable and scalable object storage service offered by AWS. This separation ensures your backups are safe even if something happens to your EBS volumes.
Efficiency: EBS snapshots are incremental backups. This means they only capture the data blocks that have changed since the last snapshot, not the entire volume every time. This saves on storage costs and reduces snapshot creation time.
Management: You can create EBS snapshots manually through the AWS Management Console, AWS Command Line Interface (CLI), or AWS SDKs. Additionally, AWS Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM) allows you to automate snapshot creation based on defined schedules and retention policies.
Restoration: EBS snapshots can be used to restore your EBS volume data. You can restore a snapshot to a new EBS volume and then attach it to your EC2 instance to regain access to your data.
Overall, EBS snapshots are a fundamental tool for protecting your data stored on EBS volumes in the AWS cloud.
Difference between Amazon Elastic Block Storage and Instance Store
| Feature | Amazon EBS | Instance Store |
| Storage Type | Block storage | Local storage on the instance |
| Persistence | Persistent | Non-persistent (ephemeral) |
| Durability | Highly durable | Not durable; data can be lost if an instance fails or is stopped |
| Snapshot | Yes (point-in-time backups) | Not available |
| Encryption | Yes | No |
| Performance | Consistent performance | Performance can vary based on instance type and workload |
| Volume Type | SSD (gp2, io1), HDD (st1, sc1) | Depends on instance type and generation |
| Resize | Yes (online) | Not available for instance stores |
| Backup | Snapshots | Not applicable |
| Use Cases | Databases, boot volumes, long-term storage | Temporary data, cache, scratch space |
| Cost | Pay for provisioned capacity (size and performance) | No additional cost beyond the instance cost |
| Availability Zone | Available in any AZ within a region | Tied to a specific instance in an AZ |
| Advantages | Data persistence, backup, scalability | High I/O performance, low latency |
| Disadvantages | Additional cost, single point of failure | Data loss risk, limited use cases |
Conclusion
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) serves as a foundational component in AWS cloud architectures, offering scalable, durable, and high-performance storage solutions. With its persistence, scalability, and snapshot capabilities, EBS empowers businesses to build resilient and efficient applications in the cloud. By leveraging the features and best practices of Amazon EBS, organizations can unlock the full potential of their cloud infrastructure and drive innovation with confidence.
Learn More About Cloud Computing
Follow me for more such content
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Jay Tillu directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Jay Tillu
Jay Tillu
Hello! I'm Jay Tillu, an Information Security Engineer at Simple2Call. I have expertise in security frameworks and compliance, including NIST, ISO 27001, and ISO 27701. My specialities include Vulnerability Management, Threat Analysis, and Incident Response. I have also earned certifications in Google Cybersecurity and Microsoft Azure. I’m always eager to connect and discuss cybersecurity—let's get in touch!