Linux for DevOps
 Niharika reddy
Niharika reddyLinux is an Open source UNIX-based operating system.
What is an Operating System(OS)?
An operating system is a collection of programs that coordinates the operation of computer hardware and software.
In simple terms, the hardware and the user cannot directly communicate with each other. They need an intermediary, which is the operating system (OS). The user communicates with the software, and the software communicates with the hardware through the OS. Therefore, the OS acts as an intermediary between the user (via software applications) and the hardware, facilitating communication, managing resources, and providing a platform for running applications.
Why Linux is popular?
Linux is popular for the following features:
Open Source
Highly Secure
Different Distributions are provided
Fast
Multi-user and Multi-tasking
Linux Architecture:
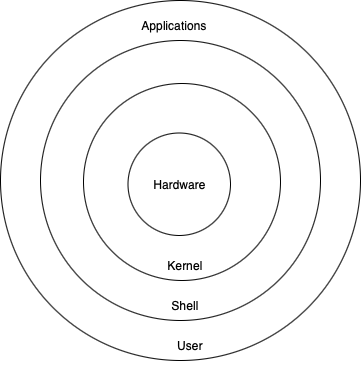
Hardware: This layer consists of physical components like RAM, CPU, Hard drive, etc.
Kernel: It is the heart of an OS. Kernel directly interacts with the hardware.
Shell: An interface between human-readable and machine language. Shell sends the message to Kernel and Kernal converts it to binary language.
File System Hierarchy:
| No. | Linux | Windows |
| 1 | We call directory | We call folder |
| 2 | We call the root user | We call administrator |
| 3 | We call package | We call software |
| 4 | We call Kernel | We call OS |
| 5 | We use ‘/’ | We use ‘\’ |
Commands: Following are a few Linux Commands
ls -Directory listing.
ls -al - Formatted listing with hidden files.
ls -lt - Sorting the formatted listing by time modification.
cd dir -Change directory to dir.
cd - Change to the home directory.
pwd - Shows the present working directory.
mkdir dir - Create a directory dir.
cat>file - Placed the standard input into the file.
touch file - Create or update the file.
rm file - Deleting the file.
rm -r dir - Deleting the director.
rm -f file - Force to remove the file.
rm -rf dir - Force to remove the directory dir.
vi/vim file, nano file - Editors.
cp file1 file2 - Copy the contents of file1 to file2.
cp -r dir1 dir2 - Copy dir1 to dir2;create dir2 if not present.
mv file1 file2 - Rename or move file1 to file2, if file2 is an existing directory.
grep pattern file - Search for a pattern in the file.
cat file - Displays the content of the file.
head file - Displays the top 10 lines of the file.
tail file - Displays the bottom 10 lines of the file.
sudo su - Superuser.
chmod - Change permission
chown - Ownership permission
chgrp - Group permission.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Niharika reddy directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
