Day 38 - Embarking on the AWS Journey: A Beginner's Guide to Cloud Basics! 🚀☁️
 Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
🌟 Day 38 of #90DaysOfDevOpsChallenge! 🚀 Today, let's embark on a new journey with AWS Basics! ☁ Congratulations on how far you've come! Let's dive into the world of Amazon Web Services (AWS), one of the leading cloud providers. 💼🔍
🔑 Start by understanding AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM allows you to securely control access to AWS resources, manage permissions, and control user authentication. Learn more about IAM here: IAM Overview
Task 1️⃣: Creating an IAM User and Launching a Linux Instance
IAM User Creation:
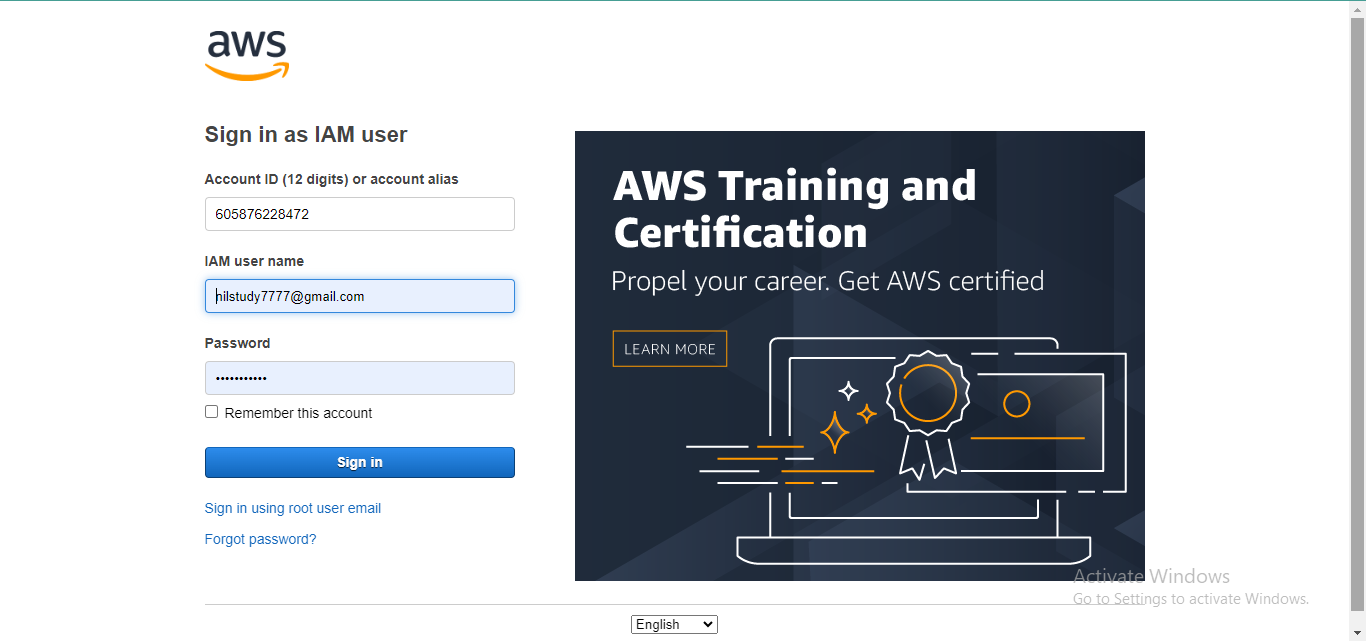
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and navigate to IAM.
- Click on "Users" and then "Add user".
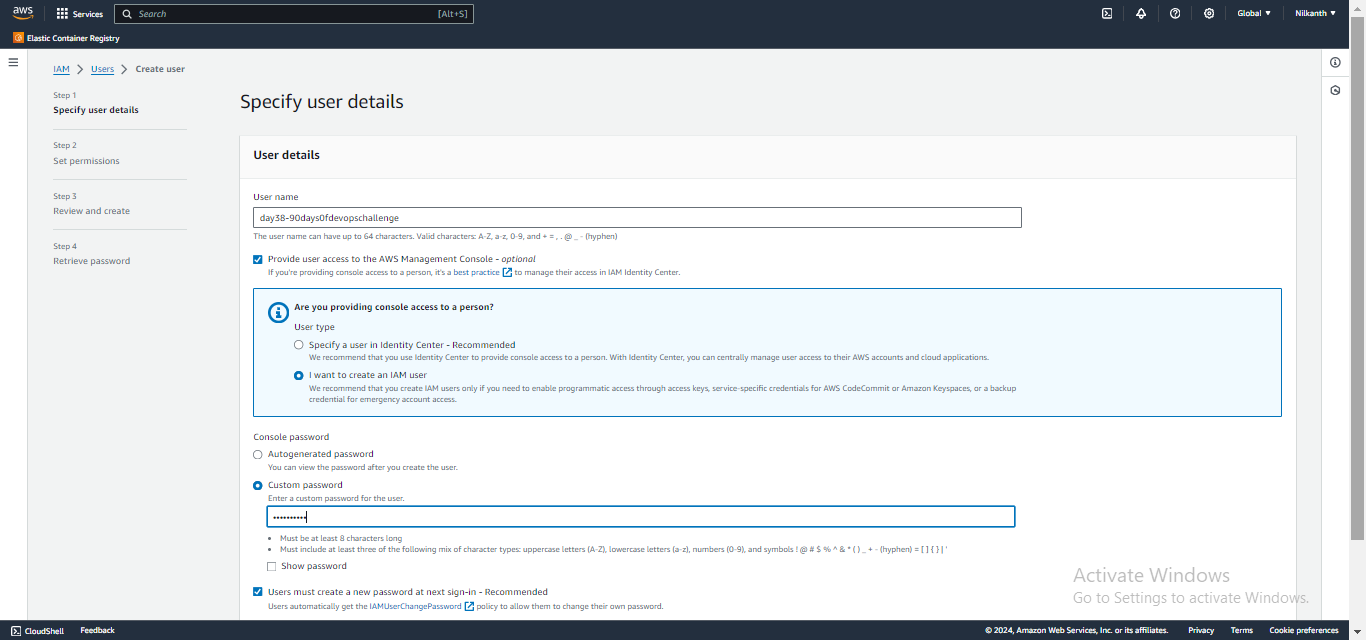
Enter a username of your choice, select "Programmatic access", and click "Next: Permissions".
- Choose "Attach existing policies directly" and select
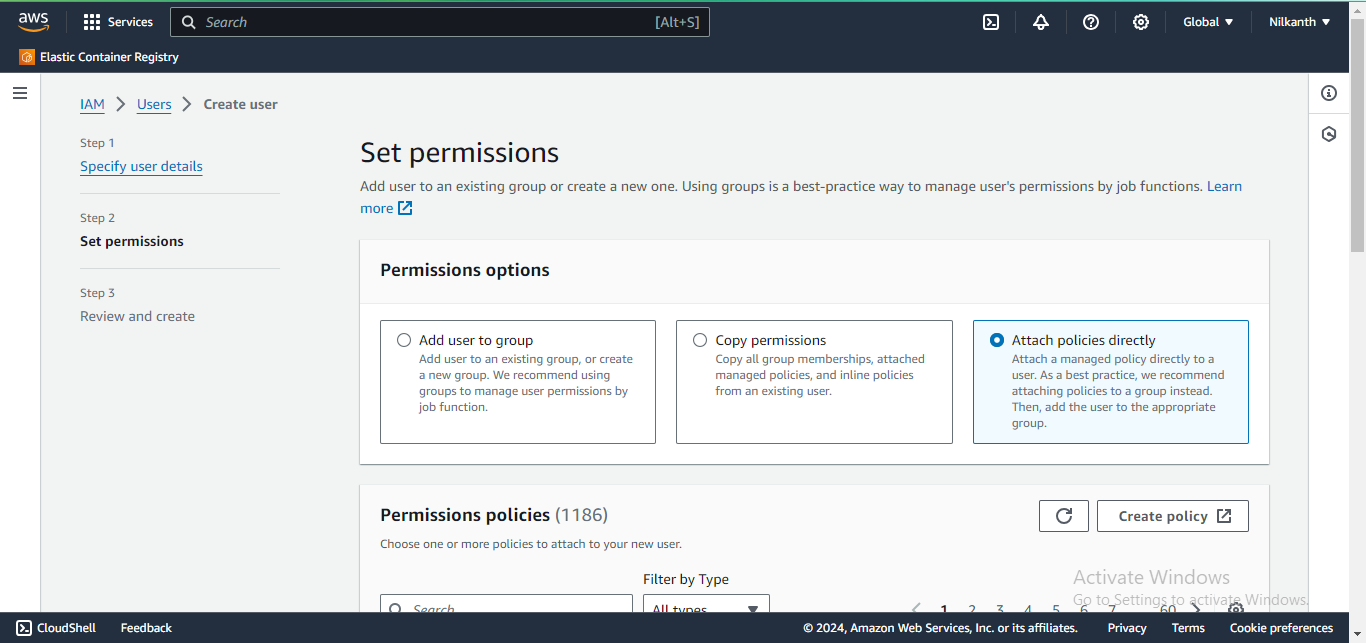
- "AmazonEC2FullAccess". Click "Next: Tags" and then "Next: Review".
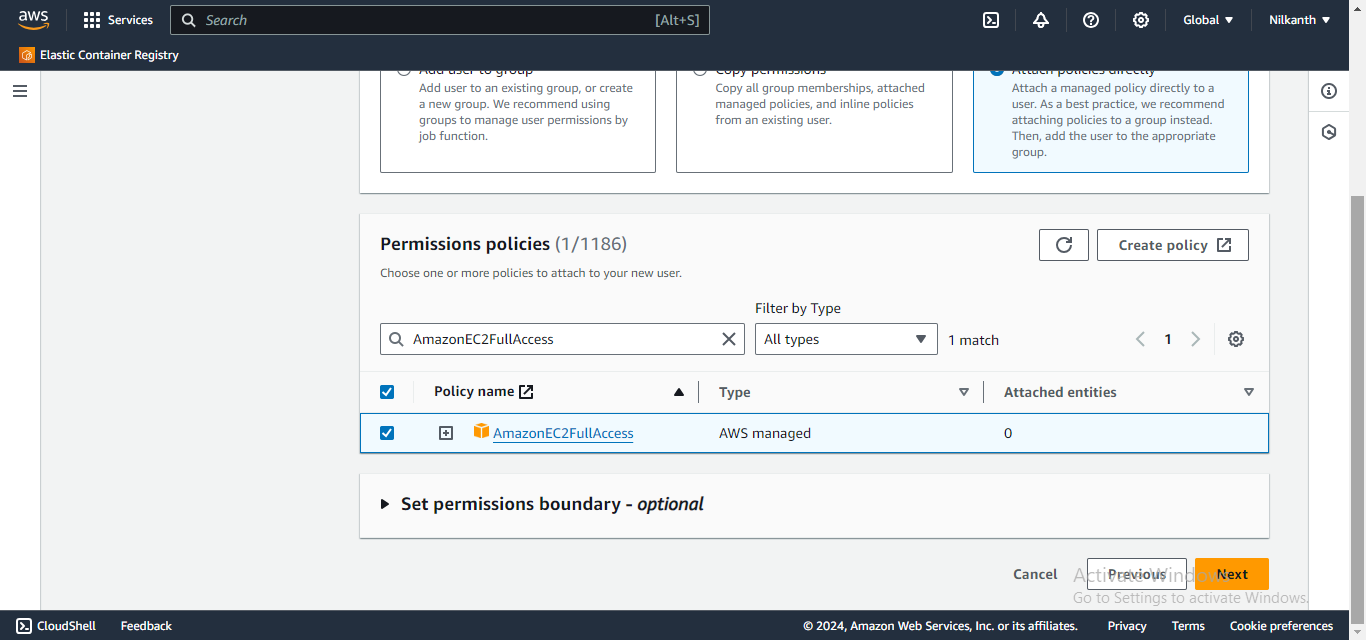
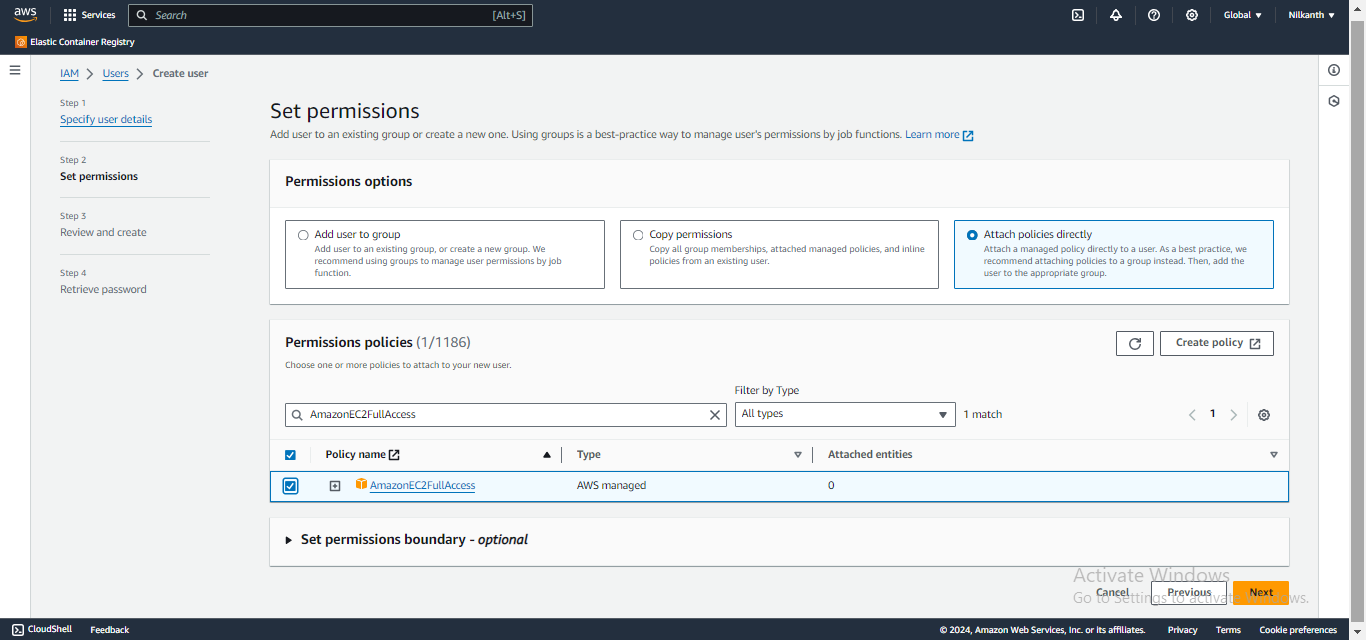
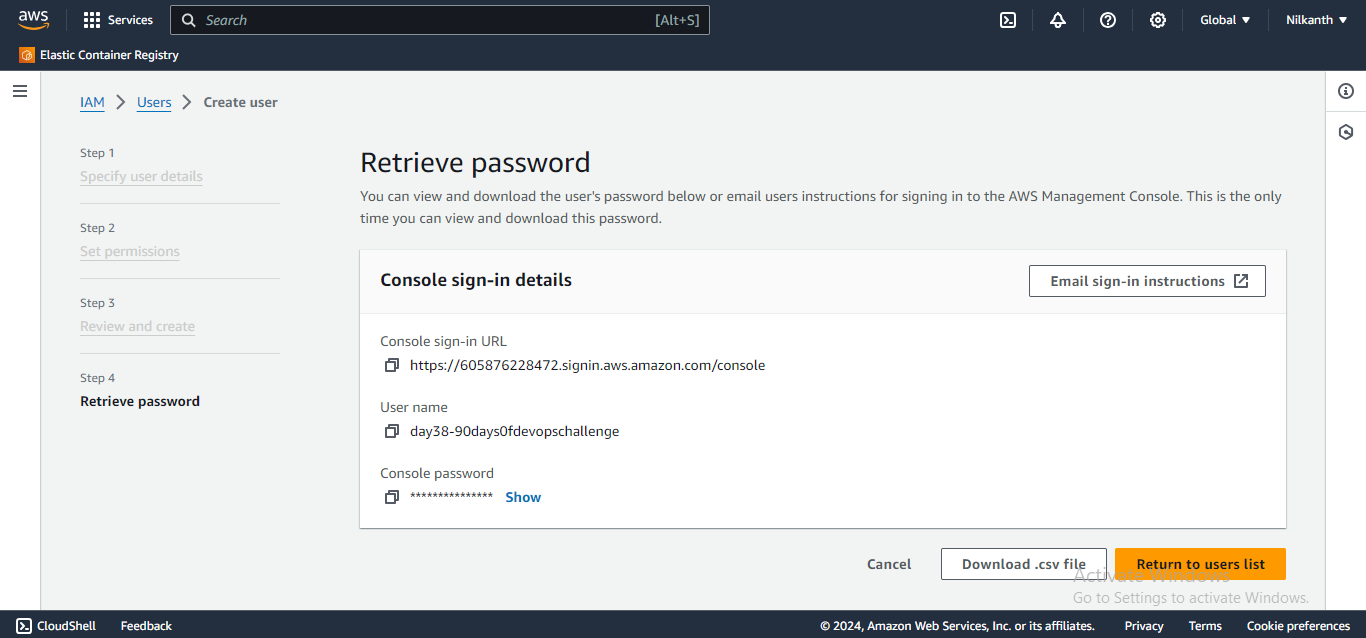
- Review the user details and click "Create user". Make sure to note down the access key and secret key. �
Launching a Linux Instance:
- Navigate to the EC2 Dashboard and click "Launch instance".
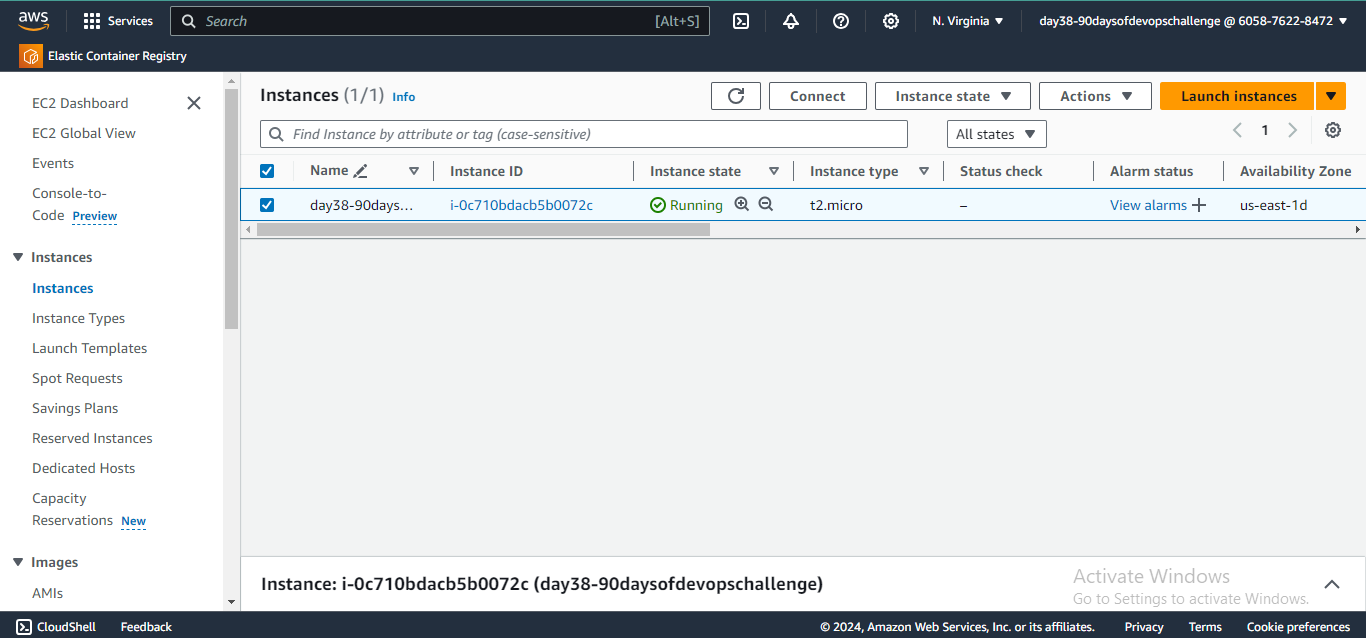
Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) for your Linux instance.
Configure the instance details, such as instance type, network settings, and IAM role. Select the IAM user created earlier.
Add storage, tags, and configure security groups to allow SSH and HTTP(S) traffic.
Review and launch the instance. Use the IAM user's access key and secret key to authenticate. 🚀
Installing Jenkins and Docker with a Shell Script:
Installation of Jenkins
Jenkins requires Java in order to run. There are multiple Java implementations that you can use. OpenJDK is the most popular one.
Update the Debian apt repositories, install OpenJDK 17, and check the installation with the below commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt install fontconfig openjdk-17-jre java -version openjdk version "17.0.8" 2023-07-18 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 17.0.8+7-Debian-1deb12u1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 17.0.8+7-Debian-1deb12u1, mixed mode, sharing)Use the below command to install Jenkins from debian-stable apt repository:
sudo wget -O /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc]" \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkinsEnter the below code to launch Docker
sudo apt-get update sudo apt install docker.ioUse the below command to check Jenkins and Docker is installed or not -
-version docker --versionJenkins and Docker is installed successfully in the machine through IAM User.
Task 2️⃣: Building the DevOps Team of Avengers
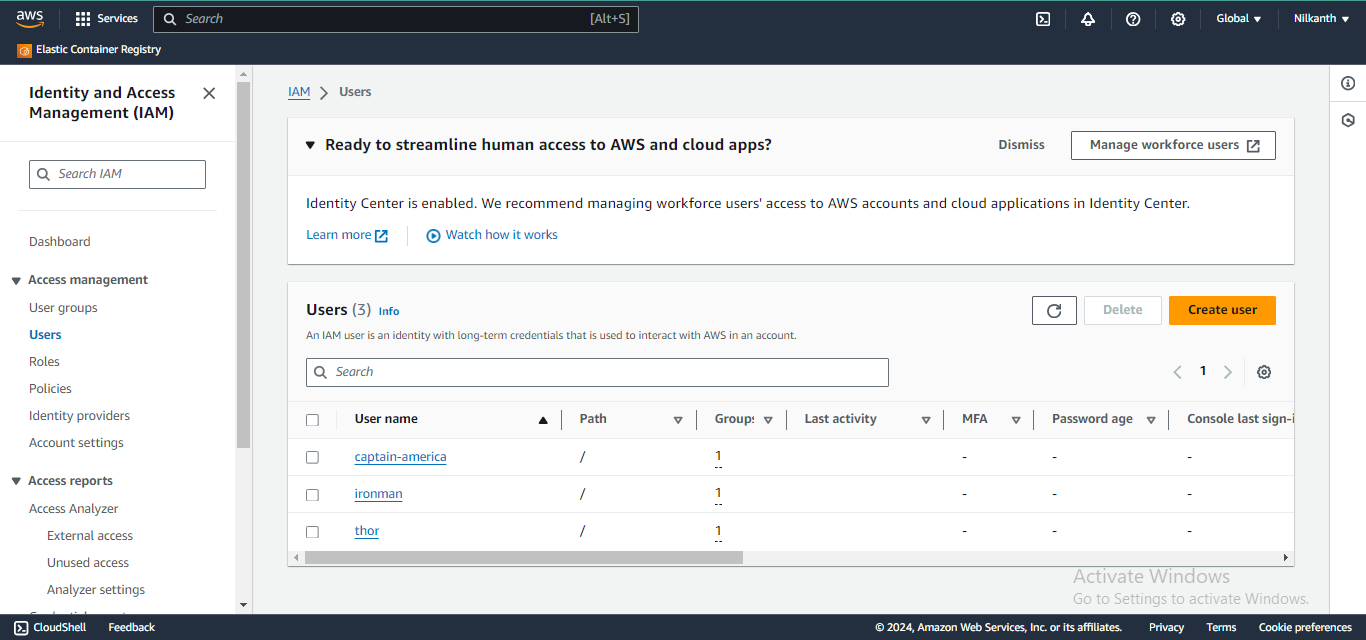
Creating IAM Users for Avengers:
Follow the same steps as Task 1 to create three IAM users with unique usernames (e.g., ironman, thor, captainamerica).
Assign these users to appropriate IAM groups (e.g., DevOps) with custom IAM policies granting necessary permissions for DevOps tasks. 👥
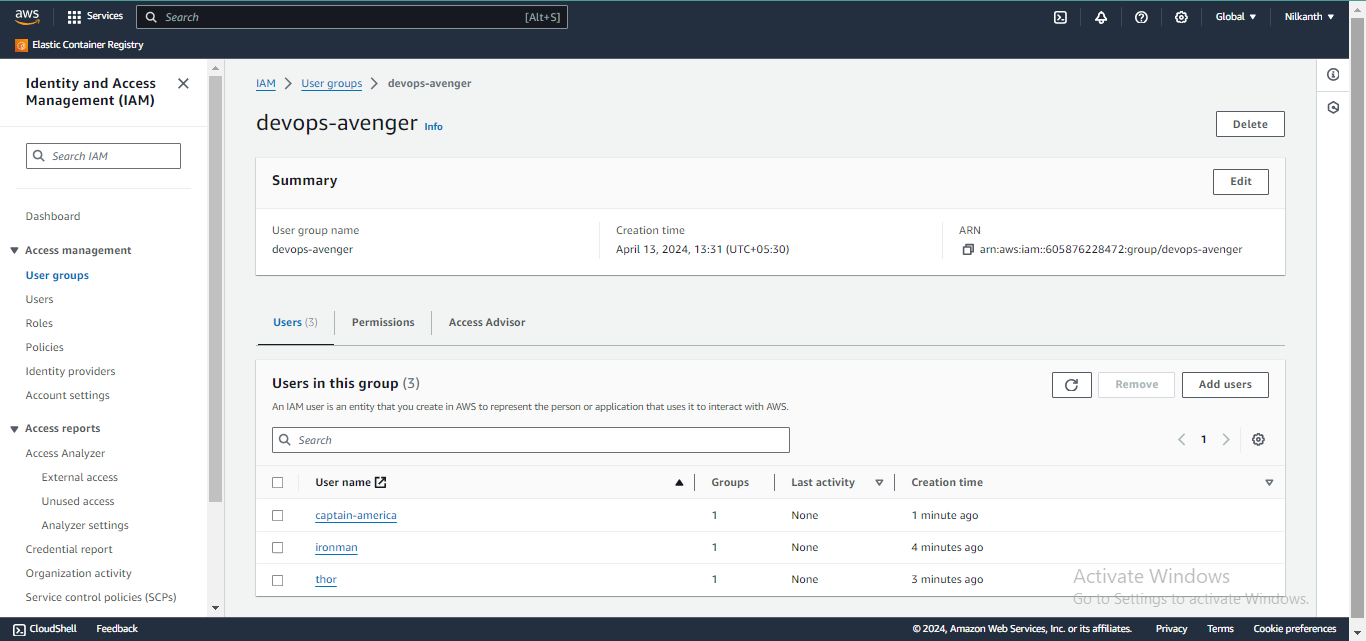
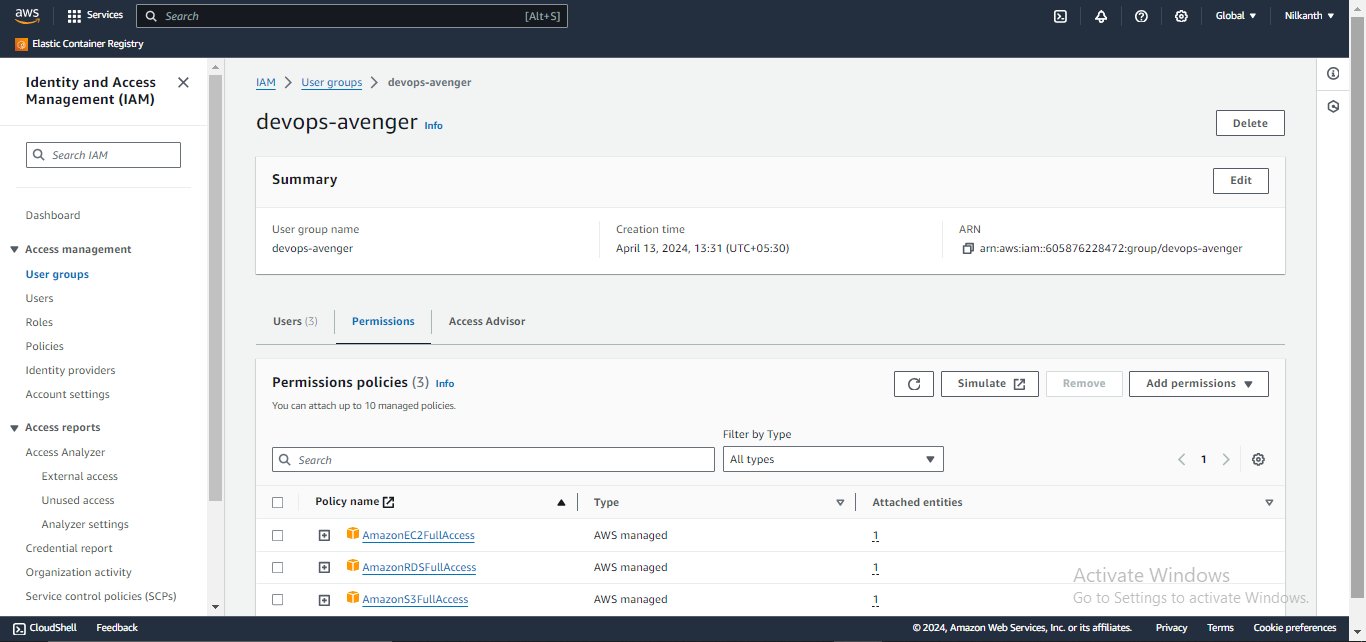
Assigning IAM Policies to DevOps Groups:
Navigate to IAM and select "Groups".🛡️
Create a new group named "DevOps" and attach policies like "AmazonEC2FullAccess", "AmazonS3FullAccess", and "AmazonRDSFullAccess".
Feel free to adjust the steps according to your preferences and requirements. 🌟🚀Happy Learning! 📚✨ #AWS #DevOps #LearningJourney #CloudComputing ☁🔧
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nilkanth Mistry directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
Embark on a 90-day DevOps journey with me as we tackle challenges, unravel complexities, and conquer the world of seamless software delivery. Join my Hashnode blog series where we'll explore hands-on DevOps scenarios, troubleshooting real-world issues, and mastering the art of efficient deployment. Let's embrace the challenges and elevate our DevOps expertise together! #DevOpsChallenges #HandsOnLearning #ContinuousImprovement