Demystifying Blockchain Technology: What You Need to Know
 Ratan Bhowmick
Ratan Bhowmick
Introduction:
In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force, promising to transform industries, redefine business processes, and empower individuals with greater control over their digital assets. Despite its growing prominence, blockchain remains a complex and often misunderstood concept for many. In this blog post, we'll unravel the mysteries surrounding blockchain technology, explore its fundamental principles, and highlight its potential applications across various sectors.
Understanding the Basics:
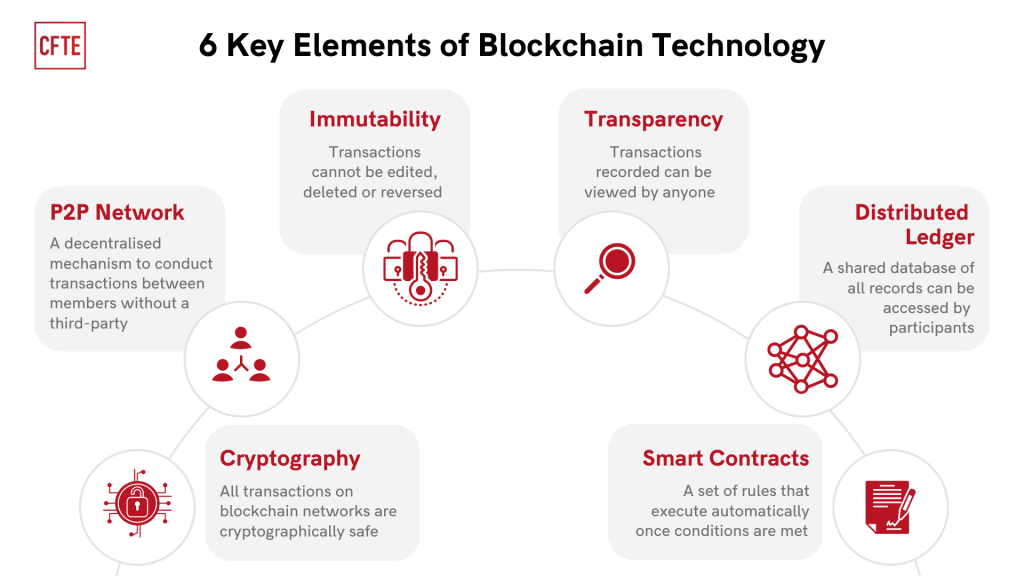
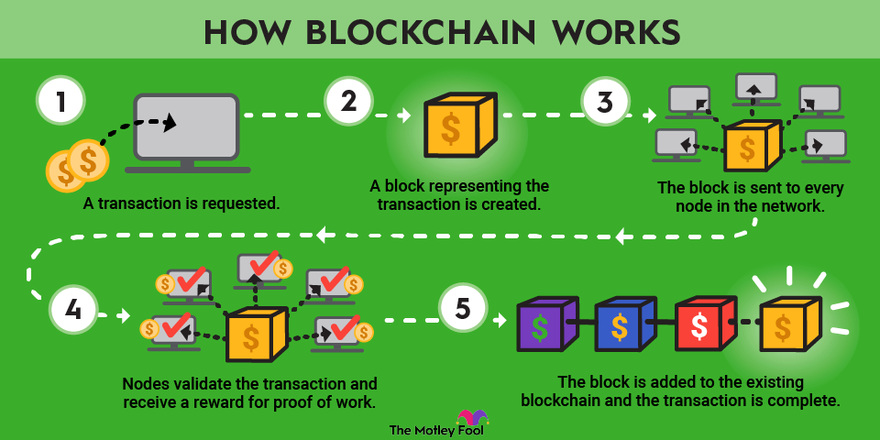
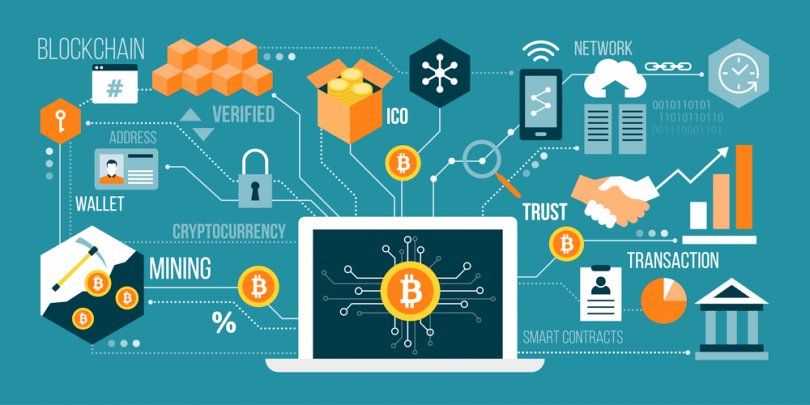
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers in a tamper-evident and transparent manner. Each block contains a timestamped batch of transactions, cryptographically linked to the previous block, forming a chronological chain of blocks. This decentralized architecture ensures that no single entity controls the network, fostering trust, transparency, and immutability of data.
Key Components of Blockchain:
# Cryptography - Blockchain relies on cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, verify identities, and ensure data integrity. Public-key cryptography enables users to generate unique digital signatures, allowing them to prove ownership of assets and authenticate transactions.
# Consensus Mechanisms - Consensus algorithms govern how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. Popular consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), each with its own advantages and trade-offs.
# Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions encoded on the blockchain. These programmable contracts automatically execute and enforce agreements when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs.
Applications of Blockchain Technology:
# Cryptocurrencies - Bitcoin, the first and most well-known blockchain application, introduced the concept of digital currency and decentralized peer-to-peer transactions. Ethereum expanded upon this idea by introducing smart contracts, enabling developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) and tokenized assets.
# Supply Chain Management - Blockchain technology holds the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility, traceability, and transparency of goods and transactions. From food safety and provenance tracking to combating counterfeit products, blockchain enhances supply chain efficiency and integrity.

# Identity Management - Blockchain-based identity solutions offer a secure and verifiable means of digital identity management, enabling individuals to control and share their personal information securely. This has implications for various industries, including healthcare, finance, and government services.
# Decentralized Finance (DeFi) - DeFi platforms leverage blockchain technology to offer a wide range of financial services, including lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management, without the need for traditional intermediaries. DeFi protocols enable greater financial inclusion, interoperability, and transparency in the global financial system.
Conclusion :
As blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, its impact on the world is becoming increasingly profound. From revolutionizing finance and supply chain management to enhancing digital identity and cybersecurity, blockchain holds the potential to reshape industries, empower individuals, and drive innovation on a global scale. By demystifying blockchain and understanding its core principles and applications, individuals and organizations can unlock the full potential of this transformative technology and seize new opportunities in the digital age.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ratan Bhowmick directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
&version=1711445320114)