Key Components and Technologies in Cloud Computing
 N Chandra Prakash Reddy
N Chandra Prakash Reddy
Virtualization
A service's virtualization keeps it separate from the real hardware it operates on.
Special software is used to create a virtual copy of the computer hardware.
Developed in the early days of mainframes.
Several operating systems and applications can run simultaneously on the same hardware thanks to virtualization.
This increases the flexibility and use of hardware.
Virtualization is a cost-effective strategy used by cloud providers to decrease hardware and maintain energy.
It makes it possible for numerous people or organizations to share a single physical resource.
This is accomplished by assigning a virtual name to each user and providing them with access information as needed for the portion of the resource they are now utilizing.
Delivering Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) in cloud computing requires hardware virtualization.
Virtualization also includes virtual environments for networking, data storage, and program execution.
Host Machine : This is the primary computer that will be used to create the virtual machine.
Guest Machine : The term "Guest Machine" refers to the actual virtual machine.
Benefits of Virtualization
As less actual hardware is required, virtualization lowers the cost of equipment purchase and maintenance.
By allowing numerous virtual machines to run on a single physical server, it improves the usage of the hardware that already exists.
By allowing numerous virtual machines to run on a single physical server, it improves the usage of the hardware that already exists.
Virtualization eliminates the need to add or remove physical servers, making it simpler to scale resources up or down in response to demand.
Testing environments may be quickly and easily created thanks to virtualization, which also minimizes development cycles and lowers expenses.
By running older software on virtual machines, virtualization can help them stay functional even if the underlying hardware degrades.
Drawbacks of Virtualization
In the long run, virtualization can save money, but it can be expensive to set up initially, particularly in the cloud.
Transitioning to the cloud requires the hire of qualified personnel who can work with it, or the training of current staff members.
Sensitive information may be at risk if data is stored on external servers, as this increases its vulnerability to hacker attacks.
Hypervisor
A specialized software called a hypervisor is used to manage virtual computers.
Hypervisors come in two varieties: Type 1 and Type 2.
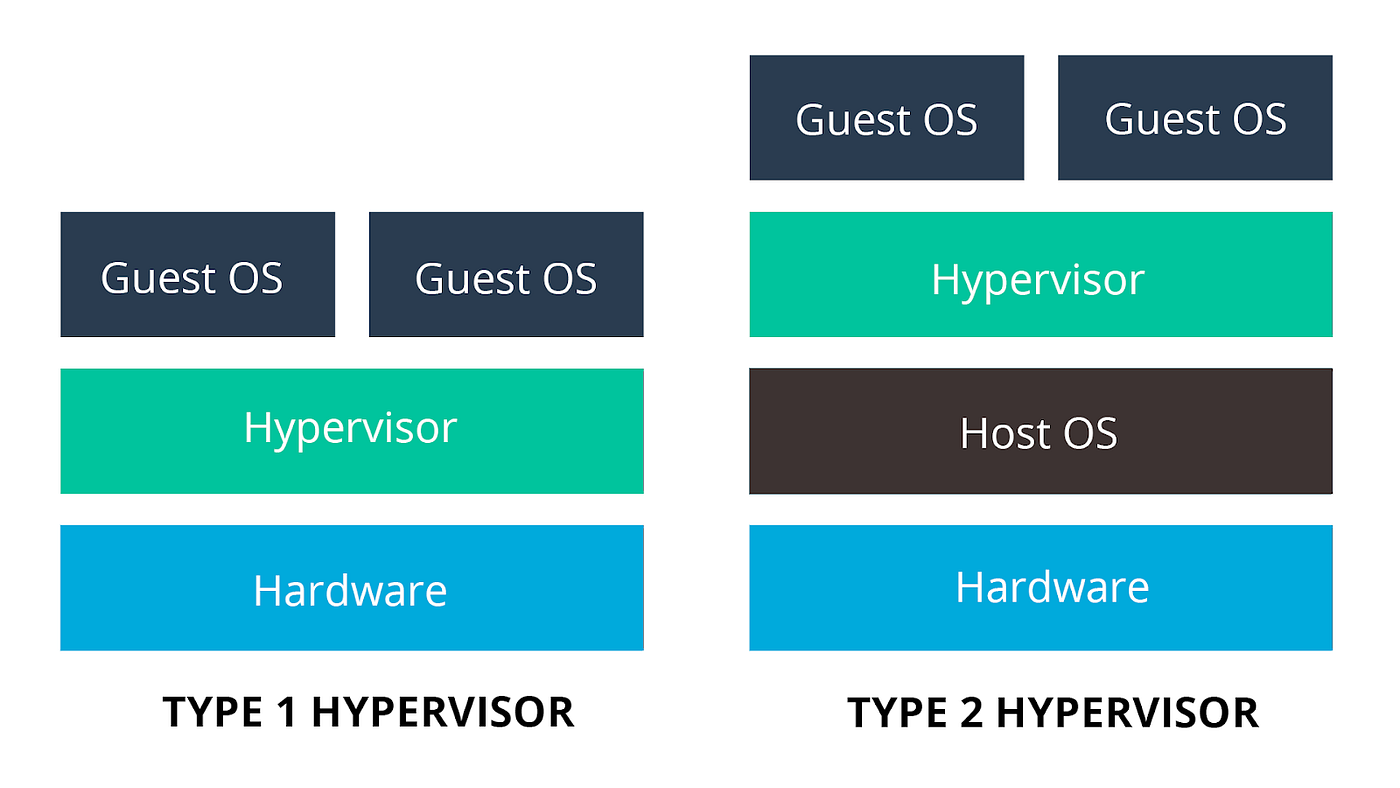
Type 1 Hypervisor / Bare Metal :
Operates directly on the hardware of the computer.
LynxSecure, RTS Hypervisor, Oracle VM, Xen, Sun xVM Server, and VirtualLogic VLX are a few examples.
Type 1 hypervisors do not require a host operating system to function.
'Bare Metal' is another term for this configuration.
Type 2 Hypervisor :
Operates as a piece of software over an already-installed operating system.
Virtual Server 2005 R2, Windows Virtual PC, VMware Workstation, Containers, VirtualBox, KVM, Microsoft Hyper V, and VMware Fusion are a few examples.
Containerization
Containerization is the process of putting an application and all of its contents into a single box, or container, to keep them neat and separate from other apps.
Containerization simplifies the management of applications by combining all of their components into a single container. Without interacting with other containers, this container can operate on a shared operating system.
Key Technologies in Containerization
Docker :
The containerization platform Docker is widely used.
It enables the creation, sharing, and operation of containers.
Containers are operated by Docker Engine.
You can distribute and save container images on the cloud using Docker Hub.

Kubernetes :
Google created Kubernetes, sometimes referred to as K8s, a free container management tool.
It manages the deployment, scaling, and control of applications in containers among computer groups.
Kubernetes ensures that applications run smoothly and scale with ease by providing features like load balancing, service discovery, and self-repairing issues.
Benefits of Containerization in Cloud Computing
Containers make it simple to transport apps between different computer systems by bundled them with all the necessary components for them to execute. App developers don't have to worry about conflicts when they create and test their programs on their personal PCs before uploading them to cloud servers.
Applications can easily accommodate variations in the number of users utilizing them since containers can be made larger or smaller as needed. In the event that an application becomes too busy, cloud systems can even modify the number of containers automatically.
Containers require less space than ordinary virtual machines because they share the host computer operating system. In addition to saving money on cloud services, this enables businesses to get more out of their PCs.
Containers maintain consistency throughout an application's development process, including testing and release. The app is less likely to malfunction when moved between different installations because all of its requirements are included in one package. When releasing the app for public use, this increases its dependability.
Orchestration
Cloud orchestration functions similarly to an orchestra's conductor, making sure that every instrument (or service) in the cloud plays in synchronization.
It defines and implements a set of rules and procedures that automate the whole service deployment process from beginning to end.
Businesses can achieve faster deployment times and better operations by replacing manual processes with automated workflows by utilizing Cloud Orchestration technologies.
These solutions utilize the power of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers, like Azure or Amazon, to automate complex deployments with little assistance from humans.
A cloud orchestration technology called Kubernetes (K8s) automates the deployment, scaling, and administration of containerized applications among server clusters.
It guarantees that workloads that are containerized in the cloud run smoothly.
Working with tools like Terraform, Ansible, and AWS CloudFormation, Kubernetes is a crucial part of cloud orchestration.
Benefits of Orchestration
It manages connections and interactions across installed workflows in both private and public cloud architecture using programmed methodologies.
Self-service resource configuration is available through orchestrated solutions from cloud managers, which accelerates service delivery over manual configuration based on individual requests.
This platform ensures security protocols, standardizes templates, and incorporates authorization checks. Administrators can check and improve already-written automation scripts.
In a cloud model, it is mostly utilized for server deployment, customer service network management, virtual machine creation, and software access.
Advantages
Benefits like speed and cost savings through automation are systematically increased by orchestration.
Businesses may quickly implement cutting-edge apps and services with its assistance, all while maintaining control and organization.
Orchestration automates and simplifies the monitoring process through the use of a single portal and an IT service model influenced by the cloud.
The creation, launching, and operation of various services provided by various systems are accelerated up by this flexibility.
Microservices
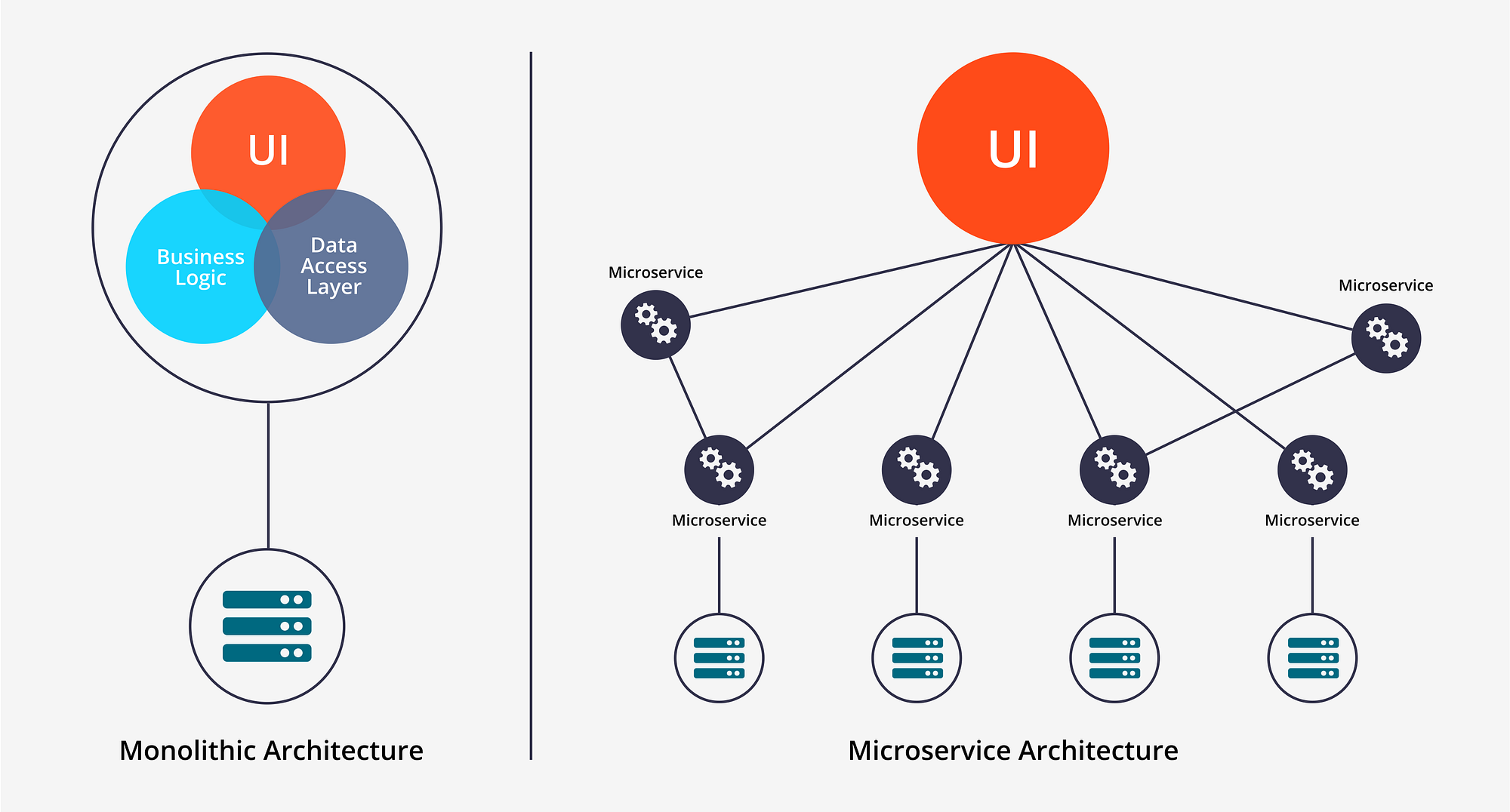
In the past, large, single-piece structures known as monolithic architectures were used to create software.
As software became more complex, they became more difficult. They struggled to keep up with the increasing complexity.
It was difficult and frequently resulted in downtime to install or upgrade them. It was not actually possible to select certain pieces.
Software can be built differently with cloud microservices.
You divide it up into smaller, autonomous pieces rather than one large one.
Every component carries out its own function and communicates with the others in accordance with established guidelines.
Software can be developed and expanded more quickly using this strategy than with the previous one.
Microservices allow you to make changes and updates without affecting other services.
They also let you quickly add new features without making users wait.
Users wouldn't even notice if you updated anything once a week, for instance.
What do cloud microservices help with ?
Problem : There are issues with the traditional methods of developing large apps.
As they get bigger, they become slower and more complex.
It becomes more complicated to add new components, which increases the amount of bugs and takes longer to create and test.
Solution : Instead, use cloud microservices.
Divide the large application into smaller components, each managed by a small group of experts.
Every component functions separately and may be modified without affecting the others.
Advantages of microservices over traditional methods
Things are less complicated and twisted since the parts are created individually.
When necessary, parts can enlarge or compress without the need for pricey materials.
It doesn't destroy the entire thing if one component breaks. Furthermore, components have improved communication with one another.
The finest tools available are used to create each component.
It is simple to introduce new features and quickly fix bugs without interfering with user experience.
How Cloud Microservices Work ?
Breaking Down Services :
Divide the program into smaller, single-task-focused services.
It is possible to independently work on and modify these services.
Separate Development and Deployment :
Every service is created and implemented independently.
Various tools can be used by various teams for different services.
Using APIs for Communication :
APIs are defined communication protocols between services.
Information sharing between services is now simple as a result.
Keeping Things Flexible :
Changes in one service don't impact the others because they are independent.
You don't have to update the entire program to update a single section.
Scaling Services Independently :
Based on its requirements, any service might expand or shrink.
When compared to less used services, busy services have the potential to grow.
Managing Data :
Every service can have its own database, utilizing the most advanced technology available.
Sharing of data across services can be managed intelligently.
Dealing with Failures :
A single service failure does not bring down the entire system.
Services are able to manage issues without crashing the entire program.
Making Updates Easier :
Microservices adapt well to sudden changes and updates.
It is possible to integrate additional functionalities without experiencing system slowdown. Enabling deployments and Continuous Delivery with DevOps Practices allows updates and new features to be published fast without affecting the operation of the entire application, since each service is deployed independently.
Watching and Fixing Issues :
Tools make it easier to monitor the performance of each service.
By doing this, conflicts can be resolved before they get out of hand.
Conclusion
Microservices, orchestration, virtualization, and containerization are essential components of modern computing.
Virtualization maximizes the use of hardware, which reduces costs and increases flexibility.
Applications are arranged using containerization for improved scalability and management.
Automation of processes through orchestration makes IT more efficient for future use and enables smooth operation.
Software is kept flexible and updated more quickly thanks to microservices, which divide it up into manageable components.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from N Chandra Prakash Reddy directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

N Chandra Prakash Reddy
N Chandra Prakash Reddy
-> I'm an enthusiastic DevOps professional with over 3+ years of hands-on expertise in cloud infrastructure management and orchestrating the deployment of applications which are ready for production. -> Excellent problem-solving skills and a proactive learner, staying updated with the latest trends in DevOps and Cloud Computing. 𝐆𝐞𝐭 𝐢𝐧 𝐓𝐨𝐮𝐜𝐡 -> 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐨𝐧 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐧 : If you're interested in engaging in technical discussions or connecting professionally, please feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn. -> 𝐄𝐦𝐚𝐢𝐥 : ncpr.0912@gmail.com