Final Deep Dive in to Ethereum — Week 5 of Learning .
 Kshitij Khanka
Kshitij Khanka
In this blog, we will be learning about The DAO Attack and Ethereum Hard Fork, Difference between Hard vs Soft Fork, Initial Coin Offerings, Sharding and Alt coins.
But let me declare something. As I said last week, I would be starting smart contracts, but I was not able to because it did not felt right to leave these topics. So let me make it up for you. I would be posting at least one post on various Protocols and Coins every week on my LinkedIn ( Here ). Make sure you connect with me there, as I would love to connect with fellow like-minded learners.

To summarize our learning from the last blog, Ethereum is a protocol deployed using blockchain. It is similar to Bitcoin but it allows you to host Smart Contract on the chain. As every action performed on blockchain (except reading) costs Gas, it allows you to write loops and various logic. Every action such as addition, division, etc, has an OPCODE ( click here to check them out ) and every OPCODE has an associated amount of Gas to it.
You can decide how much you are willing to pay for each unit of Gas. Also you can set a limit on the amount of Gas to be used, this is called Gas Limit. The amount transacted using Smart Contract is deducted from the Contract account. Samrt contracts allow you to build Decentralized Applications and Organisations where a decision is made using votes.

So as we know once a smart contract is deployed on the Ethereum chain, there exists no way of modifying it. This led to the infamous DAO Attack.
The DAO by Slock It was aimed to create a decentralized tool for investors to vote for which company or asset to invest in via DAO token. Initially 100 DAO tokens were exchanged for 1 ETH, via this people can vote. A proposal would be setup, and investors get around 7 days to vote. After that, based on majority, the smart contract will get executed. For those who did not want to invest, they could invoke a split function to eventually remove their money. But the Smart contract they hosted had a small bug which allowed an exploit of over $55 million, but as no changes could be made to the contract after deployment, the Ethereum community was in a dilemma whether to completely reverse the transaction by changing every smart contract which is a Hard Fork or to let the hacker get away with it. The story is amazingly covered by Junion. ( here )
There was a split between normal people and blockchain purists, who believed that the contract shouldn’t be messed up and rather let hacker have the money. Even the hacker led out a message saying a Hard Fork (which will make the hacker lose all of his money) will contradict the purpose of blockchain and to let him have the money as his reward, which I found absolutely funny.
A poll was out for everyone to vote, in which over 87% of people supported the Hard Fork. But then you would ask what happened to all the immutable ideology ? The rest of the 13% decided to stay on the old protocol now known as Ethereum Classic.
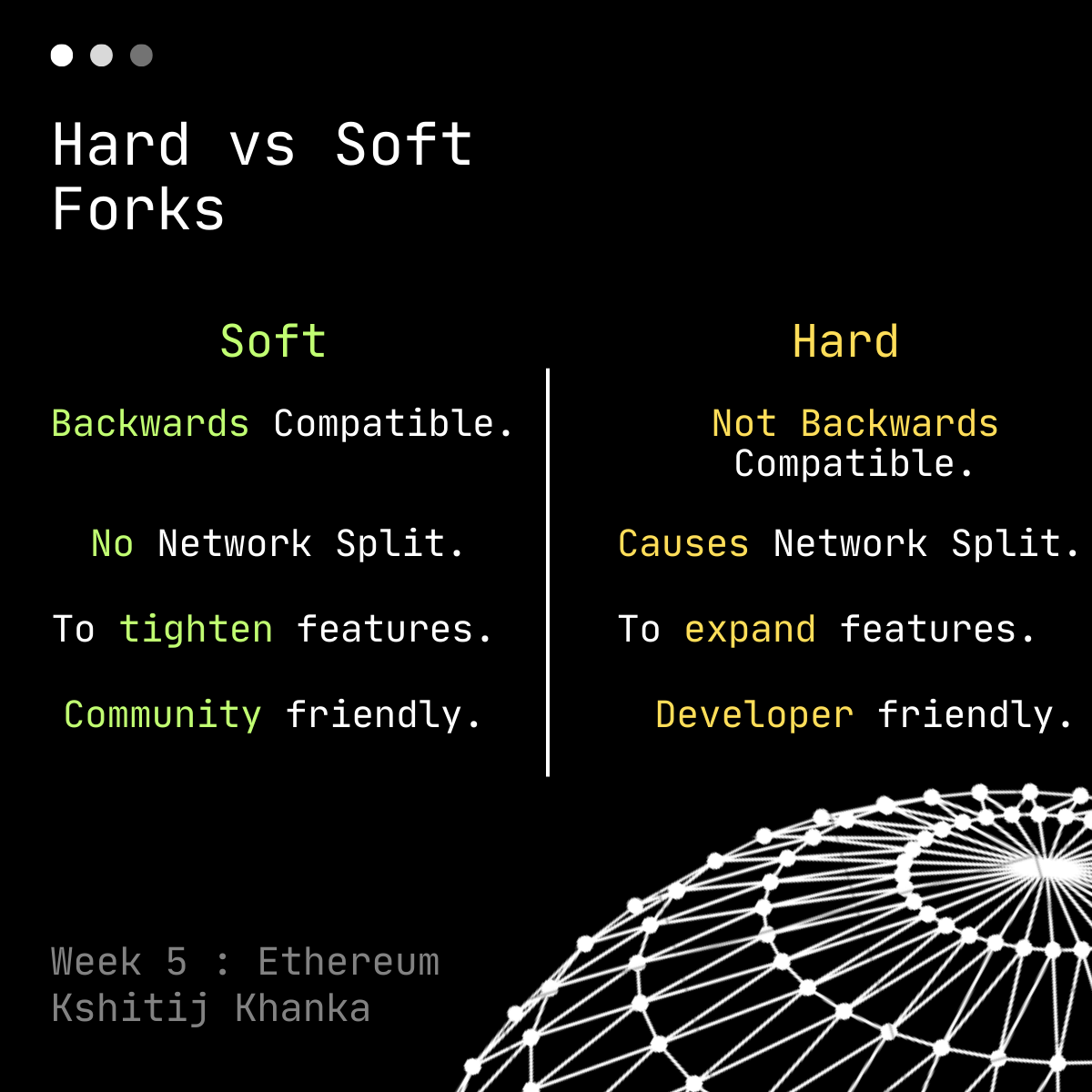
Now let's address differences between Soft and Hard Forks:-
Hard Forks aren’t backwards compatible i.e. the older chain becomes invalid. Miners need to upgrade their software to work with the new chain. So those who oppose the Hard Fork will just simply stay on old mining software.
Hard Fork causes the network to split. Example- Ethereum and Ethereum Classic.
Hard Forks are used to expand the features whereas Soft Forks are used to tighten the features. Example- Increasing/Decreasing the block size.
Hard Forks are Developer-Friendly as they can update the protocol at once, whereas in Soft Fork they would need multiple forks to reach the same conclusion.
Did a thought ever cross your mind, if the blockchain keeps expanding wouldn’t it become more difficult to maintain it and perform mining and also validate it ? Yes, eventually it would therefore came in the picture Sharding. It is a simple idea of dividing the blockchain into smaller chains and then continuing mining. This makes it a lot easier of miners who now doesn’t have to validate and maintain a large chain but instead a small chain.

What are Alt Coins and ICOs ?
Altcoin is a term that refers to every other coin which is not Bitcoin. Ps. Just so you know, our normal currency like Dollars, Euros, Rupees are referred to as Fiat currencies.
ICO stands for Initial Coin Offering, it's simply you offer money to purchase assets, just like in IPOs but unlike receiving shares you get coins. There is a small difference tho, owning shares allows you to be a part of decision-making, but it is not the case in cryptocurrency. Owning coins of a protocol doesn’t make you part of the decision-making of the particular protocol unless it is setup that way.

Source : Code Eater.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Kshitij Khanka directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
