CSS Selector
 Vikas Dubey
Vikas Dubey

Before we delve deep into CSS selectors, let's first understand what CSS is and why it's important to learn.
CSS is Cascading Style Sheets, which determines how your webpage or website appears on the screen. There are various ways to use CSS in HTML, but I recommend to use external CSS.
Let's learn how to use external CSS with your HTML code. Create a separate file with a .css extension along with your HTML file. Always link the external css in your head tag of html code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link href="first.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
Introduction
In this article I'm describing CSS selectors and their types with proper examples, using only HTML and CSS. I'm describing how to select any HTML element, and then style it with CSS using CSS selectors of different types. We will also see how can we target HTML elements particularly according to their hierarchy(HTML DOM TREE), no matter how deep the element is situated we can target it using CSS selectors through different Methods. If you're looking for something extra, make sure to follow me on this platform for upcoming informative articles about web development &, more.

Below image is the perfect example of how to use a CSS selector.
To be honest, if you want to learn about CSS, you must be comfortable with HTML. I am assuming that you are very comfortable with html.
Firstly look the above image . I am sure if you understand the above image you will never forget how to use selectors in html.
Types of Selectors
Universal selector
Individual selector
Class selector
Id selector
And selector
Combined selector
Inside element selector
Direct child
Sibling~ or + selector
Lets discuss each selector in details.
Universal Selector
This selector picks every HTML element on the page, matching with all HTML tags. It's shown by the (*) asterisk sign. Let's clarify with an example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> /** { color: #6A1B4D; font-size: 10px; background-color: cadetblue; } </style> */ </head> <body> <h2>This is heading 2</h2> <p>This style will be applied on every paragraph.</p> <p id="paragraph1">it will also effect me!</p> <p>me too!</p> </body> </html>Without Selector
This style will be applied on every paragraph.
it will also effect me!
me too!
With Selector

2.Individual Selector
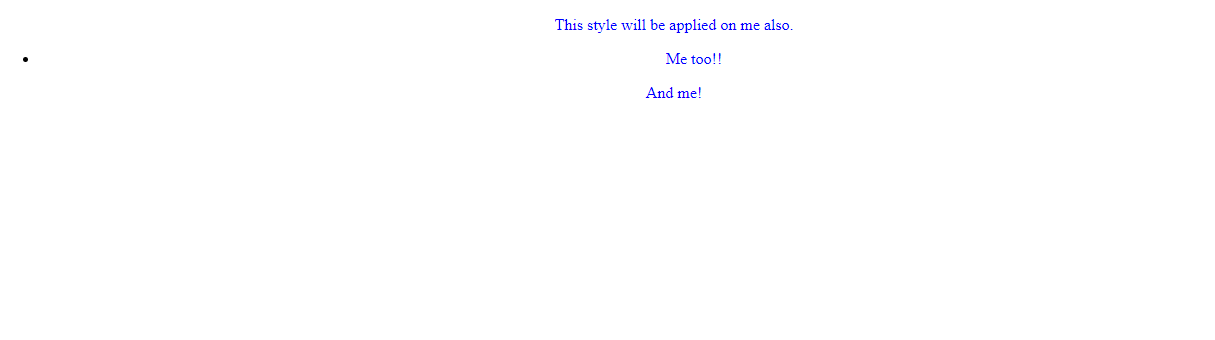
The Individual selector selects the HTML element from the document only by the element name for ex- <p> or <h2> , let it be any tag it can be selected directly by the tag name itself. Irrespective of the hierarchy the tag will be selected wherever it is situated in the document tree. In the below example :- Every <p> tag will be selected and styled.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p {
text-align: center;
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This style will be applied on me also.</p>
<ul>
<li>
<p>Me too!!</p>
</li>
</ul>
<p>And me!</p>
</body>
</html>
3. Class selector -
The class selector selects the element with a specific class attribute. It selects every single element in the document with that class name in particular. you can select multiple elements at a time and style them accordingly without repeating the same code over and over again. One element can belong to many classes, and many elements can belong to one class this is how a class selector can be used. To select elements with the class selector, use the dot character, ., followed by the name of the class. In the below example, .bg-black is the class selector here so <li> with class name, bg-black will be selected and styled.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.bg-black {
text-align: center;
color: #CAD5E2;
background-color:#0D0D0D;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This style will be applied on me also.</p>
<ul>
<li class="bg-black">
first list item
</li>
</ul>
<p>And me!</p>
</body>
</html>
4. Id selector -
The id selector is used to select an HTML element based on the id attribute value.
Every element in the HTML page must have a unique id, meaning their id should remain different no redundancy is allowed in the case of the id attribute. You cannot give the same id to other elements. To select an element with a specific ID, use the hash character, #, followed by the name of the ID value. In the below example, #head4 is the id selector here so <h4> element will be selected and styled.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#head4 {
color: blueviolet;
background-color: chocolate;
font-size: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Lets look id selector</h2>
<h4 id="head4">im heading 4 with id attribute</h4>
<p>im para</p>
<a href="#">see more</a>
<ul>
<li>item1</li>
<li>item2</li>
<li>item3</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
5. And selector -
This selector selects an HTML element which satisfies multiple conditions and these conditions are evaluated to be true. In simple words, it means an HTML element contains more than one class. for ex. <li class="bg-color font-bg">Hello world<li> to target this type of element which contains two classes then and the selector is of good use. This is also known as chained selectors.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p.bg-red.font-lg {
color: blueviolet;
background-color: #6A1B4D;
font-size: larger;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Lets look id selector</h2>
<h4 id="head4">im heading 4 with id attribute</h4>
<p>im para</p>
<a href="#">see more</a>
<p class="bg-red font-lg">this is a paragraph will be selected with chaining</p>
</body>
</html>
6. Combined selector -
The name of the selector indicates a combination of something that has to do with this selector type and it is true. One can style multiple HTML elements at the same time by targeting through the combined selector. Each element have to be separated with , in the combined selector syntax.In the following example <p>,<li>,<span> elements are styled in one line of code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p,li,span{
background-color:#6a7b77;
color: darkgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Hello combined selector</h2>
<p>i will be styled</p>
<ul>
<li>i will be styled too!!</li>
</ul>
<span>me too!</span>
</body>
</html>
7. Inside an element -
inside an element, the selector matches all elements that are descendants of a specified element. The elements specified in the inside selector are separated by whitespaces. The following example selects the <li> then <span> the element inside of an <div> element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div li span{
background-color:#6a7b77;
color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li><span>hey im span</span></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
8. Direct child -
A direct child is a child element that comes immediately below the parent in terms of hierarchy, so selecting the elements which are a direct child of a specified element is done by a direct child selector. To use a direct child selector, specify the parent element and then > symbol followed by direct children.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div > p {
background-color: #6a7b77;
color: darkgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>
Lorem ipsum, dolor sit amet consectetur ,
im styled
</p>
<ul>
<li>im list item</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
9.Sibling ~ or + selector -
The sibling selector allows you to select an element that is a sibling of another element. The sibling selector is represented by the + symbol and is used to select an element that is immediately preceded by the specified element.In the following example <p> tag is the direct child of <div> the element which is selected and styled. In the example above,.container p + p selects the second p the element that is immediately preceded by another p element, and sets its colour to red. The first p the element will not be affected by this selector.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.container p + p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
"In summary, CSS selectors are important for styling web pages and making them look good.
By knowing various types of selectors like class, ID, and attribute selectors, developers can make intricate and changing styles for their pages. CSS selectors allow targeting specific elements on a page, giving a strong tool to control how web pages appear. By becoming skilled with CSS selectors, developers can make attractive and useful websites for the best user experience." Thank you for reading!

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Vikas Dubey directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
